Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Impulse Control Disorder
-
Slides Impulse Control Disorders-Intermittent.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:01 Now, let's review the impulse control disorders starting with intermittent explosive disorder. 00:07 So, what is an impulse? Well, impulses are characterized by an inability to resist behaviors that may bring harm to one's self or others. So again, what's important here is not that there's intent to harm but it's an impulse that can't be resisted. 00:25 Anxiety or tension is often experienced prior to the impulse and then there's relief or satisfaction after the behavior is completed. Types of impulses include intermittent explosive disorder, kleptomania, pyromania, pathological gambling, and trichotillomania. When it comes to impulse control disorder features, what are some of the common features to all of these types of impulse control disorders? Well, there's a failure to resist an impulse to perform some kind of destructive act, and there's escalating tension prior to the act, and then a sense of catharsis or release after. 01:10 Some brain regions and hormones are really associated with impulsivity. 01:15 In the brain, impulsive behavior tends to be linked to the limbic system and in terms of hormones, the most associated hormone with aggressive behavior is testosterone. 01:27 The brain stem cerebrospinal fluid levels of which neurotransmitter are decreased in patients with impulse control disorder? So, we actually see serotonin decreased in their CSF.
About the Lecture
The lecture Impulse Control Disorder by Helen Farrell, MD is from the course Control Disorders.
Included Quiz Questions
Which region in the brain is most associated with impulsive behavior?
- Limbic system
- Pons
- Cerebellum
- Parietal lobe
- Medulla
Which of the following statements about impulse and impulse control disorders is FALSE?
- There is no relief or satisfaction even after the behavior is completed.
- Impulse is characterized by an inability to resist behaviors that may bring harm to oneself or to others.
- Testosterone is the hormone most associated with aggressive behavior.
- Anxiety or tension is often experience prior to the impulse.
- Serotonin is decreased in the CSF of patients with impulse control disorders.
Which of the following is NOT a type of impulse?
- Pyrophobia
- Kleptomania
- Pyromania
- Intermittent explosive disorder
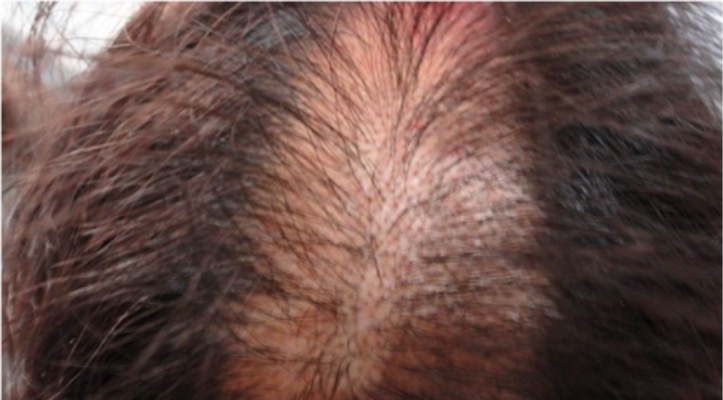
- Trichotillomania
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |