Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Male and Female Pelvic Organs: Overview
-
Slides Male and Female Pelvic Organs Overview.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
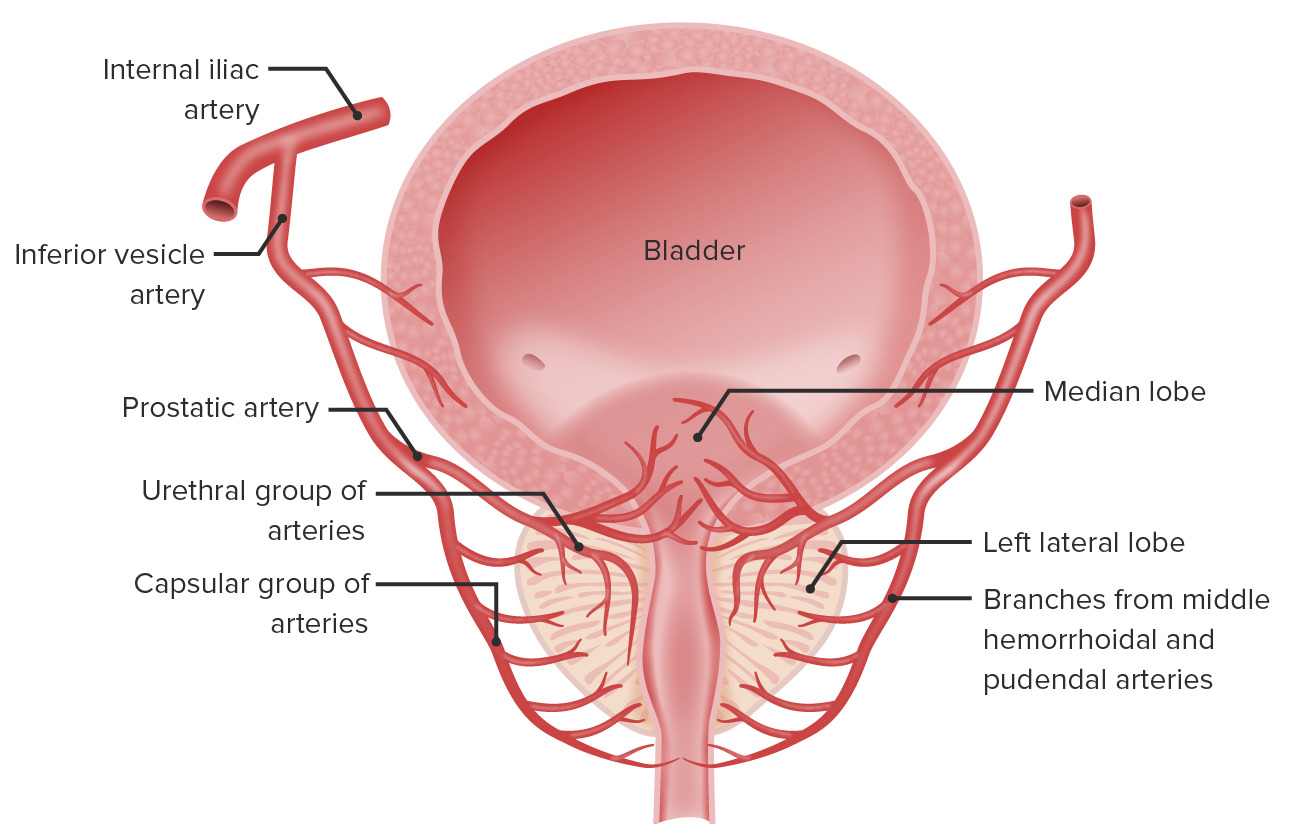
00:01 Now, let's turn our attention to the organs that reside within the pelvis by looking at a sectioned pelvis. 00:08 And we'll look at the difference between male and female before we then go on to look at these in more detail later on. 00:15 So, let's start by looking at a sectioned male pelvis. 00:18 So, what we're doing is we're looking into the right pelvic cavity. 00:23 So, all of these organs are really cut in half and we're looking at the cut surface of their right side. 00:30 So, to the left of the screen, we have the anterior aspect, And then to the right of the screen, we have the posterior aspect. 00:37 And the pelvis has been sectioned down in the mid-sagittal plane So directly down the midline of the body. 00:45 Here we can see most anteriorly. We have the pubic symphysis. 00:48 And then directly posterior to the pubic symphysis, we have the bladder. 00:53 Inferior to the bladder, we have the prostate, And then posteriorly again, within the male, we find we have the rectum. 01:00 Most posteriorly, again, you'd then find the sacrum and the coccyx. 01:04 Superiorly, lying over all of these organs, we find a layer of peritoneum. 01:10 And this peritoneum is continuous with that of the abdomen. 01:13 It is one continuous sheet. 01:16 And as you remember, the peritoneum will run down in the anterior abdominal wall. 01:20 And then it becomes reflected off the anterior abdominal wall as it runs over the superior surface of the bladder. 01:26 And it will then run up and associate itself with the rectum as it then covers the remainder of the abdomen. 01:34 So, a lot of these organs that we're talking about here are really kind of sub peritoneal. 01:39 They're very much underneath the peritoneum. 01:42 They do not have mesentery or they will come back to the rectum in a moment or two. 01:47 They do not have a mesentery that suspends them like the abdominal organs, and they're situated underneath or deep to the peritoneum. 01:55 Here we can see because of the folds of the peritoneum, as they run through the contours of those structures within the pelvis, we can see as it runs over the bladder, and then it goes towards the rectum. 02:06 It actually follows the contours of the bladder, which goes posteriorly and inferiorly. 02:12 Before then running up alongside the anterior surface of the rectum. 02:18 This creates a very important pouch that's positioned between the posterior aspect of the bladder and the anterior aspect of the rectum. 02:26 And this is known as the rectovesical pouch. 02:29 Within the female reproductive organs, and we'll see that within this space we have the uterus. 02:34 And that actually splits that space into two pouches. 02:37 We'll come back to that in a moment or two. 02:39 But here within the male we have the rectovesical pouch formed by the layer of peritoneum covering these pelvic organs forming that space between the bladder anterior and the rectum, posteriorly. 02:52 Now, if we introduce the female organs into this image. 02:56 Again, anteriorly, we can see the pubic symphysis here, and then most posteriorly will see the sacrum to the right hand side of the screen. 03:03 Again, immediately posterior to the pubic symphysis we find the bladder. 03:08 But this time, as we continue moving posteriorly, we do not immediately find the rectum. We find the uterus. 03:15 So, here between the bladder and the rectum, we find the uterus. 03:20 Running now inferiorly, along the posterior aspect of the bladder, do we find the vagina. 03:26 If we then move posterior to the uterus and the vagina, we find the rectum. 03:31 And then most posteriorly as I've mentioned, we'll have the sacrum. 03:36 So now if we introduce our layer of peritoneum onto this image, we can see exactly the same thing as occurring here. 03:43 Peritoneum is running down the anterior aspect of the anterior abdominal wall. 03:48 It then runs all the way down and reflects over the surface of the bladder. 03:53 But this time, it will then run up over the uterus. 03:57 So we can follow that green line as it comes down from the posterior surface of the anterior abdominal wall. 04:02 It runs down onto the surface of the bladder. 04:05 It then folds back on itself as it goes over the body of the uterus. 04:10 It then curves over the uterus onto its posterior surface before then running up the anterior surface of the rectum. 04:20 Now, if you imagine from the male pelvis, we didn't have the uterus, we had that layer of peritoneum. 04:26 Now the uterus has protruded through that space, and we can see it's created two pouches. 04:32 So, now between the bladder anteriorly and the uterus posteriorly, we have the vesicouterine pouch. 04:39 Positioned between the uterus anteriorly and the rectum posteriorly, we have the rectouterine pouch. 04:47 Some textbooks some older textbooks may call this a pouch of Douglas, but very much use the kind of the rectouterine pouch as a way to differentiate that from the vesicouterine pouch. 04:59 The rectouterine pouch is a really important pouch in the female as the lowest part of the peritoneal cavity. 05:06 And therefore because it's the lowest part, accumulation of free fluid, or pus can be found within this space. 05:13 If there's an infection, for example. 05:16 The way for that pus or free fluid to be removed is through a transvaginal approach. 05:22 So penetrating the posterior fornix, we'll see the posterior fornix in a later slide, by passing through the vaginal vault will enable this fluid to be drained from this space.
About the Lecture
The lecture Male and Female Pelvic Organs: Overview by James Pickering, PhD is from the course Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the location of the bladder in relation to the peritoneum?
- Inferior
- Superior
- Medial
- Lateral
- Oblique
In a female, what structure lies within the rectovesical pouch?
- Uterus
- Ovaries
- Vagina
- Sacrum
- Pubic crest
Which statement is correct about the rectouterine pouch?
- It is the lowest part of the peritoneal cavity.
- Fluid is removed through the bladder.
- Fluid is removed transrectally.
- It is the most superior part of the pelvic inlet.
- It is the most superior part of the pelvic outlet.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |