Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hypothyroidism
-
Slides Hypothyroidism EndocrinePathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
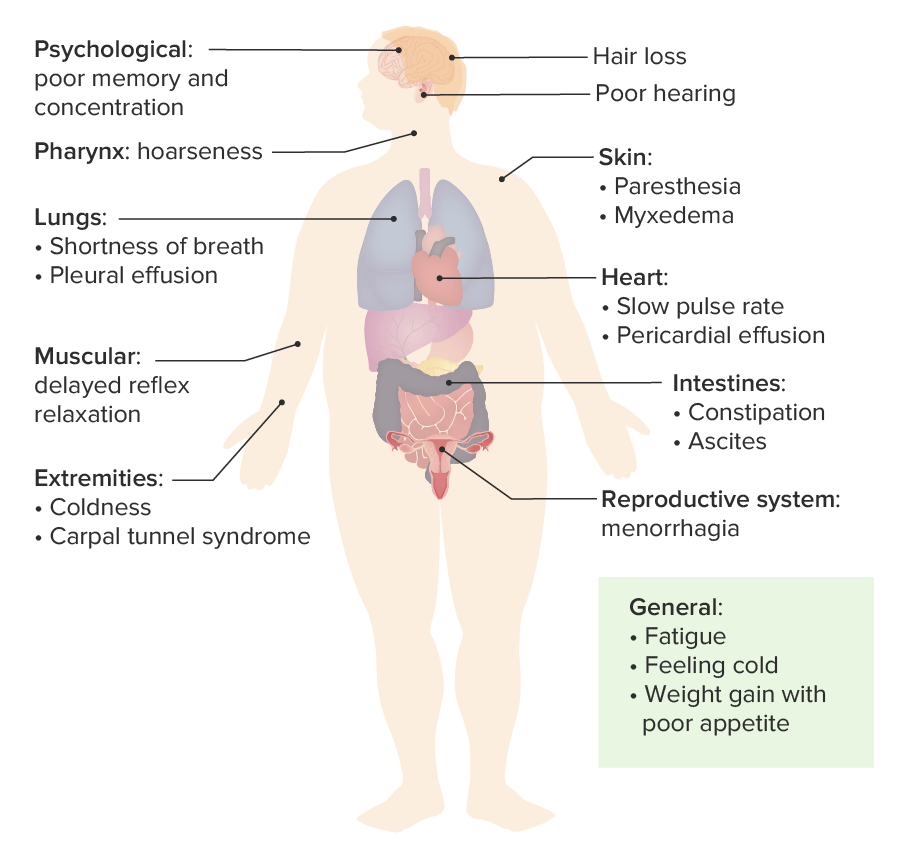
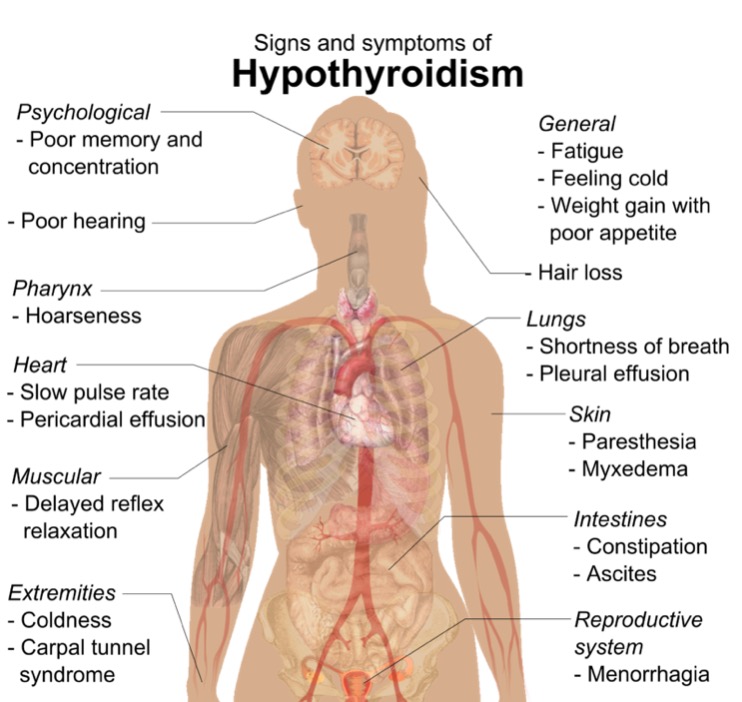
00:01 If Hashimoto is to a female, older adult, cretin… cretinism is to a child. 00:10 This one we can walk through quickly. 00:12 Iodine lacking in a pregnant woman resulting in decreased thyroid hormone nourishment to the foetus; enzymatic deficiency in the foetal thyroid gland resulting in lack of T3, T4. 00:28 Failure of the thyroid gland to properly descend into the neck where it should belong or anti-thyroid antibodies from the mother attacking the foetal thyroid, therefore may result in cretin. 00:44 What’s cretinism? Can’t miss this child, unfortunately, a new born, short stature; take a look at the face, puffy. 00:52 I want you to specifically look at the mouth, see how large it is? Because the tongue inside is macroglossic. 00:59 If you take a look at the stomach, it’s enlarged. 01:02 If you were to take a look at the skin in colour, you’d probably expect them to be yellow, why? Not because of jaundice… do not confuse this with kernicterus… this is accumulation of keratin. 01:14 Short stature, coarse facial features, large tongue, protuberant abdomen and umbilical hernia and IQ in this child unfortunately very, very low. 01:27 Let’s talk about myxoedema and hypothyroidism and this would be for an adult. 01:34 Take a look at the face in this patient on the left with hypothyroidism. 01:40 The patient was then treated with synthroid. 01:44 Upon administration, you’ll notice that months afterwards, on your right, the same patient, the puffiness on the face has now become diminished. 01:54 The myxoedema subsides upon administration of synthroid in a patient with hypothyroidism. 02:01 Would you expect such puffiness in a patient with Graves’ disease? Not at all, the myxoedema that you find in Graves’ disease will be located most likely pretibial. 02:14 Remember I showed you and have shown you pretibial myxoedema along with dermopathy of Graves’? This however is myxoedema in hypothyroidism. 02:27 Broadening, coarsening facial features, lower pitched voice… what is myxoedema? It’s the accumulation of Gags… glycosaminoglycans and hyaluronic acid in the skin subcutaneous to the fact that you even call this oedema is a misnomer, right? Because it is not fluid is the point. 02:50 It’s the fact that you are accumulating other biochemical substances therefore giving you the appearance of the puffiness. 02:58 Now, I will now mention our last topic in myxoedema that’s upcoming and that would be myxoedema coma which is the… that name will be modified in due time, but please, know it now. 03:12 There’s been worst case hypothyroidism where your patient has not gone into a coma only after hypothyroidism is completely and relentlessly taken its course in your patient. 03:27 Myxoedema coma occurs in patients with long standing, untreated, relentless, severe hypo… hypothyroidism, not hyper. 03:40 Often precipitated by stress such as systemic illness or surgery. 03:45 Presentation: hypothyroidism with mental status changes to the point of absolute stupor, seizures and coma and perhaps death. 03:54 Mortality… no joke, look at this 50 percent! You want to do everything in your power to prevent your patient with hypothyroidism ever getting into such as state because you’ll probably never get them back. 04:10 Topic now goes to subclinical hypothyroidism. 04:12 The last time we talked about this was subclinical… well, the related topic earlier was subclinical hyperthyroidism. 04:25 Subclinical hyperthyroidism is extremely common in our society. 04:30 What subclinical means is the fact that the patient is not exhibiting or expressing overt symptoms of hypo or hyperthyroidism, thus you call it subclinical. 04:43 On the wards and on your boards, do not get subclinical confused with sub-acute; one has nothing to do with the other. 04:52 Subclinical means that the patient appears as though, on biochemical exam, that there is decrease in T3, T4 with a slight elevation of TSH, but the patient is not presenting with severe hypothyroid symptoms… mild. 05:10 15 to 20 percent of individuals over the age of 60 will be suffering from subclinical hypothyroidism, but they don’t even know it. 05:19 Usually caused by a Hashimoto-type of event.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hypothyroidism by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Thyroid Gland Disorders.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the most common cause of congenital hypothyroidism in the world?
- Lack of iodine in the pregnant woman's diet
- Excessive exposure to sunlight during pregnancy
- Fetal thyroid enzyme deficiency
- Thyroid dysgenesis
- Consumption of certain medications during pregnancy
n an infant with congenital hypothyroidism who is not treated, what are the typical signs and symptoms that can be seen after 2 months? Select all that apply. Pot belly Pallor Puffy face Protruding umbilicus Poked out tongue
- Pot belly
- Rapid weight loss
- Pallor
- Puffy face
- Protruding umbilicus
What must be accumulated to produce myxedema in hypothyroid patients?
- Glycosaminoglycans
- Lymphocytes and eosinophils
- Albumin and plasma
- LDL and fatty acids
- Thyroid hormone bound to TBG
Myxoedema coma occurs in patients with...?
- Long standing, untreated, severe hypothyroidism
- Newly diagnosed, mild hypothyroidism
- Acute, viral thyroiditis
- Over-treatment with synthetic thyroid hormones
- Chronic, untreated hyperthyroidism
What best describes subclinical hypothyroidism?
- Elevated TSH with normal free T4
- Elevated bound T4 with normal free T4
- Normal TSH with low free T4
- Elevated TBG with normal TSH
- Low free T3 with normal free T4
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |