Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Acute Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): Definition and Epidemiology
-
Slides OtitisMedia InfectiousDiseases.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
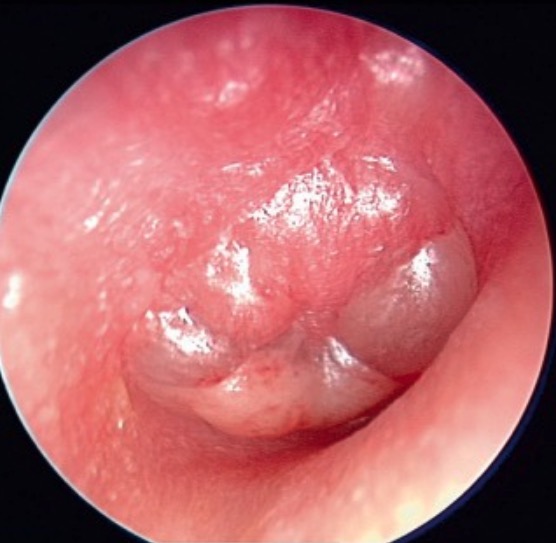
00:01 In our discussion of upper respiratory tract infections, we turn now to otitis media. 00:08 Acute otitis media is an illness marked by the rapid onset of signs and symptoms of inflammation of the middle ear. 00:19 And it is incredibly common. 00:22 By the age of three, two-thirds of kids have had at least one episode and a third of kids have had three or more. 00:36 So pediatricians know this disease very well. 00:43 As an aside, this is not a common infection in adults. 00:51 So if one of your patients is an adult and you diagnosed acute otitis media, you should question why. 01:02 Because they may well have some serious reason for abstracting the Eustachian tube. 01:12 An example would be nasopharyngeal carcinoma or some form of lymphoma. 01:19 So always worry about acute otitis media in an adult. 01:26 The highest incidence is from the ages of 6 to 24 months of age. 01:35 Males more than females perhaps because of anatomical distortion of the Eustachian tube in Down syndrome patients, they have an increased incidence. 01:48 And there are increased incidences in kids who’ve had their first episode very young. 01:56 There seems to be an increased incidence in Native Americans, in Eskimos, and Aboriginals. 02:06 So why the Eustachian tube dysfunction? Well, it’s developmental. 02:14 The Eustachian tubes of children are more horizontal and have a narrower diameter. 02:22 And of course, that increases the risk for stasis of fluid in the Eustachian tube. 02:30 Bacteria love warm static fluid and they’re able to colonize. 02:38 As a result, most of otitis media occurs as a result of respiratory tract infections. 02:47 Starts out with a viral infection causing congestion of the mucosa, of the Eustachian tube, then obstruction and the accumulation of infected secretions behind the obstruction. 03:01 Some persons who were born with a cleft palate can also have frequent episodes of acute otitis media. 03:10 And if you can imagine that a person with a cleft palate, it’s often of the soft palate. 03:17 It can extend all the way anteriorly, but it’s often of the soft palate. 03:23 So when they speak, they have a difficult time controlling secretions going up into the nasopharynx. 03:31 They’re unable to say easily the letter K for example. 03:36 So when try to say K, actually air comes out of the nasopharynx. 03:42 And that may produce secretions going up into the Eustachian tubes. 03:47 So patients with a cleft palate are predisposed. 03:51 And there are environmental reasons for there to be congestion in the Eustachian tubes. 03:58 Patients with seasonal rhinitis frequently have otitis. 04:06 Patients who are exposed to smoke of any kind. 04:12 Patients who smoke and patients who receive second-hand smoke. 04:17 And then the immunocompromised, either they develop it or they’re born with an immunodeficiency or they acquire an immunodeficiency. 04:29 So you have to be exposed to a microorganism and have a problem in the Eustachian tube viral or bacterial.
About the Lecture
The lecture Acute Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): Definition and Epidemiology by John Fisher, MD is from the course Upper Respiratory Infections. It contains the following chapters:
- Acute Otitis Media – Definition and Epidemiology
- Acute Otitis Media – Pathology
Included Quiz Questions
Approximately what percentage of children have at least 1 episode of acute otitis media by the age of 3-4 years?
- 60%
- 20%
- 90%
- 10%
- Less than 5%
Which of the following patient profiles is most susceptible to eustachian tube dysfunction?
- A 18-month-old boy with trisomy 21
- A 52-year-old woman
- A 2-year-old girl
- An 8-year-old Caucasian boy who is otherwise healthy
- An 18-year-old Hispanic male
Which of the following is the most common risk factor for the development of acute otitis media?
- Viral upper respiratory tract infections
- Cleft palate
- Immunodeficiency
- Subclinical cleft palate
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |