Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Pelvic Imaging in Early Pregnancy
-
Slides Pelvic Imaging in Early Pregnanc.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
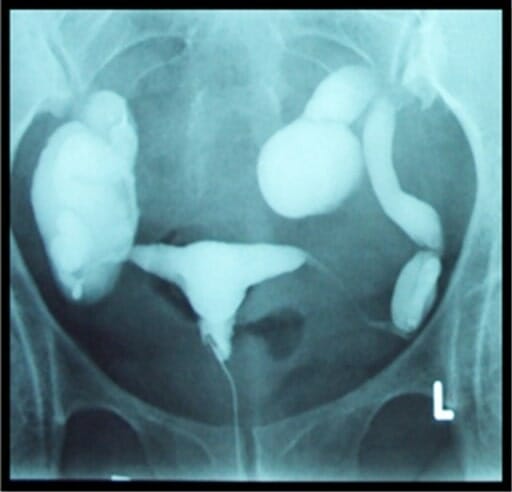
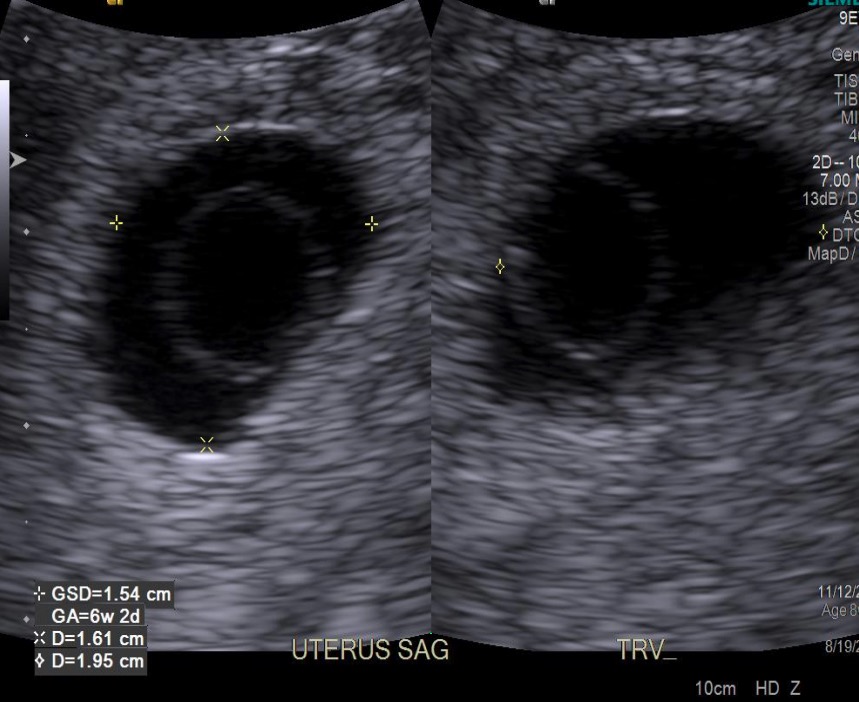
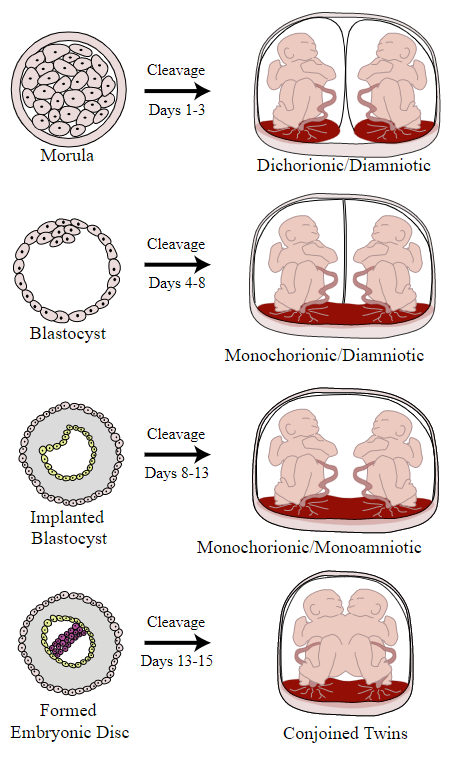
00:01 So let's discuss pelvic imaging performed during early pregnancy. 00:05 Pregnancy is often imaged with the use of ultrasound because there is no radiation associated with ultrasound. 00:10 Ultrasound is the very safe alternative to other types of imaging during pregnancy. 00:14 During first trimester pregnancy, ultrasound is used for a variety of different reasons. 00:19 It includes dating, viability of the fetus, abnormalities of the embryo, placental abnormalities can be evaluated with ultrasound, evaluating for ectopic pregnancy in a patient that comes in with pelvic pain and evaluating for the number of embryos. 00:36 Advanced OB ultrasound can also be used in the second and third trimesters. 00:40 It can help you detect fetal anomalies. 00:42 It can evaluate for amniotic fluid, it can determine fetal position in a patient where the fetal position is unknown. 00:49 And it can also help guide invasive procedures. 00:52 So in today's lecture we're gonna be discussing primarily first trimester ultrasound. 00:56 So let's review some anatomy before we begin. 00:59 So first trimester anatomy includes the presence of an embryo which we see on this diagram. The embryo surrounded by the amnion, which contains amniotic fluid, and then the outer layer is the chorion. 01:13 We see here the chorionic villi which are seen within the placenta. 01:17 There's also the presence of a yolk sac which we see relatively early in pregnancy. 01:23 So let's take a look at these structures on an ultrasound now. 01:26 So a gestational sac is the earliest sign of intrauterine pregnancy. 01:30 Usually, a yolk sac is also seen very early on so as we see here, this is the normal appearance of a gestational sac. 01:38 This echogenic rim around it is called the normal decidual reaction. 01:42 Inside of the gestational sac is this very thin membrane which represents the yolk sac. 01:48 And this is usually visualized between about 3 and 5 weeks of gestation. 01:54 The embryo and the fetal heart rate are usually seen by about 5 or 6 weeks of gestation. 01:59 So this is an example of how an ultrasound forms the image of a fetal heart rate. 02:03 And you can see here, a normal fetus within a normal gestational sac. 02:09 One way to remember this is five alive. 02:12 So when the embryo reaches 5 weeks of gestation, that's when we see the heart rate. The normal fetal heart rate ranges between about 120 and 160 beats per minute. 02:23 So let's take a look at these ultrasound images here, these are again an ultrasound kind of close up of an embryo within a gestational sac and you can see the surrounding placenta here. 02:35 This is another image of the same thing in a different position so again you can see the embryo, you can see the surrounding gestational sac with amniotic fluid and then again the surrounding placenta. 02:47 Twin gestation is one of the things that we look for when we perform our first trimester ultrasound, so this is just an example of a twin gestation. 02:55 We have an embryo here which is labelled embryo A and then we have another embryo here labelled embryo B. 03:02 This is again normal placenta and the normal gestational sac with amniotic fluid. 03:07 So the presence of two or more embryos within an endometrial cavity, represents a twin gestation. 03:13 So let's take a look a little bit further at the different types of twin gestation. 03:17 So twin gestations, the different types of twin gestations are based on when cleavage occurs at the time of gestation. 03:24 So early cleavage, occurring at days 1 to 3, results in a dichorionic, diamniotic twin gestation. 03:31 Days 4 through 8, so a little bit later on, if the cleavage occurs at that stage then you have a monochorionic, diamniotic gestation. 03:40 A little bit later, so cleavage occurring at the days about 8 to 13, results on a monochorionic, monoamniotic gestation. 03:48 So this is a single sac containing both fetuses. 03:52 And very late gestation, cleavage occurring at about days 13 to 15, actually results in conjoined twins. 04:00 So this is obviously very, very rare. 04:01 The most common is the dichorionic, diamniotic cleavage and so you have two completely separate sacs for each of the different embryos.
About the Lecture
The lecture Pelvic Imaging in Early Pregnancy by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Abdominal Radiology. It contains the following chapters:
- Pelvic Imaging in Early Pregnancy
- Twin Gestation
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following sentences is FALSE?
- The earliest sign of an intrauterine pregnancy is a yolk sac.
- The yolk sac lies within the gestational sac.
- Chorionic villi are seen within the placenta.
- The amnion is a thin membrane surrounding the amniotic fluid.
- The chorion lies outside the amniotic membrane.
Which of the following is NOT true of ultrasound during pregnancy?
- It lacks the ability to identify abnormalities of the embryo.
- It is used for dating and determining the viability of the fetus.
- It helps to identify any abnormalities in the fetus.
- The fetal position can be determined.
- Amniotic infusion procedure can be performed with ultrasound guidance.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |