Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Pediatric Cholecystitis (Inflammation of the Gallbladder)
-
Slides PancreatitisCholecystitis Pediatrics.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
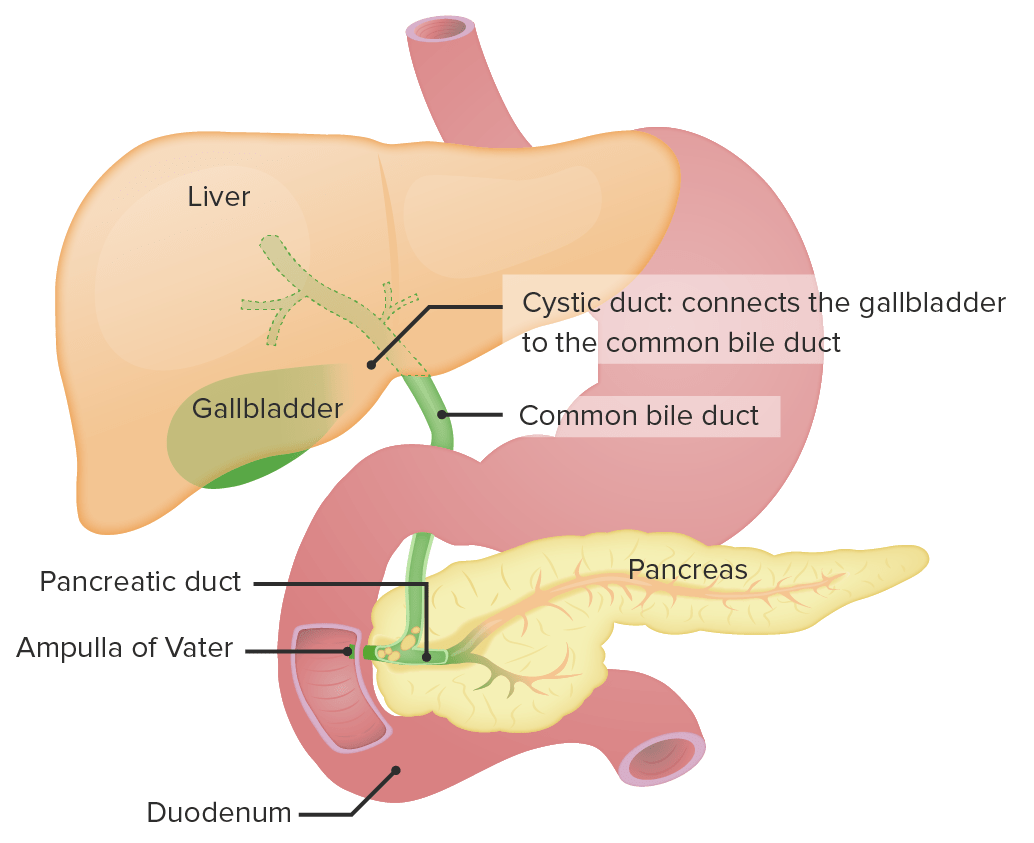
00:02 Let’s shift gears now to talk about cholecystitis or inflammation of the gallbladder. 00:09 Here’s a 15-year-old girl who’s coming in with fever and severe abdominal pain. 00:15 She’s been losing weight despite noticing abdominal bloating. 00:19 And she’s rushed into the OR. 00:21 Notice she has a very high BMI. 00:24 She has acute sharp right upper quadrant pain that radiates to here back and they found gallstones and a thickened gallbladder wall. 00:34 This patient has cholecystitis. 00:38 So cholecystitis is an inflammation and often infection of the gallbladder itself. 00:46 It’s strongly associated with the present of the gallstones inside the gallbladder. 00:52 90% of cases are associated with gallstones. 00:57 It is a common indication for abdominal surgery. 01:00 It is more common in older women than in younger women, but we absolutely see this in adolescents as well. 01:07 There are some rare causes of inflammation of the gallbladder wall that are associated with other systemic diseases like Kawasaki’s disease, which can cause gallbladder enlargement. 01:21 But most of cholecystitis is a result of the obstruction of the neck or a cystic duct usually from a stone and like I said, that’s about 90% of cases. 01:32 The most common reason for emergent cholecystectomy is cholecystitis. 01:40 And we see it typically in children with predisposing risk factors. 01:44 Examples would be sickle cell disease where they have a higher red blood cell turnover. 01:52 So let’s look at some risk factors for gallstones. 01:56 Certainly females are at higher risk. 02:00 Obesity is more common. 02:02 Pregnancy is a risk factor for cholecystitis. 02:06 Patients with hemolysis such as patients with hemoglobinopathies, hereditary spherocytosis or red blood cell membrane fragility. 02:17 Patients with infection are at increased risk. 02:20 A patient with hemolytic uremic syndrome for example is going to have a high rate of red blood cell breakdown, which could result in a gallstone formation and subsequent cholecystitis. 02:31 This is true for patients with red blood cell breakdown for sepsis as well. 02:37 Other examples, patients with TPN or total parenteral nutrition. 02:41 These patients are at increased risk for gallbladders. 02:44 Patients with ileal and resection may also be at increased risk for gallstones. 02:49 Because of that problems with enterohepatic circulation and it can just be idiopathic. 02:55 Some kids just get them and we don’t know why. 02:59 Classic symptoms will include abdominal pain, which is acute, sharp and colicky. 03:05 These patients may have epigastric or right upper quadrant pain around the gallbladder site. 03:13 It can also radiate around to the back, especially in the right scapular region on the back. 03:19 These patients typically will have fever and they may develop nausea and vomiting as well. 03:25 Usually they have anorexia and they have some bloating of their intestinal wall from edema. 03:31 It’s key to understand that nausea and vomiting is common. 03:34 Anorexia is common and their nausea and vomiting is often slightly delayed from when they eat. 03:42 If they are forced to eat or if they decide they have to eat, they’ll have significant pain, maybe a half hour to 45 minutes to an hour later as they have that delay before their gallbladder tries to constrict to extrude the juices necessary for food digestion. 04:03 Physical exam findings, you will note fever and dehydration, right upper quadrant tenderness with guarding and they may have Murphy’s sign. 04:10 Let’s go over Murphy’s sign carefully. 04:12 Basically, what you’ll do is as shown in this picture, you will push down underneath the rib cage on that right side in the right upper quadrant. 04:23 Before you ask the patient to – Before you push down on the patient’s abdominal wall, you will ask the patient to breathe all the way out. 04:33 So that their lungs are collapsed. 04:36 Then you will push in and ask them to take a deep breath. 04:39 That deep breath will push down on the gallbladder as the lungs expand and the gallbladder will be pushed into your hand. 04:48 This is Murphy’s sign. 04:49 And this will be painful as they inhale against that hand which is pressed into the right upper quadrant. 04:58 If you suspect this disease, ultrasound has a high specificity for illness. 05:03 Here, you can see an inflamed gallbladder wall on ultrasound and some biliary sludging. 05:09 So these patients will have findings on ultrasound that are very likely to be diagnostic. 05:17 Treatment is simply surgical removal. 05:21 We have to mitigate risk factors in individuals who are at risk in terms of should we remove their gallbladder prior to having any episodes. 05:32 But generally what’s going to happen is patients will come in with an acute cholecystectomy and it will have to be removed.
About the Lecture
The lecture Pediatric Cholecystitis (Inflammation of the Gallbladder) by Brian Alverson, MD is from the course Pediatric Gastroenterology.
Included Quiz Questions
Risk factors for cholecystitis include all EXCEPT which of the following?
- Patients with duodenal atresia
- Patients on total parenteral nutrition
- Patients with hemoglobinopathy
- Patients who are female
- Patients with sepsis
A positive Murphy's sign is highly indicative of acute cholecystitis. Which of the following statements demonstrates this maneuver?
- Pain during inhalation as the examiner places his/her hand over the rt. upper quadrant
- Pain during exhalation as the examiner places his/her hand over the rt. upper quadrant
- Pain in rt. lower quadrant on palpation of the lt. lower quadrant
- Pain during hyper-extension of the rt. hip joint
- Pain on palpation over McBurney's point
An obese teenager comes to the ER with episodes of vomiting and RUQ pain radiating to her right scapula. Which of the following imaging modality would be most helpful to confirm acute cholecystitis?
- Abdominal ultrasound
- CT abdomen
- MRI abdomen
- Plain x-ray of abdomen
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Not a typical pediatric disease but a very important topic nonetheless. Thank you!