Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Anti-HIV Agents: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NsRTIs) – Antiviral Drugs
-
Slides Anti-Virals Antimicrobials.pdf
-
Slides Anti-HIV Agents NsRTIs.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
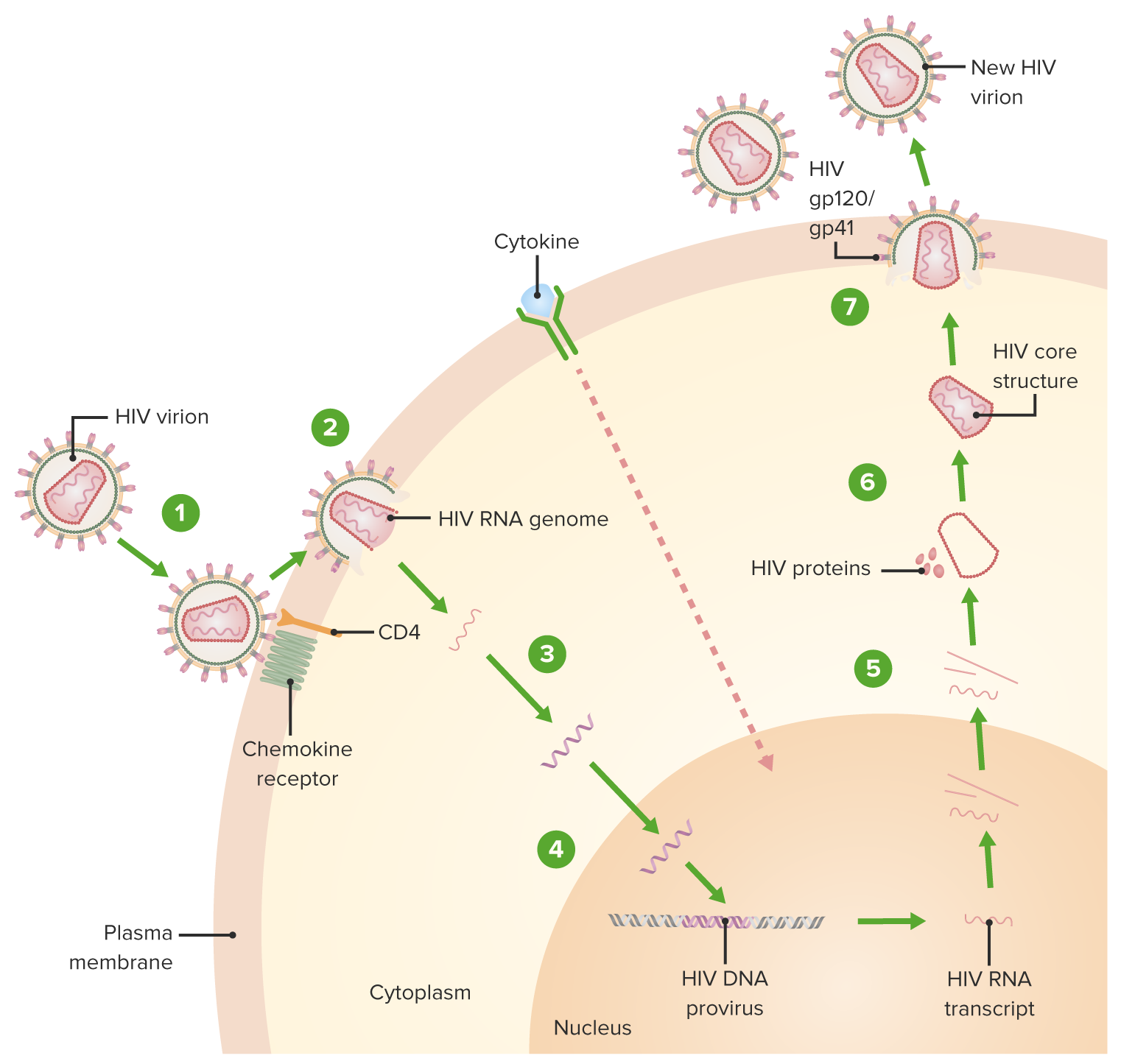
00:01 Let's move on to the next section. 00:03 So you remember that molecule called the reverse transcriptase. 00:07 We have targets at the reverse transcriptase. 00:10 Remember that DNA is made up of nucleosides and nucleotides. 00:16 We're going to look at them based on what they're targeting. 00:18 So there's the nucleoside and the nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors are either called NSRTIs NtRTis and then we have another category called the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors or the NNRTIs. 00:36 Now these are divided in our pharmacology lecture into first and second generation more for you so that you can keep a track of these medications out in clinical practice. 00:46 It's not commonly divided up this way. 00:49 Okay, let's focus on the NSRTIs. 00:53 So there's a huge list here. 00:55 And I don't expect you to know all of the drugs. 00:58 It's impossible. 01:00 But I think if you take a look at the ones that are in boldface, these are the ones that you are probably going to come across in clinical practice. 01:08 You do not need to know that this particular drug is NSRTIs or NNRTI, I think that that's an unreasonable request. 01:15 But if you know how the drugs work in general, I think that that will work you well. 01:20 Now the NSRTIs are mostly anti metabolic drugs. 01:25 What what that means is that an interferes with the metabolism and development of the DNA particle or the RNA transcription. 01:34 Now we use three or more drugs at the same time for HIV treatment kind of like we do with tuberculosis and we try to do these different drugs or use these different drugs from different classes so we don't use two NSRTs at the same time. 01:53 HAART stands for highly active antiretroviral therapy. 02:00 So this is generally multi drug regimen and these regimens are shown to reduce or reverse the decrease of the CD4 counts. 02:10 We also, which is our target is to reduce morbidity and mortality from the HIV illness. 02:19 Now the NSRTIs act on the viral reverse transcriptase. 02:24 Remember that the viral reverse transcriptase is much different from the mammalian reverse transcriptase. 02:30 So it made sense that we could target this very different enzyme and have fewer side effects for the human host. 02:39 The NSRTIs lack a 3' Prime hydroxyl group on the ribose ring, so that the next nucleotide can't bind to that chain the NSRTIS are converted by the host cell kinase to triphosphates that block the binding of the nucleotides to the D site of the reverse transcriptase and they act as a chain terminator. 03:03 So the chain is no longer being produced. 03:07 Now all NSRTIs may cause lactic acidosis and can cause hepatomegaly. 03:13 So watch your amino transferase levels closely when you're administering this drug from an exam point of view, you want to remember that they can cause a mild hepatitis and can cause severe hepatomegaly and you know, you may be asked to watch you may be asked which enzyme to watch. 03:31 I doubt they would particularly target ALT as your choice on the exam at the USMLE level, but they certainly will if you're writing your Internal Medicine boards. 03:42 The next on our list is abacavir, so it's a it's actually quite a good drug. 03:48 Has very good aural availability. 03:50 It has a half-life of 12 to 24 hours and resistance is also unlikely because it requires several point mutations on the part of the HIV virus to be resistant to this drug. 04:02 Side effects include hypersensitivity reactions. 04:06 And occasionally, these can be so severe that can become fatal. 04:11 Up to 5% of HIV patients had fatal reactions in the initial deployment of this drug. 04:19 Next on our list is emtricitabine. 04:21 Emtricitabine has good oral availability. 04:24 It is excreted by the kidneys and the dosage is once a day. 04:30 So it's actually a fairly convenient medication. 04:33 It is contraindicated in pregnancy in small children and patients who have underlying hepatic dysfunction. 04:40 Iamivudine is another NSRTI It's often used in heart therapy for HIV patients. 04:46 We also use this medication actually in hepatitis the toxicity and Adverse Events are certainly present, GI/GU symptoms which include mild gastric distress. 04:59 You can also get neurological side effects which include some mild headaches, you'll often get fatigued in these patients. 05:06 In fact, I see that quite often in the patients coming from the HIV Clinic and of course you can have insomnia the cause of which would be unknown. 05:15 Finally on our list. We have zalcitabine. 05:17 It is distributed to most tissues including into the central nervous system. 05:21 So you can see where this particular drug would be useful. 05:24 It is also regionally excreted. 05:26 We adjust the dose in in renal failure again, it is metabolized through cytochrome p450. 05:32 So this is a bit of a disadvantage because a lot of time patients who are on this medication are also on Rifampin. 05:38 So if the patient has tuberculosis as well as HIV and they're on Rifampin, remember that this particular drug can be affected by the Rifampin. 05:47 In terms of toxicity, again, we have pancreatitis. 05:51 We can also get ulcerations of the esophagus neurological side effects. 05:56 You can get in peripheral neuropathy. 05:59 It depends on what dose you're on but certainly it's something that we need to consider. 06:04 Zidovudine is used to come under another name that's utterly unpronounceable. 06:09 It's distributed to most tissues. 06:11 It's a limited via both the kidney and via the liver, toxicities of this medication include bone marrow suppression. 06:20 And this is a particular concern in patients with HIV. 06:23 Anemia is also seen in patients on this drug, and of course neutropenia. 06:28 In terms of your side effects, usually gastric distress is something that we are concerned about. 06:33 One thing I want to mention is a disease called Fanconi syndrome. 06:38 If you can burn this into your memory the fanconi syndrome and this particular drug, you will get at least one question right on your exams neuro includes headache, insomnia and fatigue.
About the Lecture
The lecture Anti-HIV Agents: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NsRTIs) – Antiviral Drugs by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Antimicrobial Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which findings are most consistent with the side effect profile of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors?
- Lactic acidosis and hepatic steatosis
- Respiratory acidosis and acute kidney injury
- Metabolic acidosis and cholestasis
- Respiratory acidosis and heart failure
- Lactic acidosis and obstructive uropathy
What best describes highly active retroviral therapy (HAART)?
- Co-administration of different drugs that inhibit viral replication by several mechanisms
- Single antiretroviral drug therapy to reduce the chances of drug resistance
- Sequential introduction of multiple drugs to increase the likelihood of treatment success
- Use of antiretroviral medications that are also active against tuberculosis
- Use of at least 2 drugs from the same group of antiretroviral medications
Which nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor is most likely associated with a severe hypersensitivity reaction?
- Abacavir
- Didanosine
- Emtricitabine
- Lamivudine
- Zidovudine
What medication may cause esophageal ulceration?
- Zalcitabine
- Abacavir
- Emtricitabine
- Lamivudine
- Stavudine
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
good lecture explaining everything about: Anti-HIV Agents: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NsRTIs) – Antiviral Drugs