Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Male Perineum and Penis
-
Slides Male Perineum and Penis.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
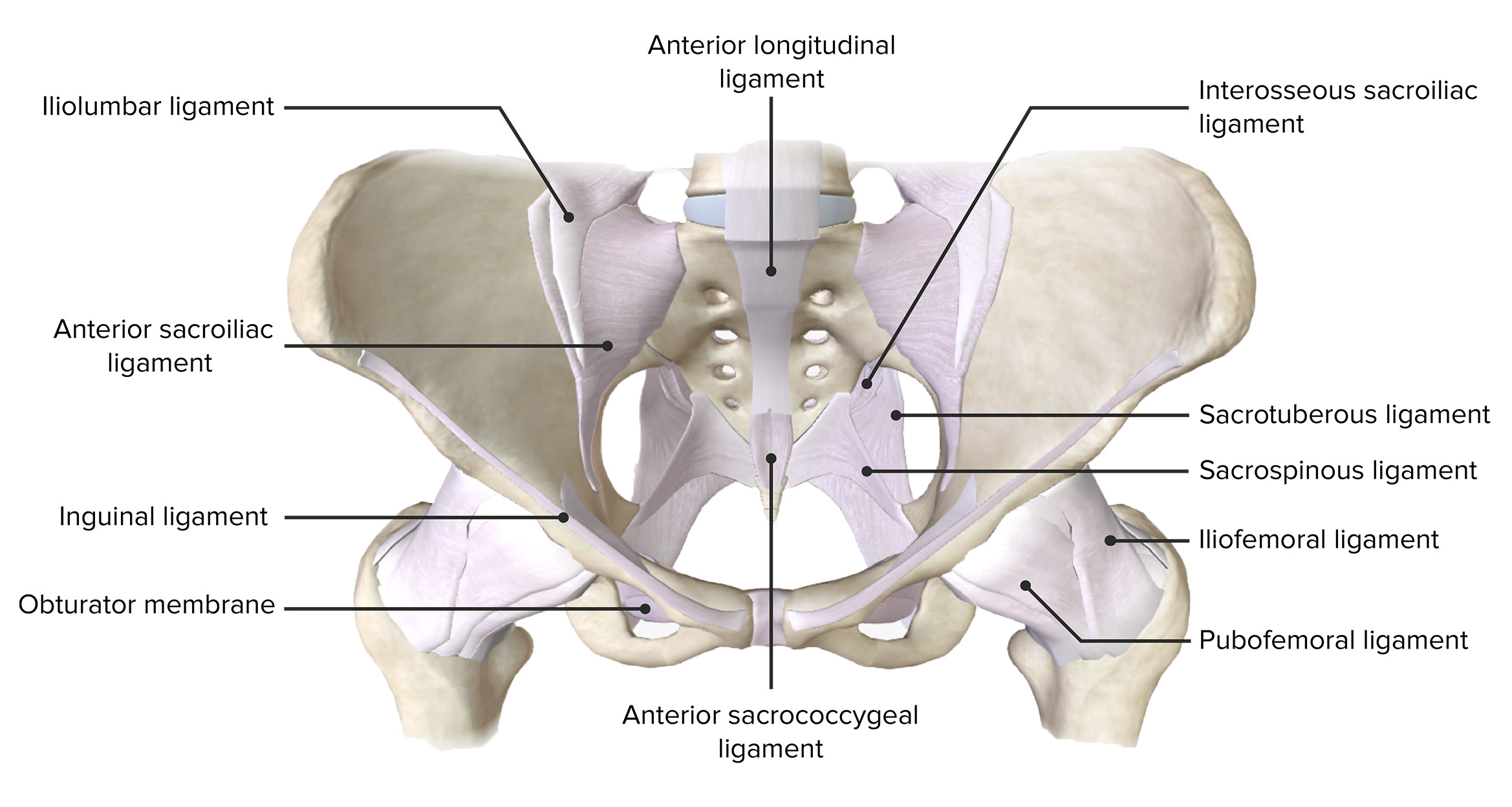
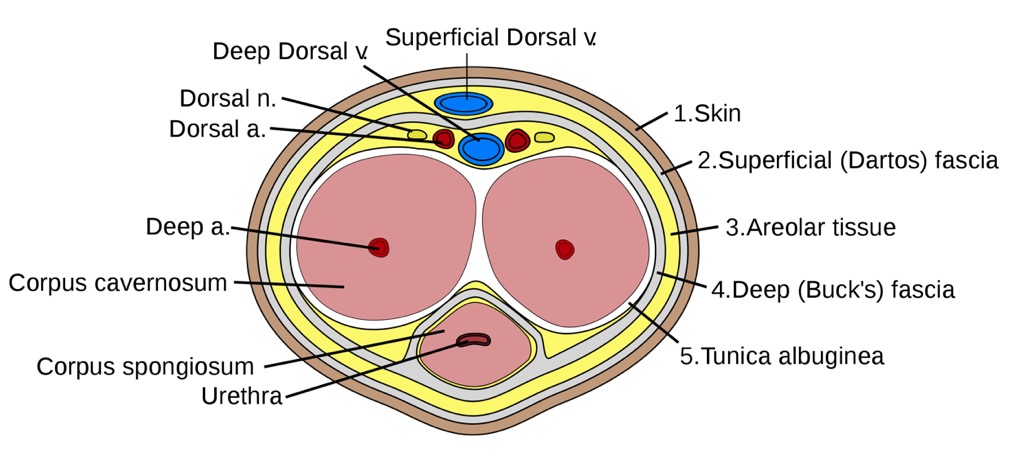
00:01 So, let's start off by looking at the male perineum. 00:04 So, here we're looking at exactly the same space that we described a moment or two ago. 00:09 Here we're looking at the anterior aspect of the pelvis, which is just been tilted posteriorly. 00:15 So the top of the screen we have the pubic symphysis and here we have the two ischiopubic rami emerging infra laterally away from the midline. 00:24 And in the middle of that space, we have the perineal membrane. 00:27 So, we're looking into the superficial perineal pouch. 00:31 What we haven't got here is the skin that would overlay this as the most superficial boundary. 00:37 So, here we're looking at the superficial perineal pouch and the perineal membrane. 00:42 So, in the male, what we need to add on are some important structures. 00:47 So here we can see the deep transverse perineal muscle within that deep perineal pouch. 00:53 We can see the external urethral sphincter here as well. 00:56 And here we've got the bulbourethral glands, which we can see. 01:00 We've also got various perineal blood vessels, and we'll come back to those in a moment or two. 01:05 But they have come from the internal pudendal as it's running along that ischiopubic rami that's part of that pudendal canal, we spoke about previously. 01:15 So, here we are looking in the deep transverse perineal muscle. 01:19 So these structures are residing within that deep perineal pouch. 01:22 Now we're going to add on the layer, which is the perineal membrane to form that superficial pouch. 01:29 So again, we're looking at a similar position here. 01:32 We can see the perineal membrane. 01:33 And now we can add on the erectile tissue of the external genitalia of the penis. 01:39 So here we can see the structures, which are essentially hanging off the ischiopubic ramus and the perineal membrane. 01:46 So, if we have a closer look, we can start looking at the anatomy in this space. 01:50 So, here we can see we've got the cruise of the penis. 01:53 These are overlying thickenings of that ischiocavernosus muscle. 01:58 And here we can see the bulb of the penis, which is formed by that bulbospongiosus muscle overlying it. 02:04 So this is part of the erectile tissue. 02:07 These tissues are essentially large sponges that can fill with blood are becoming gorged during sexual arousal. 02:16 So what we have surrounding them a series of muscles that when they contract, they have to compress that blood within that spongy tissue to maintain an erection. 02:27 So, here we can see surrounding both the crus of the penis and the bulb of the penis. 02:32 Those muscles we mentioned previously. 02:35 These two erectile tissues will be coming gorged with blood during sexual arousal, and then the muscles overlying them as they contract will prevent venous drainage of that blood from that tissue. 02:47 And we've sustained sexual arousal, those muscles will maintain contraction holding the blood within that erectile tissue. 02:55 We also have in the superficial perineal pouch, that final muscle which is a superficial transverse perineal muscle. 03:03 So let's just have a look at this from a different perspective here. 03:06 Here we can see part of the erectile tissue of the penis, which is hanging from the perineal membrane. 03:12 So here we can see the pubic symphysis and we've got the perineal membrane. 03:16 So everything inferior or superficial to that perineal membrane is in the superficial perineal punch. 03:22 Hanging from it we have a series of erectile tissues. 03:27 These are essentially like I said, sponges that fill with blood upon sexual arousal. 03:32 And these are fixed to the perineal membrane. 03:35 We have parts of those erectile tissues that extend distally and these are no longer fixed to the perineum membrane. 03:42 And this is the mobile part of the male penis. 03:45 And obviously, that position can change again, with sexual arousal leading to an erection of the penis. 03:51 So here we can start seeing some additional structures. 03:54 The root of the penis here we can see the bulb, the beginning of that erectile tissue. 03:59 And then we can see running lateral to it. 04:01 We have the crus of the penis. 04:03 And there's a left and right ones of these. 04:06 We then have the shaft of the penis is these three erectile columns come together. 04:10 And here we can see the crus of the penis then becomes the corpus cavernosum. 04:15 We have two of those which reside within the mobile shaft of the penis. 04:19 The bulb of the penis then becomes continuous with the corpus spongiosum. 04:24 And here we can see this is lying along the inferior or the more ventral aspect of the penis. 04:29 Remember, the orientation of the penis is that of it being erect. 04:33 So, we can see the corpus spongiosum is positioned on the ventral aspect of the penis. 04:38 The tip of the penis is characterized by the glands, which is a dilation of the corpus spongiosum. 04:44 And that will go and surround the distal end of the corpus cavernosum. 04:48 So let's have a look at the penis in a bit more detail. 04:51 And to do that, we'll have a look at a cross section that's been taken off the penis we can see here. 04:56 So now we can see the two corpora cavernosa lying laterally in the shaft of the penis. 05:01 And these are positioned more dorsally so towards that superficial aspect we can see at the top of the penis. 05:08 And then lying more ventrally, we can see the corpus spongiosum. 05:13 Running through the corpus spongiosum is going to be the urethra that is passed through the urogenital triangle that urethral opening and then the urethra is running through the corpus spongiosum taking both urine and semen. 05:26 Surrounding the corpora cavernosa we have a tough fibrous layer. 05:30 This is known as the tunica albuginea. 05:33 We have a layer of fascia that surrounds that, and then we have the skin that surrounds that of the penis. 05:38 And that skin is then finding on the most superficial aspects of the superficial perineal pouch. 05:45 If we then have a look at the penis as a whole in cross section, we can remind ourselves of here, the bladder. 05:51 We have the urethra leaving the bladder and passing through the prostate and this is the prostatic urethra. 05:57 We then have the membranous urethra that passes through the perineal membrane. 06:02 We then have the urethra passing through the bulb of the penis, so the bulbous portion. 06:07 And then we have the urethra passing through the penile portion, that mobile aspect to the penis. 06:13 Remember, the urethra then before we get to the external urethral meatus becomes the navicular fossa. 06:18 A slight dilation before it becomes the external urethral meatus. 06:23 If we then have a look at the skin, which is very much around the superficial perineal pouch, then here we can bring in the anterior aspect which is the pubic symphysis or where it would be positioned. 06:34 Obviously, the external genitalia is in view here. 06:37 We can see we then have the coccyx here. 06:39 We can then draw in the position of the urogenital and the anal triangles that make up the perineum. 06:46 So here we have that diamond shape. 06:48 And here we have that line running between the two ischial tuberosities, separating the urogenital triangle and the anal triangle. 06:56 Here we can see the position of the perineal body where a lot of the muscles we spoke about converge together. 07:02 Deep superficial transverse perineal muscles for example, as well as the anal sphincter and bulbospongiosus. 07:09 If we remove those, we can then bring in some surface landmarks. 07:13 So, here we have the anus. We have the raphe. 07:16 We then have the scrotum, which has the raphe leading over it. 07:18 And then we have the penis. 07:20 The final part we can see there is the glans of the penis, which we saw is that expanded region of the corpus spongiosum. 07:27 So, here we can see now how the skin surrounding the penis is in relationship to the glans of the penis. 07:33 The expanded aspect of the corpus spongiosum. 07:36 So, here we can see the external urethral orifice or meatus. 07:40 Here we can see the glans penis. 07:42 We can see the corona or the dilated edge of the glans of the penis. 07:46 We can see the neck of the glans here as it's then tapering down as the corpus spongiosum. 07:51 And here we can see the frenulum where the skin runs in towards that glands. 07:56 The skin of the penis is surrounding the entirety of the shaft and it can then also extend over and surround the glans of the penis.
About the Lecture
The lecture Male Perineum and Penis by James Pickering, PhD is from the course Perineum.
Included Quiz Questions
What is a component of the root of the penis? Select all that apply.
- Bulb
- Crus
- Shaft
- Corpus cavernosum
- Corpus spongiosum
Through which part of the penis passes the urethra?
- Corpus spongiosum
- Corpus cavernosum
- Tunica albuginea
- Deep fascia of penis
- Skin
What is the most proximal part of the urethra?
- Prostatic urethra
- Membranous urethra
- Bulbous urethra
- Penile urethra
What is the area of skin that runs into the glans of the penis?
- Frenulum
- Corona
- Neck
- Head
- External orifice
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |