Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Endometrial Hyperplasia
-
Slides Uterus Female Repro.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
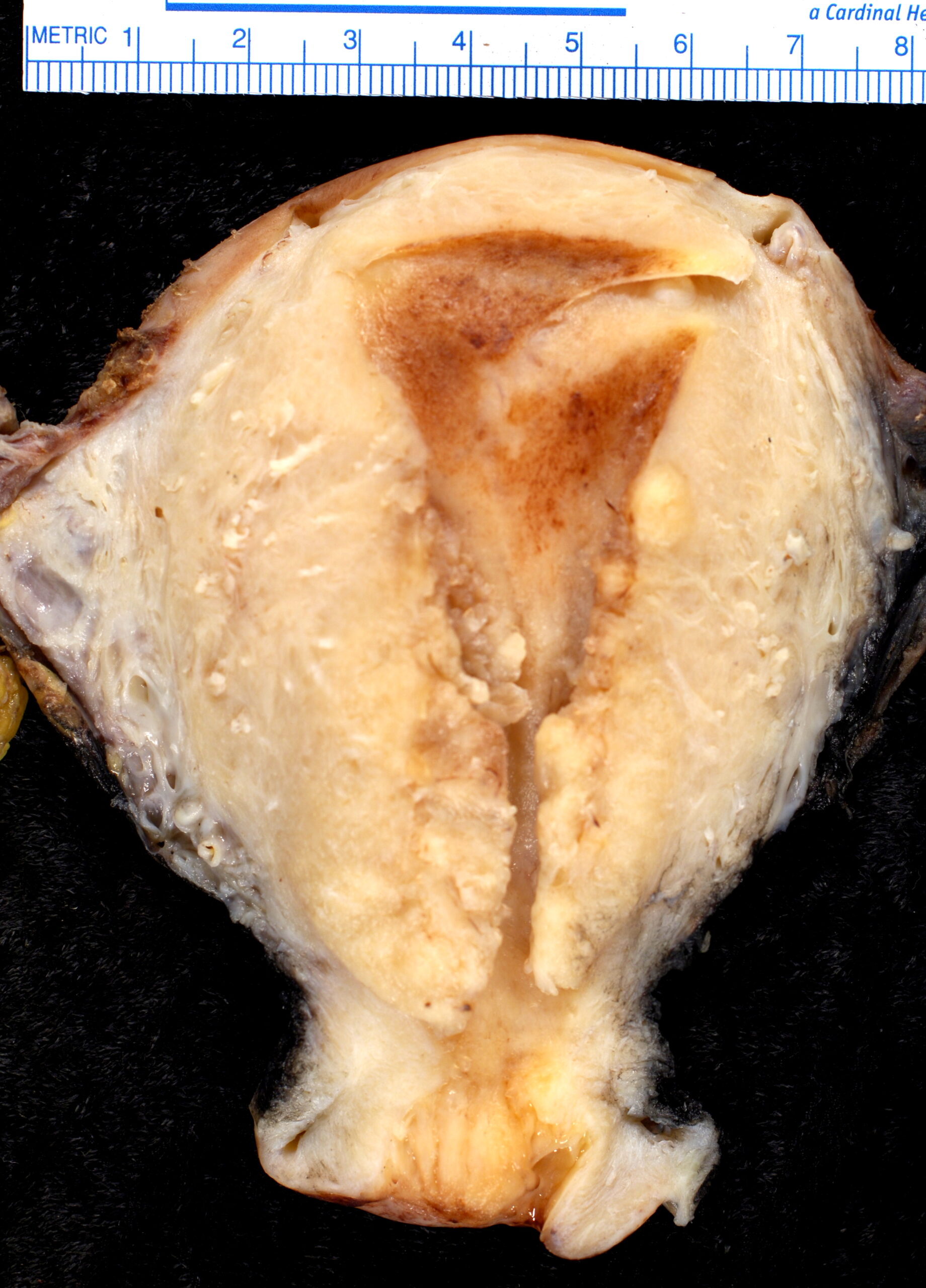
00:01 Here we have endometrial hyperplasia. 00:04 From now on, the two conditions that you want to group together include endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial carcinoma. 00:12 The reason for that is because when it comes to prognosis and what your next step of management would be, you’d find this to be quite interesting and unfortunate. 00:21 Endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma, both extremely responsive to estrogen. 00:26 So therefore, related to abnormally high, prolonged level of estrogen stimulation. 00:33 So what might you be thinking about? You might be thinking about a lady who had early menarche, late menopause. 00:38 Whew. 00:39 tons of exposure to estrogen. 00:42 What else? Maybe she ends up developing polycystic ovarian syndrome and polycystic ovarian syndrome is quite a bit of estrogen that the female is producing. 00:52 Also, she maybe perhaps is a candidate for hormone replacement therapy. 00:59 A hormone that in fact that you’re replacing is estrogen. 01:01 Unfortunately, there’s every possibility that she might then develop endometrial hyperplasia/endometrial cancer. 01:11 Detected by abnormal bleeding especially post menopausal. 01:16 So what are you going to find? You’d do a pelvic exam and, when you do so, if you take a look at the cervical os, from the cervical os, you’d notice that there’s bleeding. 01:24 That should clue you that perhaps your patient is suffering from endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma. 01:30 It is a risk factor for endometrial cancer Endometrial Hyperplasia (EH), is categorized into two primary groups: Endometrial Hyperplasia Without Atypia: Here, the endometrium shows an increase in the number of glands relative to the surrounding tissue, with a ratio greater than 2:1. 01:51 The glands can appear slightly overcrowded, expanded, and may bulge outwards, which is termed luminal outpouching. 02:00 There are no abnormal features in the cell nuclei within these glands. 02:04 The risk of this condition progressing to endometrial cancer if left untreated is less than 10% Endometrial Hyperplasia With Atypia: This condition is also known as atypical hyperplasia or endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia (EIN). 02:26 The gland-to-stroma ratio is further increased here, and there's noticeable disorganization in the glandular structure along with abnormal, atypical nuclei. 02:36 If EH with atypia is not treated, the risk of progression to endometrial carcinoma ranges from 15 to 40%. 02:45 Additionally, there's a significant possibility, up to 40%, that patients with EH with atypia may already have endometrial carcinoma in one or more areas not sampled by biopsy. 02:58 For Premenopausal patients who have endometrial hyperplasia Without Atypia and who wish to maintain fertility, progestin therapy along with regular checks of the endometrium is recommended. 03:11 For those without additional risk factors for endometrial cancer, like obesity or a family history of cancer, and who cannot take progestins, simply watching and regular endometrial sampling is an acceptable alternative. 03:26 For Postmenopausal Patients who have endometrial hyperplasia Without Atypia, progestins can be used for treatment. However, if there are any risk factors that increase the chance of endometrial cancer, or if progestins aren't suitable, a hysterectomy may be the recommended course of action. 03:48 For Premenopausal patients who have endometrial hyperplasia With Atypia and who want to preserve their fertility progestin therapy is administered, along with regular sampling of their endometrium. 04:03 For Postmenopausal Patients or premenopausal patients who have finished childbearing and who have endometrial hyperplasia With Atypia, a hysterectomy is generally recommended.
About the Lecture
The lecture Endometrial Hyperplasia by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Uterine and Fallopian Tube Disease.
Included Quiz Questions
By what common mechanism do PCOS, early menarche, and hormone replacement therapy predispose to the development of endometrial hyperplasia?
- Exposure to estrogen levels that are abnormally high relative to progesterone levels
- High cyclical testosterone exposure
- Insulin resistance
- Exposure to high levels of FSH/LH
- Exposure to progesterone levels that are abnormally high relative to estrogen levels
A postmenopausal woman comes to the office for her annual physical exam. Which of the following presentations should alert the physician to the possibility of endometrial hyperplasia?
- Vaginal bleeding
- Severe pelvic pain
- Cyclical abdominal pain
- Clue cells on Pap smear
- Increased urinary frequency and palpable pelvic mass
Which of these findings on an endometrial biopsy has the highest risk of progression to endometrial carcinoma?
- Endometrial hyperplasia with atypia
- Endometrial hyperplasia without atypia
- Hyperplastic stroma
- Chronic endometritis
- Endometrial polyps
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |