Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Deep Vein Thrombosis: Definition
-
Slides 10 VascularMedicine advanced.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
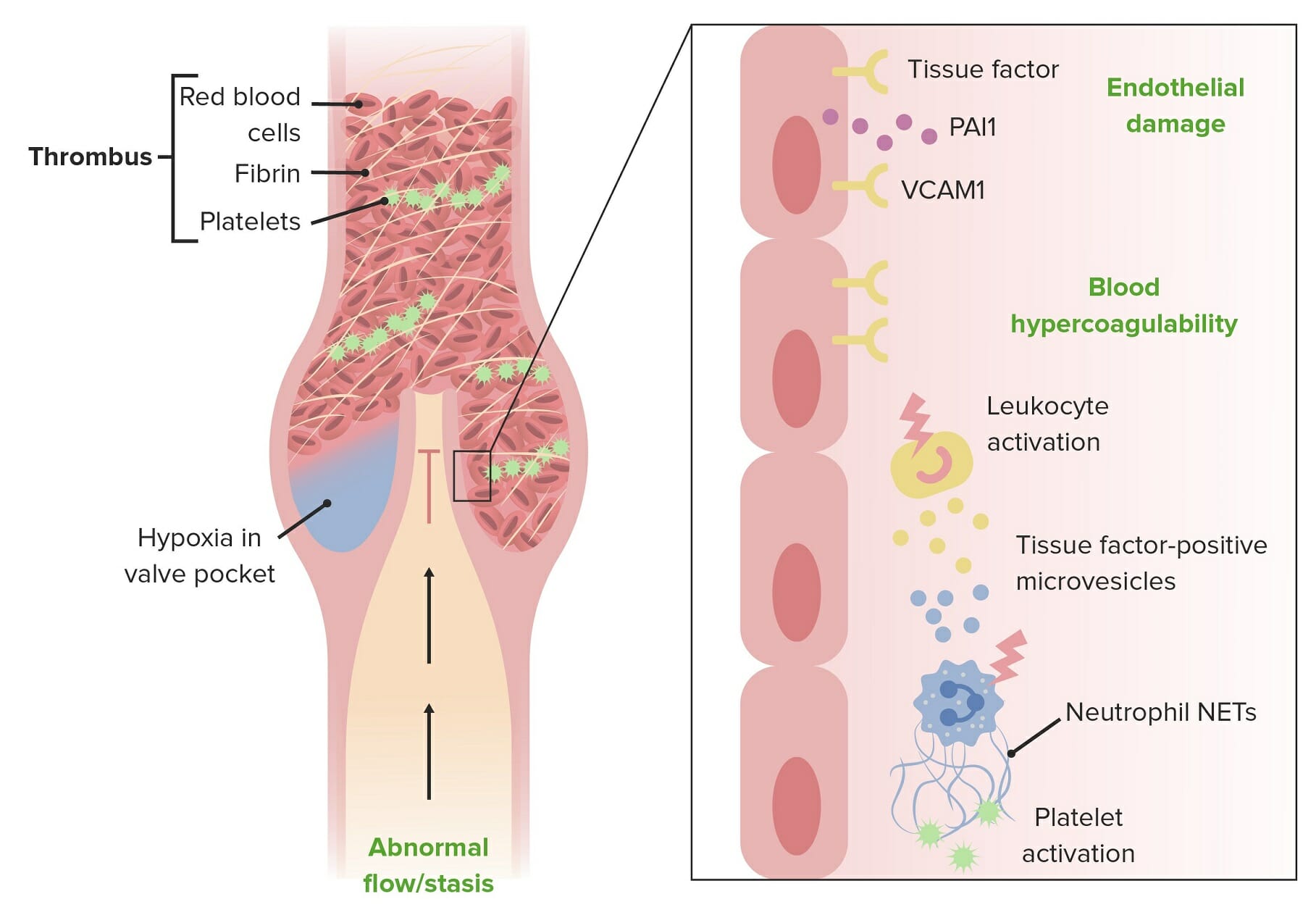
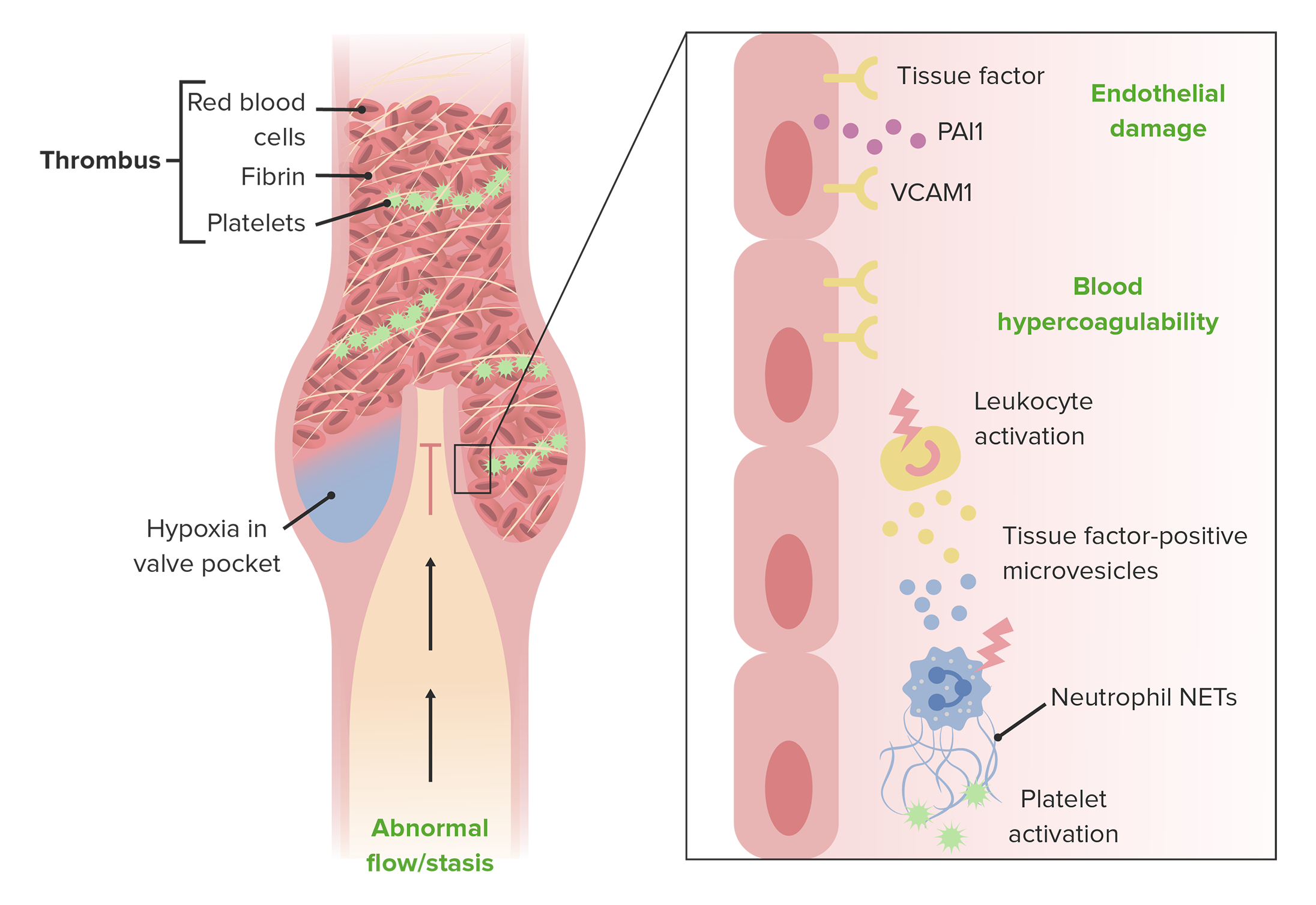
00:01 Advanced vascular medicine: We'll now consider, in greater detail, deep venous thrombosis, with an eye towards the potentially fatal complication of pulmonary embolism. Deep venous thrombosis is exceedingly common, particularly in hospitalized patients, and is a great cause of rehospitalization, morbidity, and as I said, even mortality. So we're going to look at deep venous thrombosis in much more detail compared to previous. 00:31 First of all, let's review some of the definition. Deep venous thrombosis is a thrombus (a blood clot) within a deep vein—not a superficial vein that you can see on the surface, but a deep vein. It's associated with breaking off of the clot and embolizing of the clot into the lung. And blockage of the main artery of the lung or one if its branches by an embolus may cause severe symptoms, may cause decrease in blood pressure, and can even be fatal. 01:04 DVT and pulmonary embolism are often lumped together using the term venous thromboembolism, and you can see in that term, we're including both the clot in the vein and the embolism to the lung. The obstruction in the vein is caused by the thrombus that breaks free and is carried away with the blood flow up to the lung. 01:29 Now, one of the great problems in clinical medicine is that most DVT and pulmonary embolism is silent. You can see here in this pyramid, which you've seen before, that the overwhelming majority of patients with DVT and pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. So that's one of the reasons why it's important to be looking for it with nonivasive tests that we'll mention later (for example, ultrasound). A small percentage of patients, the DVT and pulmonary embolism become symptomatic, and fortunately, a very small number but somewhere around 6% of patients with pulmonary embolism die from the pulmonary embolism. It's often in the setting of severe illnesses of another type, such as cancer and heart failure and so forth, where the final blow that kills the patient is a fatal pulmonary embolus.
About the Lecture
The lecture Deep Vein Thrombosis: Definition by Joseph Alpert, MD is from the course Venous Diseases.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following statements regarding a DVT/PE is correct?
- Non-invasive tests, such as ultrasounds, are helpful in making the diagnosis.
- DVTs are usually easy to diagnose because of their severe symptom profile.
- DVTs may occur only in the deep veins of the legs.
- “Varicose vein” is another term to describe a DVT.
- Most DVT/PE thromboembolisms are fatal.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |