Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Deep Layer of the Posterior Compartment of the Leg
-
Slide Deep Layer of the Posterior Compartment.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
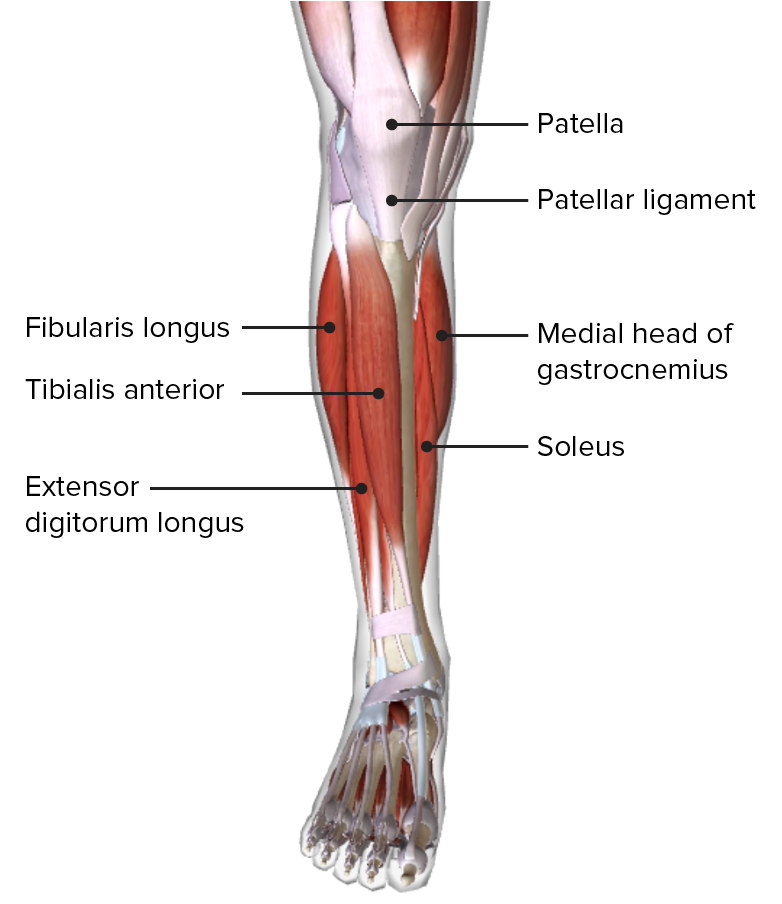
00:01 So now let's have a look at the deep layer of the posterior compartment. 00:05 We've previously looked at the superficial layer. 00:07 So now let's go deeper and look at these muscles in this location. 00:12 So here we can see, we have a posterior surface of a right leg, we can start adding in a series of muscles which we find in this deep layer starting with popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, and all of these muscles are forming that deep compartment within the posterior aspect of the leg. 00:37 So four muscles to worry about. 00:39 Here's popliteus. 00:41 It's originating from the lateral femoral condyle, and then it runs transversely across to the medial aspect where it's running onto the posterior surface of the tibia, just above that soleal line. 00:53 It's very important in helping to stabilize the knee. 00:56 So it resists lateral rotation of the tibia on the femur. 01:01 So this is a very important muscle that helps to lock the knee joint in position, especially when you're standing upright. 01:08 It also helps to unlock the knee joint, so a laterally rotates the femur on a fixed tibia. 01:14 This means that when you're actually beginning to start that movement process, it helps to unlock the knee to allow flexion to occur. 01:22 So the popliteus may be a small muscle but it is very important. 01:26 Let's move on to tibialis posterior here, we had tibialis anterior in the anterior compartment. 01:32 So we've got its sibling here on the posterior surface of the leg. 01:37 Here we can see tibialis posterior is originating from both the tibia, the fibular and the interosseous membrane and it passes its tendon under the medial malleolus as it passes under the medial malleolus. 01:50 It runs all the way towards a series of bones within the foot. 01:54 The cuneiforms, navicular, metatarsals and the cuboid bone. 01:59 So it has a long splayed out tendon that once it gets onto the sole of the foot, bypassing under the medial malleolus, it inserts into a number of bony structures. 02:09 The function of tibialis posterior is both one of plantar flexion and to support inversion of the foot. 02:17 If we then look to flexor digitorum longus, we can see this thin slender muscle originates from the posterior surface of the tibia, this time below soleal line, and it runs all the way down to the distal phalanges of the second to fifth digits. 02:32 Remember, it's not going to the large great big toe. 02:35 Flexor digitorum longus, a long flexor, the digits of the toe. 02:40 So it's going towards the second to five digits, the distal phalanges. 02:45 The function of this muscle is to flex the second to fifth digits and also help with plantar flexion of the ankle. 02:55 Now let's go to flexor hallucis longus. 02:58 Flexor hallucis longus, as its name suggests, is going to the great toe, the big toe, the first digit of the foot. 03:05 We can see it here, originating from the interosseous membrane. 03:09 It comes also from the lower two thirds of both the posterior fibular. 03:14 It then passes all the way down towards the distal phalanx of the first digit. 03:19 This makes sense because it's flexor hallucis longus. 03:22 So it's going to the first digit the great toe. 03:25 The function of this muscle is flexion of that one specific digit, the great toe, and it also can help with very mild plantar flexion. 03:35 The deepest layer of the posterior compartment is innervated by the tibial nerve. 03:40 Remember, the tibial nerve passes all the way down the posterior aspect of the leg. 03:45 And as it does, so it's associated with a number of structures, hearing through the tibial nerve associated with tibialis, posterior, flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus. 03:56 And all of these muscles are passing down behind the medial malleolus of the tibia. 04:02 They're kept in position via the flexor retinaculum. 04:06 So here we can see the flexor retinaculum, which is coming from the medial malleolus and also inserting onto the calcaneus. 04:12 Similar to other retinacular we're seeing, these help to hold the structures in position. 04:17 They help to hold the tendons in position and also helps to hold that nerve in position as well. 04:24 So the leg is a very complicated structure that has a large number of muscles located within it. 04:30 We've seen we've had the anterior compartment, the lateral compartment, the superficial posterior compartments, and also the deep posterior compartment. 04:40 You can see in all of these various compartments, there's a large number of nerves and muscles associated with them. 04:46 Importantly, the deep fibular nerve supplies those muscles in the anterior compartment. 04:51 The superficial fibular nerve supplies muscles in the lateral compartment and the tibial nerve supplies all muscles within both the superficial and deep posterior compartments.
About the Lecture
The lecture Deep Layer of the Posterior Compartment of the Leg by James Pickering, PhD is from the course Anatomy of the Leg.
Included Quiz Questions
What muscle is NOT part of the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg?
- Soleus
- Popliteus
- Tibialis posterior
- Flexor digitorum longus
- Flexor hallucis longus
What is the origin of the popliteus?
- Lateral femoral condyle
- Medial femoral condyle
- Posterior surface of the tibia above the soleal line
- Anterior surface of the tibia above the soleal line
- Interosseous membrane
What is the insertion site of the tibialis posterior?
- Cuboid
- Posterior surface of the tibia above the soleal line
- Fibula
- Interosseous membrane
- Anterior surface of the tibia above the soleal line
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |