Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Case: 42-year-old Woman with Loss of Hearing
-
Strowd CNS Tumors Inherited Tumor Syndromes.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
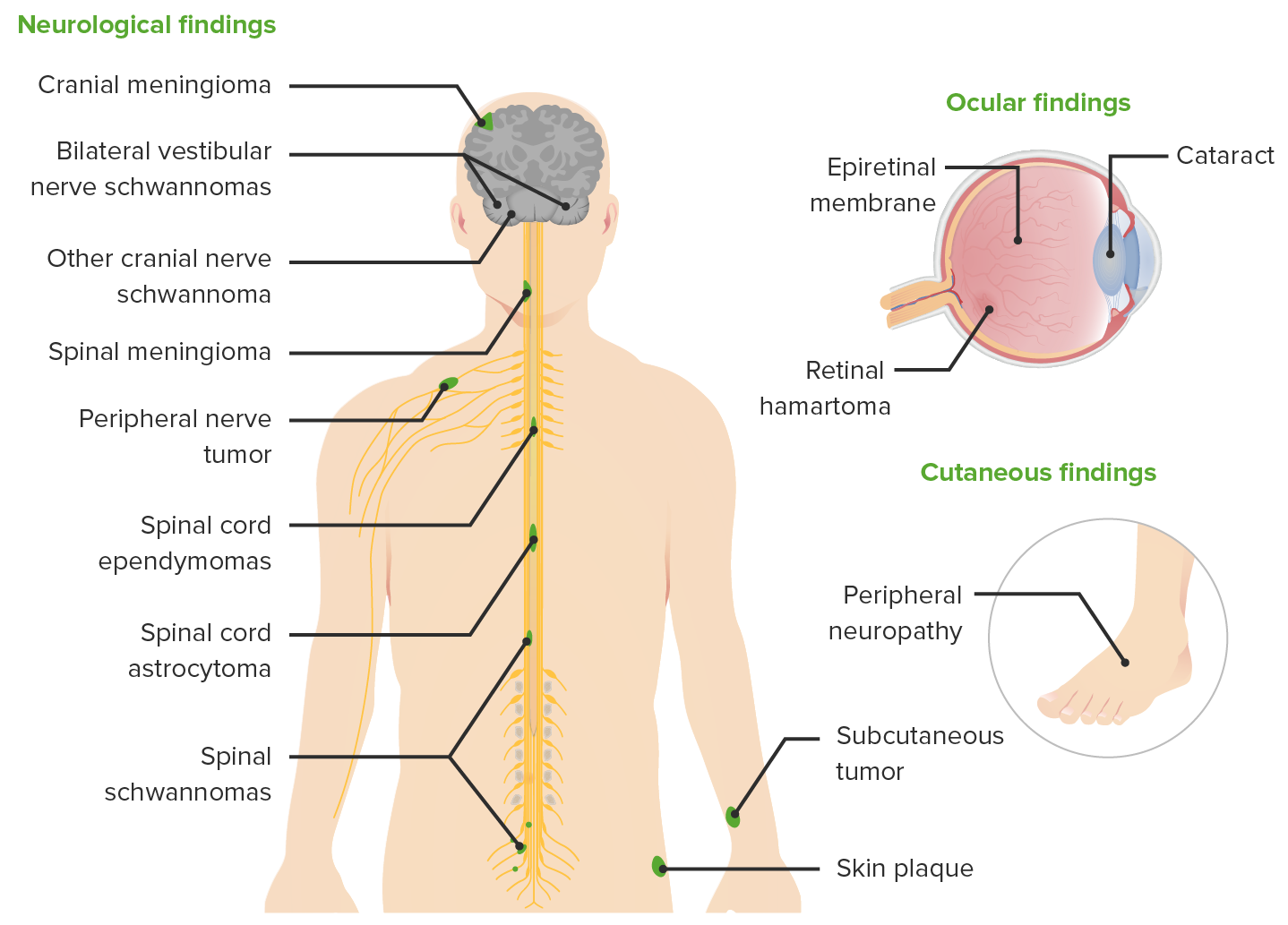
00:01 So now let's shift to NF2. And let's start with a case. 00:05 A 42-year-old woman with hearing loss. 00:09 This woman reported no past medical history and was not taking medications. 00:13 And initially presented 10 years ago with right sided hearing difficulty. 00:18 She was found to have two small enhancing lesions in the bilateral internal auditory canals. 00:24 Those are the areas where the vestibulocochlear nerve and the facial nerve travel. 00:29 Audiometry showed normal hearing and a word recognition score of 100%. 00:35 She was recommended for annual surveillance imaging, and audiometry or hearing tests every six months, but she failed to return for follow-up. 00:44 She presented 10 years later with new complaints of worsening right sided hearing loss, including difficulty speaking on the telephone, hearing the television without looking directly at the screen, and with conversational speech in settings where there was a lot of background noise. 01:00 All symptoms of hearing loss. 01:03 So what's the tumor? What's the diagnosis? Well, there are a few important points about this clinical case. 01:10 This patient has bilateral lesions in the internal auditory canals, which should tip us off to think about bilateral vestibular schwannomas. 01:20 She presents with progressive hearing loss, which is consistent with a growing tumor, probably a benign tumor. 01:27 And here's her imaging. 01:29 On the left we see a T1 post-contrast image showing two lesions one on the right, which you can see highlighted by the green arrow and the other on the left, which you can see highlighted in the red arrow. 01:41 Both of these are in the area of the internal auditory canal, where the vestibulocochlear nerve travels. 01:48 And the imaging appearance is most consistent or concerning for a vestibular schwannoma. 01:54 Remember these are tumors at the CP angle. 01:57 And at the CP angle, we say, AMEN. 01:59 And we think about acoustic neuromas, meningiomas, epidermoid cysts, and other types of neuromas like a facial neuroma. 02:06 And the imaging feature here with this lesion in the auditory canal suggests a vestibular schwannoma. 02:14 Over the course of the 10 years without frequent surveillance imaging, this right-sided tumor grew dramatically. 02:21 And you can see not only the tumor within the internal auditory canal, but that area which is spread into the CPE angle has enlarged significantly. 02:30 That's not the case for the lesion on the left. 02:32 And we'll find out that in this patient, tumors do not all grow the same. 02:38 So what's the diagnosis? Is this NF1, NF2, schwannomatosis, or tuberous sclerosis? What's not NF1? We learned that NF1 we see cutaneous lesions. 02:51 Cafe-au-lait macules, neurofibromas, and other similar findings, which we don't hear about in this patient. 02:57 Tuberous sclerosis. 02:59 Typically presents with seizures, brain findings, kidney tumors, and other lesions, often with a paucity of cutaneous manifestations and we don't see vestibular schwannomas. 03:10 So we don't like the diagnosis of TS. 03:13 Schwannomatosis is closely related to NF2. 03:16 Patients develop schwannomas, multiple schwannomas. 03:20 But typically, these are peripheral schwannomas. 03:23 Out in the arms or legs, and very typically in the legs. 03:26 We typically don't see vestibular schwannomas. 03:29 This patient's presentation is classic for NF2. 03:34 This patient has bilateral vestibular schwannomas, and hearing loss. 03:38 And both of those should raise prominent suspicion for a diagnosis of NF2.
About the Lecture
The lecture Case: 42-year-old Woman with Loss of Hearing by Roy Strowd, MD is from the course CNS Tumors.
Included Quiz Questions
A patient with neurofibromatosis type 2 would most likely demonstrate which of the following?
- Hearing loss
- Radiculopathy
- Upward gaze palsy
- Milky nipple discharge
- Seizures
On what part of the body are schwannomas most commonly found?
- Cerebellopontine angle
- Optic chiasm
- Parasagittal region
- Area postrema
- Medial longitudinal fasciculus
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |