Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Adductor Compartment, Thenar, and Hypothenar Eminences
-
Slide Thenar Adductor Hypothenar Eminence.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
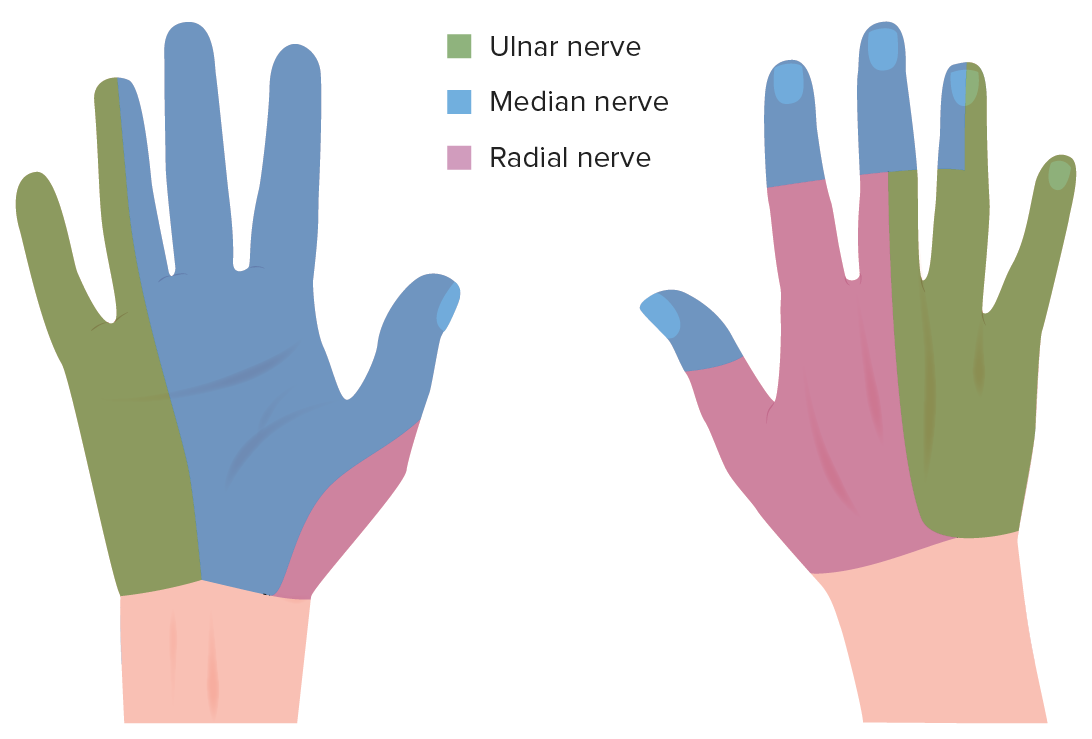
00:01 So, let's talk about the thenar eminence and really, there are three muscles we need to worry about within this space. The first one is abductor pollicis brevis. 00:11 You may remember, it had a sibling called abductor pollicis longus. 00:15 We encountered that when we looked at the forearm. 00:18 This is the shorter version and it's located purely within the hand. 00:22 Deep to that, we have flexor pollicis brevis and we can see the muscle flexor policis brevis there. 00:28 You'll again remember, we had flexor pollicis longus. 00:32 And then, finally, we have opponens pollicis and we can see that situated within the hand in this thenar eminence. 00:40 If we then look at these muscles specifically, let's have a look at opponens pollicis. 00:45 We can see that it's originating from the flexor retinaculum. 00:49 So, this is a band of tissue that forms the carpal tunnel. We'll come back to it towards the end of the lecture. 00:54 It helps to contain all the flexor tendons, similar to what the extensor retinaculum did on the dorsal surface. 01:02 But opponens pollicis is coming from the flexor retinaculum, the trapezium, and it passes all the way towards the first metacarpal and it attaches onto its lateral side. 01:13 So, here, we've got opponens pollicis. The function of opponens pollicis is the medial rotation of the thumb as you can see. Then, we have flexor pollicis brevis. 01:24 Flexor pollicis brevis also comes from the flexor retinaculum and the trapezium. 01:29 It similarly passes towards the thumb where it attaches to the proximal phalanx of the thumb. 01:36 The function of flexor pollicis brevis is to flex the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint. 01:43 We'll come to the axis of the thumb and what flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction look like in a moment or two but this muscle, as it name suggests, flexes the thumb but at the metacarpophalangeal joint because it's attaching to the proximal phalanx. 01:59 The final muscle in this thenar eminence I want to talk about is abductor pollicis brevis. 02:04 And here, we can see abductor pollicis brevis again comes from the flexor retinaculum. 02:09 It also comes from the scaphoid and trapezium bones of the hand. 02:14 It passes all the way towards the proximal phalanx of the thumb. 02:18 As its name suggests, it's associated with abduction of the thumb. 02:24 So, the nerve supply to this thenar eminence is from the median nerve. 02:29 But specifically, the recurrent branch of the median nerve. 02:32 So, the median nerve passes from the forearm into the hand, passing within the carpal tunnel, and then, it gives a small branch that goes back on itself to supply these muscles, hence, the recurrent branch of the median nerve. This nerve is very superficial. 02:48 So, any superficial damage to the thenar eminence of the hand can risk damaging this nerve. 02:54 Now, let's have a look at the adductor compartment and the hypothenar eminence. 03:00 So, the adductor compartment is made up of adductor pollicis and here, we can see it has a couple of heads. 03:08 We can see we have a transverse head and we also have an oblique head. 03:13 The transverse head is coming from the third metacarpal and the oblique head is coming from the capitate bone. 03:20 We can also see it's got an origin from the second metacarpal but it passes laterally towards the medial side of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. 03:30 So, a few origin sites there for adductor pollicis but it passes towards the medial side of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. 03:40 As you can imagine, contraction of this muscle leads to adduction of the thumb. 03:45 Although it's positioned in a place very similar to that of the thenar eminence, this muscle is actually supplied by the ulnar nerve and the deep branch of the ulnar nerve that we can see here. 03:56 If we then move to the hypothenar eminence, we can see the hypothenar eminence is really on this medial aspect of the hand. And it has a few muscles. 04:06 The first one here is opponens digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis and abductor digiti minimi. 04:15 So, a whole series of muscles which are smaller than the thenar eminence and they form the hypothenar eminence, these three muscles. 04:24 Let's have a look at opponens digiti minimi first. 04:27 You can see that it's originating from the hook of the hamate bone and it passes towards the medial border of the fifth metacarpal. 04:36 The function of this muscle is to help rotate and draw the fifth metacarpal anteriorly. 04:43 So, it helps to form that grip by bringing your little finger towards the center of your palm. 04:48 If we then look at flexor digiti minimi brevis, this is the sibling of the longest version. 04:54 You could see that it's again, coming from the hook of the hamate bone, and it passes all the way to the proximal phalanx of the little finger. 05:03 The function of this muscle as its name suggests is to flex the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. 05:10 So, it helps to flex the little finger. The final muscle within this space is abductor digiti minimi and this muscle again comes from a carpal bone within the wrist, but this time, the pisiform, not the hook of the hamate and it comes from the pisiform and then, passes towards the proximal phalanx of the little finger. 05:32 The function of this muscle as its name suggests is one of abduction and it abducts the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. 05:41 So, it helps to move the little finger away from the midline of the hand. 05:46 These muscles are supplied by that ulnar nerve again, that branch of the ulnar nerve, and that is supplying the hypothenar eminence. 05:54 So, all of the muscles within this space are supplied by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve.
About the Lecture
The lecture Adductor Compartment, Thenar, and Hypothenar Eminences by James Pickering, PhD is from the course Anatomy of the Hand.
Included Quiz Questions
The adductor pollicis muscle inserts onto which site?
- Medial side of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
- Distal phalanx of the second digit
- Lateral side of the distal phalanx of the thumb
- Lateral side of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
- Medial side of the distal phalanx of the thumb
What is the function of the opponens digiti minimi?
- Rotates and draws anteriorly the 5th metacarpal
- Rotates and draws posteriorly the 5th metacarpal
- Extends and draws anteriorly the 5th metacarpal
- Extends and draws posteriorly the 5th metacarpal
- Extends and draws anteriorly the 2nd metacarpal
Which muscle originates from the pisiform?
- Abductor digiti minimi
- Flexor digiti minimi
- Opponens digiti minimi
- Abductor pollicis brevis
- Flexor pollicis brevis
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |