Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Detection Bias
-
Slides 05 CausationBiasInformation Epidemiology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
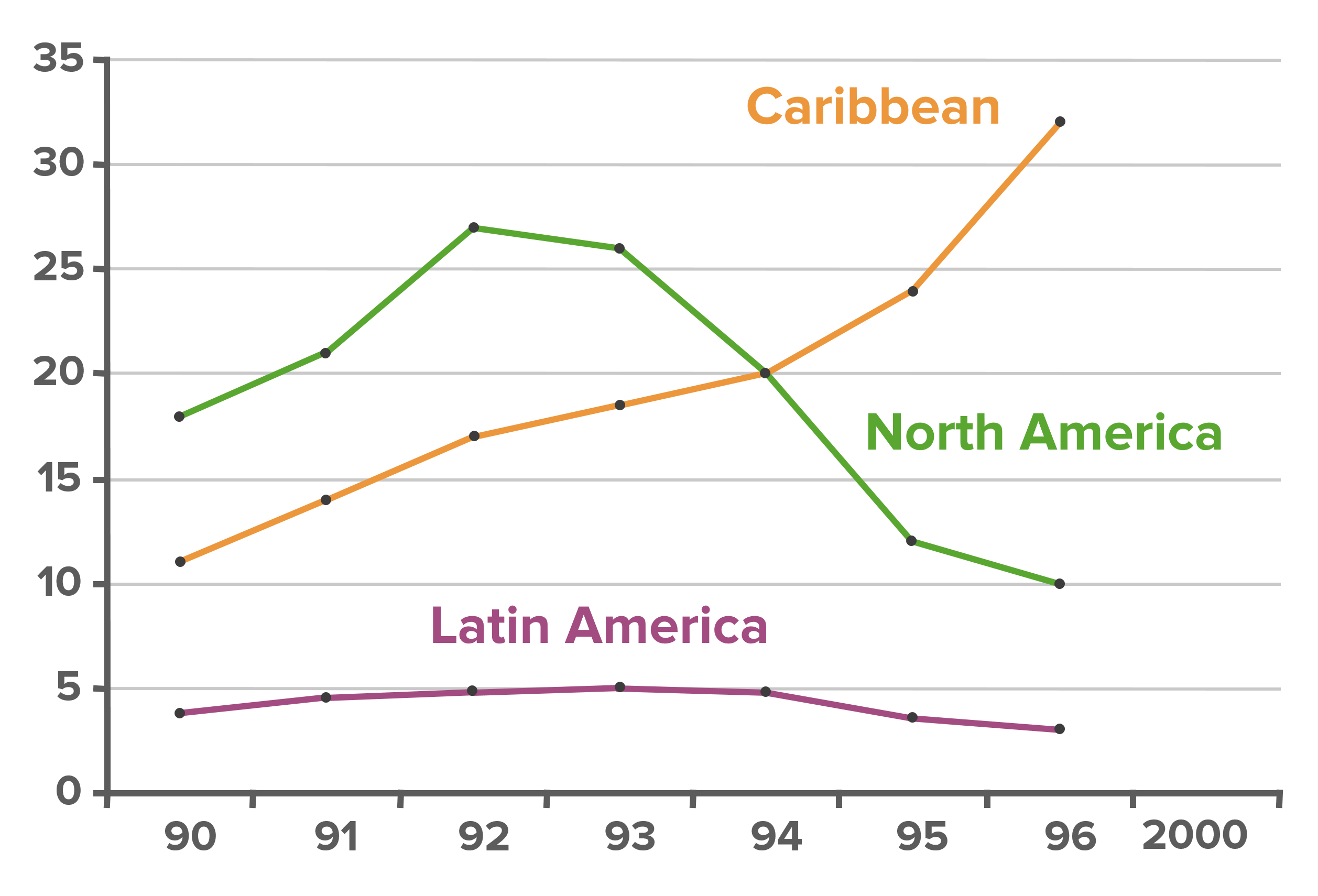
00:00 The next kind of bias is my personal favorite, that’s detection bias cuz detection bias resolves a lot in surveillance studies. 00:08 This is when the act of looking for an effect erroneously gives you the impression that effect actually exist or that it’s larger than it actually is. 00:17 So imagine you have a phenomenon and you’re looking for that phenomenon. 00:22 Are you going to find it? Yes, you are, by the very act of looking for it you’re going to find it, that doesn’t mean it suddenly arose, it might have been there all along so your presence there has an effect on how you view the data collection process. 00:39 So here’s an example. 00:42 Let’s say doctors are more likely to examine obese patients for diabetes than they do thin patients. 00:49 We know that’s to be true because we know that obesity is a risk factor for diabetes, therefore, they're more likely to find diabetes amongst obese patients than they are in thinner patients. 01:00 This gives rise to something called a syndemic. 01:03 A syndemic is when we have an epidemic that’s based on synergy between two different diseases in this case diabetes and obesity. 01:11 It might be true, it might not but it’s entirely conceivable that it will give you a huge impression of the prevalence of a certain kind of condition in a certain kind of person. 01:21 My personal favorite is this graph that I show all my students. 01:27 So this shows us the new AIDS cases per year from 1990 to about 2000 in three different regions in the world - Latin America, the Caribbean and North America. 01:37 In North America the new AIDS cases declined in the early to mid 1990s. 01:42 We think due to new therapies being introduced. 01:46 In the Caribbean in the same time period, the number of AIDS cases increased dramatically and I always ask my students, why was that? Why do you think it went up so dramatically in the Caribbean? And I hear all sorts of theories things like, oh, because there are more travelers were coming in from different AIDS endemic areas or the rate of sex work increased or a variety of different kinds of theories. 02:08 In truth, what was happening in the Caribbean is we started looking for more AIDS cases so we found more AIDS cases. 02:15 It was always high but we only noticed it in the late 1990s so that graph has the appearance of an increase but there wasn’t an increase, that’s classic detection bias.
About the Lecture
The lecture Detection Bias by Raywat Deonandan, PhD is from the course Statistical Biases.
Included Quiz Questions
A study is conducted to examine the association between thrombocytopenia and the diagnosis of a rare form of cancer. The study leads to an increase in screening and early detection of this type of cancer in the subjects. Which type of bias does the vignette portray?
- Detection bias
- Confirmation bias
- Misclassification bias
- Response bias
- Reporting bias
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
My favorite part about the lecture is the last example. Presentation and lecture is understandable however I wasn't quite sure whether i grasped it or not. That last part made me to understand the topic better. Thanks, Dr. Raywat !