Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Labor Stage 3: Postpartum Hemorrhage – Therapies and Treatment
-
Slides PostpartumHemorrhage Obstetrics.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
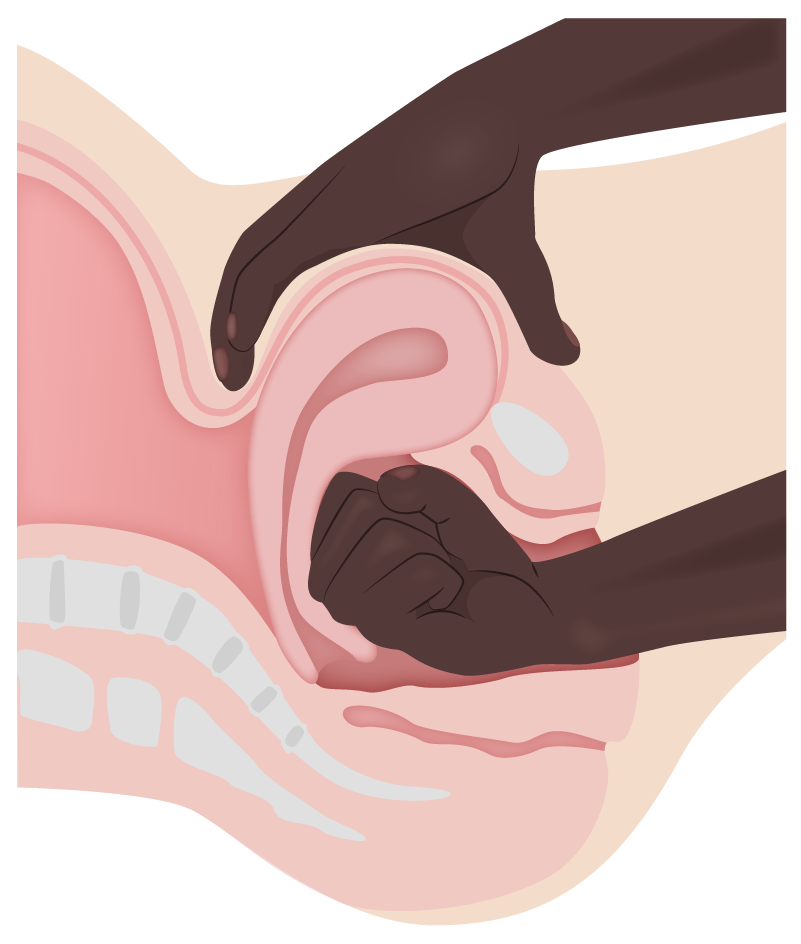
00:02 So let's talk about Tone as we said this does account for most of our postpartum hemorrhages. 00:07 We attempt to prevent atony by active management of the third stage of labor in each delivery. 00:13 This means giving oxytocin after the delivery of the placenta. 00:16 And for the reasons mentioned before, some patients are prone to atony despite the prophylactic treatment. 00:23 You want to manage that with uterine massage. 00:25 And this is how it's performed as you can see here. 00:28 One thing to know is important to first empty the bladder to make sure your uterine massage is more effective. 00:34 Next you want to give additional oxytocin. 00:38 And if you still have an atony you want to consider using other uterotonic agents. 00:43 Let's go through those in a little detail. 00:46 So our first uterotonic agent to talk about is Methlyergonivine. 00:50 So this is methrogen. 00:51 Now it is a very good medication to help contract the uterus. 00:55 But it is contraindicated in hypertension and can increase the blood pressure . 01:00 Next is PGF2 Alpha or Hemabay. 01:03 This is also a great uterotonic agent but it is contraindicated in patients that have asthma. 01:08 And then third is misoprostol. 01:11 This can be given vaginally or it can be given rectally or orally. 01:15 Vaginally is less effective because the patient is bleeding and so usually they can't absorb the misoprostol as effectively. 01:22 So you would want to consider your oral or rectal route. 01:25 And there are no real indications to give a misoprostol. 01:30 So what's our direct therapy for retained products of conception. 01:34 That's either be going to manual exploration to remove the placenta or D&C. 01:40 You should be suspicious for retained products of conception. 01:43 If the placenta is not removed intact. 01:45 Remember when we deliver our placenta we give gentle downward traction on the cord, uterine massage, and we expect the placenta to deliver as one piece. 01:54 If you don't have a deliver that way or you have to manually remove it, you should be suspicious for retained products of conception. 02:01 You want to make sure you inspect your placenta to make sure that no cotyledons are missing as well. 02:08 Now when we have trauma meaning lacerations to the cervix, the perineum, the vaginal tract we want to repair those. 02:17 You repair those just by as you can see here in the picture. 02:21 Stitching them close. 02:22 You can either use chromic or bicral. 02:24 And you want to do that to stop the bleeding. 02:27 Now if you have a hematoma, you want to just apply pressure to that to help the bleeding not to expand. 02:34 Hematomas can be particularly dangerous because they are not in a confined space so you can actually lose a lot of blood through extravagation into hematoma. 02:45 Now for our thrombin disorder. 02:47 What's the therapy for that? Well that's going to be blood products. 02:50 Let's go through this in a little detail. 02:52 Now, for packed red blood cells we give that. 02:55 We expect after one unit, the blood level will go up 1 gram per decalitre on the hemoglobin. 03:00 Or if you looking at her hematocrit it should increase by 3%. 03:03 If you are given platelets, 1 unit should cause the platelets to increase by 5,000 to 10,000. 03:10 If you are given fresh frozen plasma which has Fibrinogen, antithrombin III, factors V and VIII, one unit cause of the Fibrinogen to increase by 10 milligrams per decalitre. 03:22 And with Cryoprecipitate which is Fibrinogen, factors VIII and factor XIII as well as von Willebrand's factor, one unit will also cause the Fibrinogen to increase by 10 milligrams per decalitre. 03:34 This is important slide to pay attention to. 03:37 Because even if we have a thrombin disorder or if we have someone that has bled to the point that they've now transition into DIC, this is how we're going to correct that problem. 03:49 So here's some other treatments for postpartum hemorrhage. 03:52 Uterine artery embolization. 03:54 So this is a procedure that's done by interventional radiologist. 03:58 So a patient is taken to an interventional radiologist suite. 04:01 The uterine artery is located on arteriogram and is embolize. 04:06 So patients are candidates for this procedure. 04:09 If they are bleeding but they are stable. 04:13 Another option is uterine packing. 04:15 We can place belly balloons. 04:17 We can place lapse sponges. 04:18 We can place any type of packing inside the uterus. 04:21 This works really well for our patients that are having subinvolution issues or if they have retained products that you've had to piecemeal out. 04:30 Also manual compression will help with bleeding. 04:33 This particular procedure here is called the "B-Lynch suture." This is going to send the uterus down and cause manual compression to help clear our postpartum hemorrhage. 04:44 If a patient is continuing to bleed then you may need to consider take her to the operating room and doing an exploratory laparotomy. 04:52 When you do that the first thing you are going to try to do is arterial ligation. 04:56 So you at first try to ligate the uterine arteries. 05:00 If this doesn't work you can consider your ovarian arteries. 05:04 And finally if you've done all of these measures that you can that are conservative and our patient continues to bleed, then we need to do hysterectomy to treat them. 05:12 Remember though, not only you are going to correct the initial cause of postpartum hemorrhage, but you are also going to be looking for that patient to possibly to be going into DIC. 05:22 And that is only corrected by given those correct blood products.
About the Lecture
The lecture Labor Stage 3: Postpartum Hemorrhage – Therapies and Treatment by Veronica Gillispie, MD, MAS, FACOG is from the course Intrapartum Care. It contains the following chapters:
- Directed Therapies and other Treatments for Postpartum Hemorrhage
- Directed Therapy for Thrombin Disorders
Included Quiz Questions
A 25-year-old G1P1 with a history of asthma and no other medical problems just delivered her baby by cesarean section after arrest of the first stage of labor after prolonged rupture of membranes. In the operating room, there is a suspicion for chorioamnionitis and difficulty achieving uterine tone after uterine massage, removal of products of placenta and membranous tissues, and closure of the hysterotomy and she is receiving oxytocin infusion. Which of the following treatments should be given immediately to help limit the uterine atony?
- Methylergonovine (Methergine)
- PGF-2 alpha (Hemabate)
- Antibiotics only to treat the root cause
- Fresh frozen plasma
- Cryoprecipitate
Methylergonovine is contraindicated in which of the following medical conditions?
- Hypertension
- Asthma
- Diabetes
- Von Willebrand disorder
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation
What is an important first step in assuring effective bimanual uterine massage to treat uterine atony?
- Empty the bladder
- Assure maternal anesthesia
- Insertion of foley catheter balloon into the uterus
- Use a step stool to obtain the proper angle and leverage
- First try at least three uterotonic medications prior to attempting uterine massage.
How much should a patient's hemoglobin increase after administering two units of packed red blood cells?
- 2 g/dL
- 1 g/dL
- 5 g/dL
- 3 g/dL
- 0.5 g/dL
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |