Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Fetal Growth Restriction
-
Slides FetalGrowthRestriction Obstetrics.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
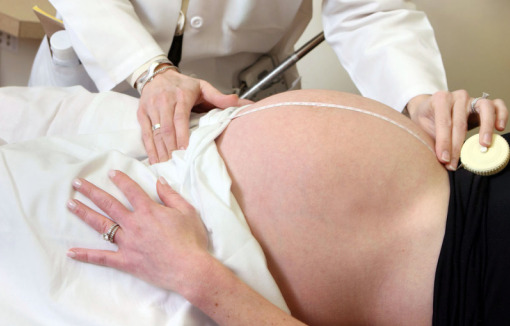
00:01 Now we'll discuss fetal growth restriction. 00:04 Fetal growth restriction is defined as the estimated fetal weight of less than the 10th percentile, or an abdominal circumference less than the 10th percentile. 00:14 Now there are several causes and we are going to divide these into maternal, fetal and placental. 00:20 So starting with maternal, these factors can be anything, from pre-pregnancy medical conditions. 00:25 Such as chronic hypertension, diabetes. 00:29 Substance abuse such as cocaine, tobacco, amphetamines, alcohol. 00:34 Pregnancy related conditions such as preeclampsia. 00:37 Multifetal gestation or infections. 00:41 And mostly infections we're speaking of the TORCHeS. 00:43 And that's discussed in another lecture. 00:45 It's important to note however that malaria is a number one cause of infectious reasons for fetal growth restriction worldwide. 00:54 Now moving on to fetal reasons for fetal grow restriction. 00:58 Usually those are divided into chromosomal abnormalities and anatomical abnormalities. 01:04 For chromosomal abnormalities, the Trisomy 21, 13 and 18 are the most common. 01:10 And those we usually screen for with our aneuploidy screening in the 1st trimester or 2nd trimester. 01:17 Anatomical abnormalities are things such as cardiac and renal. 01:21 We screen for those on an anatomy ultrasound between 18 and 22 weeks of gestation. 01:28 Now placental issues. 01:30 Now there are various reasons why the placenta can cause growth restriction. 01:33 From the things we've already discussed. 01:36 These are anything that will affect the blood vessels going to the placenta. 01:40 That can lead to fetal growth restriction. 01:44 So how do we screen for fetal growth restriction. 01:46 Well, for every patient after 24 weeks when they come in for their prenatal visit, we measure the fundal height. 01:52 So with a measuring tape, we measure from the pubic symphysis to the top of the uterus. 01:57 We expect that measurement to plus or minus 3 centimeters of the gestational age. 02:02 So for example, if a patient is 30 weeks pregnant they can measure as small as 27 centimeters or as large as 33 centimeters. 02:11 And that's considered normal. 02:13 If a patient is measuring less than 3 centimeters of the gestational age, an ultrasound is warranted to determine if the fetus is indeed growth restricted. 02:21 So when we do that ultrasound, we're looking at the head circumference and biparietal diameter, the abdominal circumference as well as the femur length. 02:33 If those together add up to less than the 10th percentile, then the fetus indeed has fetal growth restriction. 02:41 How do we manage fetal growth restriction? Well, most importantly we want to increase surveillance of that fetus. 02:47 We want to measure fetal growth by ultrasound every 3 to 4 weeks. 02:51 We would like to see interval growth during that time. 02:54 If we stop seeing interval growth, that is concerning and we would actually start looking for our time to deliver that fetus. 03:01 We also want to look at the amniotic fluid volume. 03:04 We expect to see a maximum vertical pocket of at least 2 centimeters. 03:09 If we see less than that, then that fetus is suffering from oligohydramnios. 03:13 The umbilical artery Doppler. 03:17 So this is also an important management tool that we use with fetal growth restriction to see if our baby is at increased risk for intrauterine fetal demise. 03:26 What we're looking for is to see that we have flow during systolic and diastolic. 03:31 We start seeing some issues with growth when we have absent in diastolic flow and worse if we have reversal flow. 03:39 If we start seeing that on our Doppler's that indicates it's time for delivery. 03:44 And then a non-stress test or biophysical profile. 03:46 This is another way to assess the status of our fetus. 03:50 And these are discussed in a little bit more detail in other lecture set.
About the Lecture
The lecture Fetal Growth Restriction by Veronica Gillispie, MD, MAS, FACOG is from the course Antenatal Care. It contains the following chapters:
- Fetal Growth Restriction
- Management of Fetal Growth Restriction
Included Quiz Questions
What is the definition of fetal growth restriction?
- The estimated fetal weight by ultrasound is less than the 10ᵗʰ percentile for gestational age.
- The fundal height measures less than the gestational age.
- The estimated fetal weight by ultrasound is less than the 20ᵗʰ percentile for gestational age.
- The fundal height measures less than two centimeters than the gestational age.
- The estimated fetal weight is less than the 5ᵗʰ percentile for its gestational age.
What is the most common infectious cause of fetal growth restriction?
- Malaria
- Toxoplasmosis
- Syphilis
- Rubella
- Group B Streptococcus
Which of the following is a cause of fetal growth restriction?
- Chromosomal aneuploidy
- Gestational diabetes
- Placenta accreta
- Placenta previa
- Preeclampsia
In the case of fetal growth restriction, what other factor must be regularly monitored every three to four weeks in addition to monitoring interval fetal growth?
- Amniotic fluid level
- Placental width
- Contraction stress tests
- Maternal serum glucose levels
- Maternal urine toxicology screens
Which of the following would be an indication for delivery of a growth restricted fetus?
- Absent end-diastolic flow on umbilical artery doppler
- Single deepest vertical pocket of amniotic fluid being less than 3 cm
- Persistent maternal tobacco abuse
- Development of maternal hypertension
- Estimated fetal weight less than tenth percentile
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |