Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
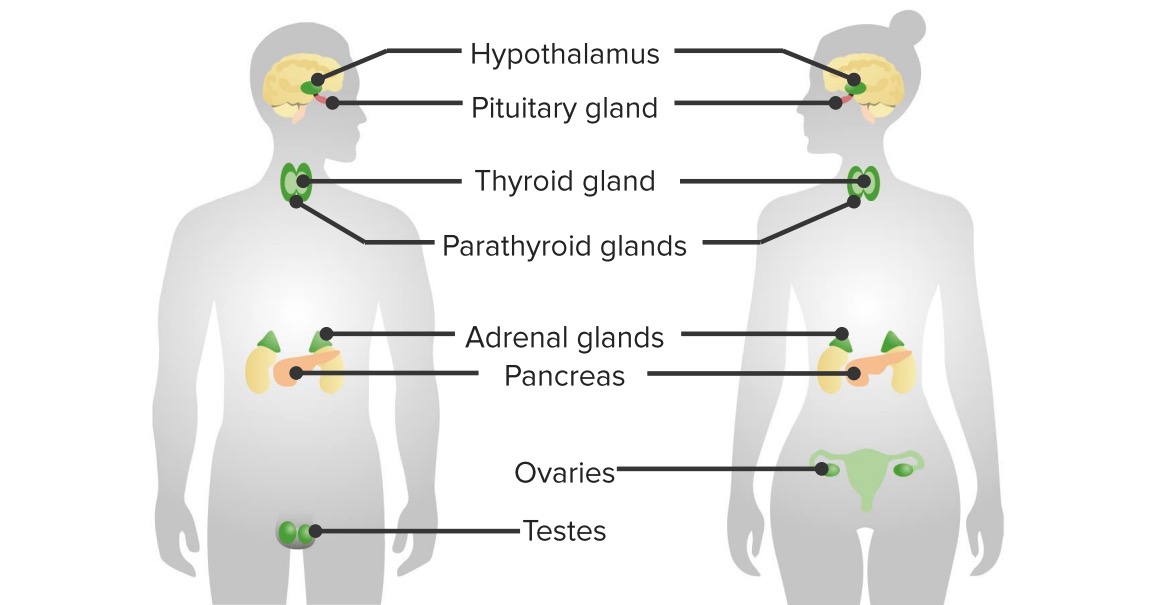
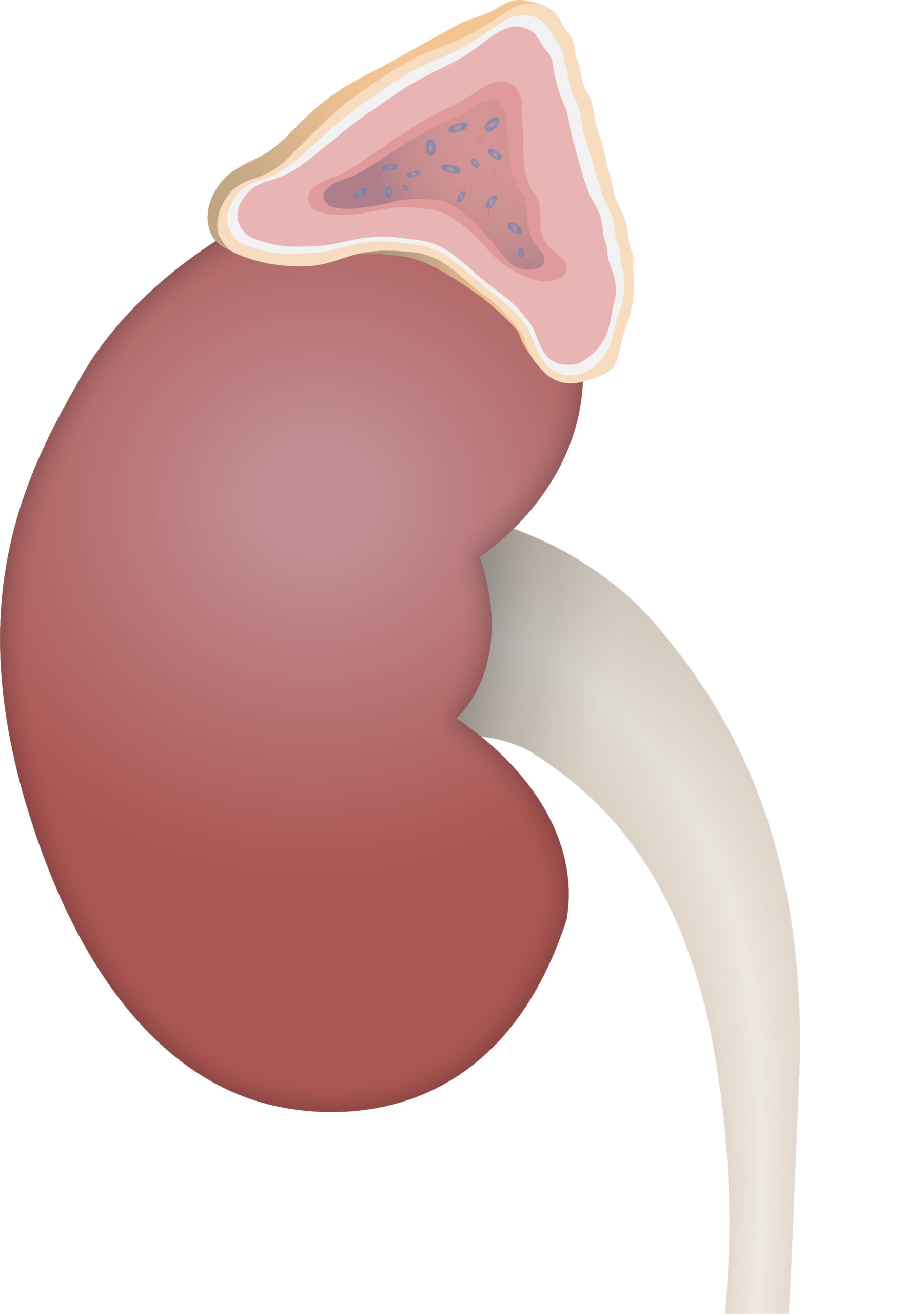
Overview of the Adrenal Gland – Adrenal Cortex
-
Slides AdrenalCortex EndocrinePathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:01 The adrenal-adrenal cortex, site of synthesis, secretion of steroid hormones, all steroid hormones will pass through the membrane. 00:08 All steroid hormones from the adrenal cortex are located… the receptors are located where? In the cytoplasm, keep that in mind. 00:15 Our topic here specifically of your cortex is going to be the cortisol, cortisol, cortisol a.k.a. glucocorticoids. 00:21 In pharmacology, oh my goodness, makes you know about glucocorticoids and all of its effects. 00:29 Big time… cortisol, prednisone… big time, used in many conditions, aren’t they? For example, you might use it for immunosuppression on-on purpose, especially if you have a renal transplant recipient or an organ transplant recipient. 00:44 Prednisone can be used for pain. 00:46 I mean, it’s-it’s... the uses of it are ridiculous. 00:49 Even plastic surgeons will use forms of cortisol so that they can delay wound healing, right? So, glucocorticoids are all over the place. 00:57 We’ll talk more later. 01:00 Increase serum glucose, what does cortisol do? It is, it is a stress hormone. 01:06 If it’s a stress hormone, then what is it going to do? It’s going to do everything in its power so that it increases glycolysis or gluconeogenesis? Good, gluconeogenesis. 01:17 So, therefore, it will inhibit insulin release or it will allow for insulin resistance of the receptors, it will break down the protein catabolic, not anabolic. 01:30 If you ever met a… an athlete who wishes to build up muscle by taking… well, by this… it’s a little bit different, but here specifically though, it’s going to break down the protein so that you have the substrates for gluconeogenesis, normally speaking. 01:50 Oppose inflammatory response, thus you know steroids inhibits what enzyme in the arachidonic acid pathway, phospholipase a2. 02:00 Therefore, you will not have your prostaglandins and such for inflammation, anti-inflammatory. 02:08 Potential vascular effects of catecholamines and by that, we mean permissive effect, permissive action. 02:14 Now, corticoid activity, what’s going on in the fasciculata? When the fasciculata was a cortisol, the glomerulosa would be your aldosterone. 02:27 If you’re not familiar with the picture of your glomerulosa, go back to the previous illustration and there, I showed you aldosterone synthase. 02:37 Angiotensin II, which was converted from angiotensin I to angiotensin II by the ace enzyme in your lung, responsible for releasing your aldosterone. 02:50 That would be your number one feedback, do not ever forget that. 02:54 And what does it do? Mineralocorticoid is going to reabsorb sodium and water from your collecting duct to principal cells. 03:02 Obviously, with this, the discussion takes you into the sodium potassium pump and also ENaC referring to epithelium-sodium channel and aldosterone can work on both to reabsorb your sodium. 03:17 In the reticularis, we have DHEA, dehydroepiandrosterone. 03:21 As a general theme, here we have androgens being produced. 03:24 Here are the major secretagogue will still be ACTH, remember that you will be forming androstenedione. 03:31 If at any point in time, we have an enzyme deficiency, increased activity of reticularis, then you have something called virilisation of your female, what does that mean to you? She might have excess acne, she might have increased muscle mass like that of a male and the most important sign of virilisation will be enlargement of the clitoris, clitoromegaly. 03:55 What about the adrenal medulla? The adrenal medulla basically has one function that you want to keep in mind, it’s responsible for catecholamine synthesis, specifically epinephrine.
About the Lecture
The lecture Overview of the Adrenal Gland – Adrenal Cortex by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Adrenal Gland Disorders.
Included Quiz Questions
What is NOT a function of cortisol?
- Increase sodium retention
- Increase serum glucose
- Create a catabolic protein state
- Oppose inflammatory response
- Potentiate vascular effects of catecholamines
What is the molecule responsible for the release of aldosterone?
- Angiotensin II
- ACTH
- Renin
- ACE
- Cortisol
A female patient presents with increased muscle mass and clitoral enlargement. Which hormone may be present in excess?
- DHEA
- Cortisol
- Glucocorticoids
- Aldosterone
- Angiotensin II
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |