Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Extracellular Fluid (ECF) and Intracellular Fluid (ICF): Water & Sodium Pathophysiology
-
Slides WaterandSodiumPathophysiology RenalPathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
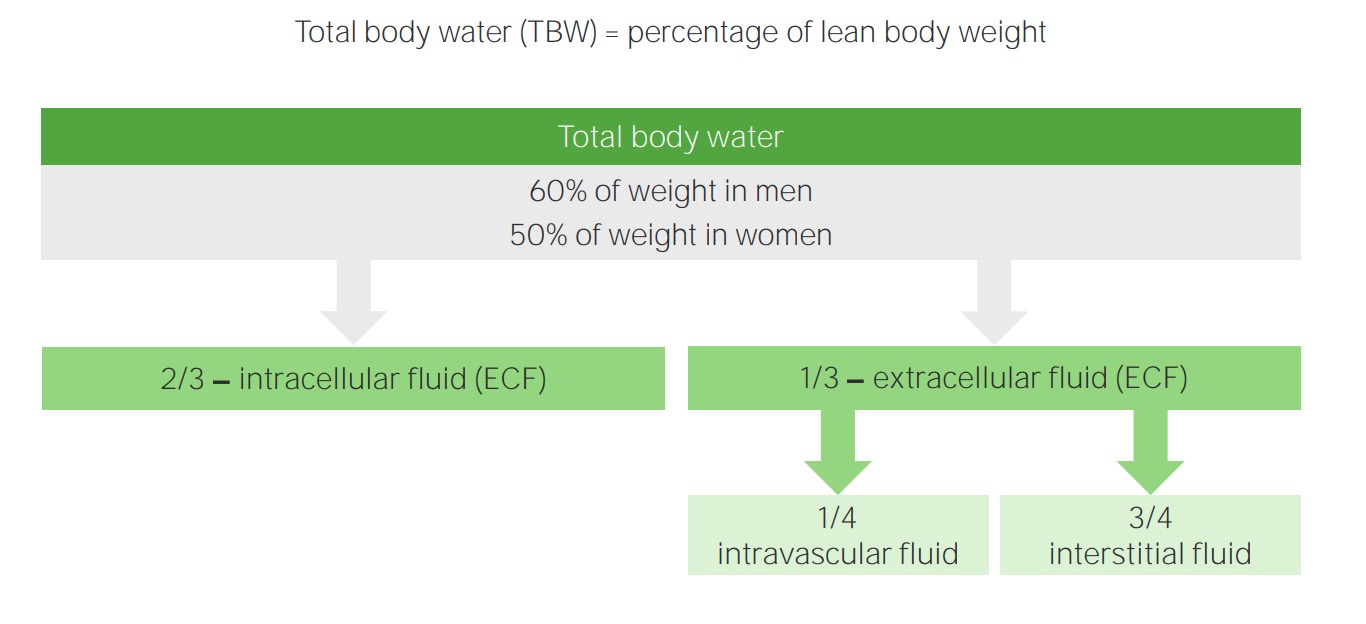
00:01 Students have always asked me "Dr. Raj, I am having a hard time keeping straight and organized the feedback mechanisms for water and sodium pathophysiology." This is probably the most important section here. You go through as far as laying down the foundation of figuring out the two compartments of ECF and ICF. What kind of hormones would be involved and a little bit of a clinical tag that I will be putting in for you along with the physiology so that you clearly know how to move on to in the next lecture series of isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic fluid disorders. Let us now begin. Basic definitions. Well, it comes down to the kidneys, doesn't it really? Really. In terms of being able to properly control and regulate your fluids. Electroneutrality of body fluid compartments become importance of back and basic physiology when you are dealing with action potentials and all. And you are dealing with electroneutrality whenever you have a positive ion such as sodium, of course, being the most infamous of them all and along with it must be a chloride so that you can have proper electroneutrality as an example. Composition between ICF and ECF is basically what this line is saying. For example, when we talked about total body water, you should know that majority of your total body water is where? Good. ICF. 2/3, isn't it? Simple things that you knew and you know that you keep repeating so that it becomes part of your unconscious reflex. ECF, would you tell me as to what is the most important component clinically for us to measure in your ECF. And you're telling me the vascular compartment, isn't it? The plasma compartment. The effective circulating volume compartment. All of this is the same name. They are all synonyms for your plasma compartment being a measly 1/4. 02:12 Now clinically most clinicians were used as being 1/3, not saying that is wrong, but at this point, I highly recommend that you think of the plasma compartment being 1/4 and the interstitium being 3/4. Body fluid compartments, we will take a look at this. When we were dealing with the particular box known as the Darrow-Yannet box, which is being around for a long time and there is a reason for that because it properly would be one of the most effective measures for you to clinically be able to see conceptually in your head the shifting of fluids between your ECF and ICF and there is a particular chronological order that you should already know, but we will then reinforce through clinical examples. Regulation of water balance and osmolality will become the topic initially here before we get into isotonic fluid disorders. At some point, we have to have certain IV fluid definitions. For example, the patient that was sweating excessively coming in having low blood pressure, what are you going to do with that patient? Without even blinking, give that patient IV fluids, of what type? Good. Normal saline at 0.9%. This we must talk about and give you definitions of what saline is. What is it? The electroneutrality component of sodium, cation, anion, chloride, electroneutrality. 03:38 You see as to how everything is coming together and then finally regulation of volume. Remember the osmolality is an extremely sensitive indicator in our body, isn't not? Osmolality is extremely monitored closely and as soon as there is any little change in osmolality, then its the ADH that comes in. That is the osmolality and at some point, we will have to switch over to volume it may then take priority especially if you are losing volume in excess.
About the Lecture
The lecture Extracellular Fluid (ECF) and Intracellular Fluid (ICF): Water & Sodium Pathophysiology by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Fluid and Electrolyte Balance.
Included Quiz Questions
What fraction of extracellular fluid is contained in the intravascular compartment?
- 1/4
- 3/4
- 2/3
- 1/3
- 1/12
Which of the following is NOT considered equivalent to the plasma compartment?
- Interstitial fluid compartment
- Vascular compartment
- 1/12 of total body water
- ¼ of extracellular fluid volume
- Effective circulating volume
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |