Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Introduction to Kinetics | Pharmacokinetics (PK)
-
Slides Pharmacokinetics Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
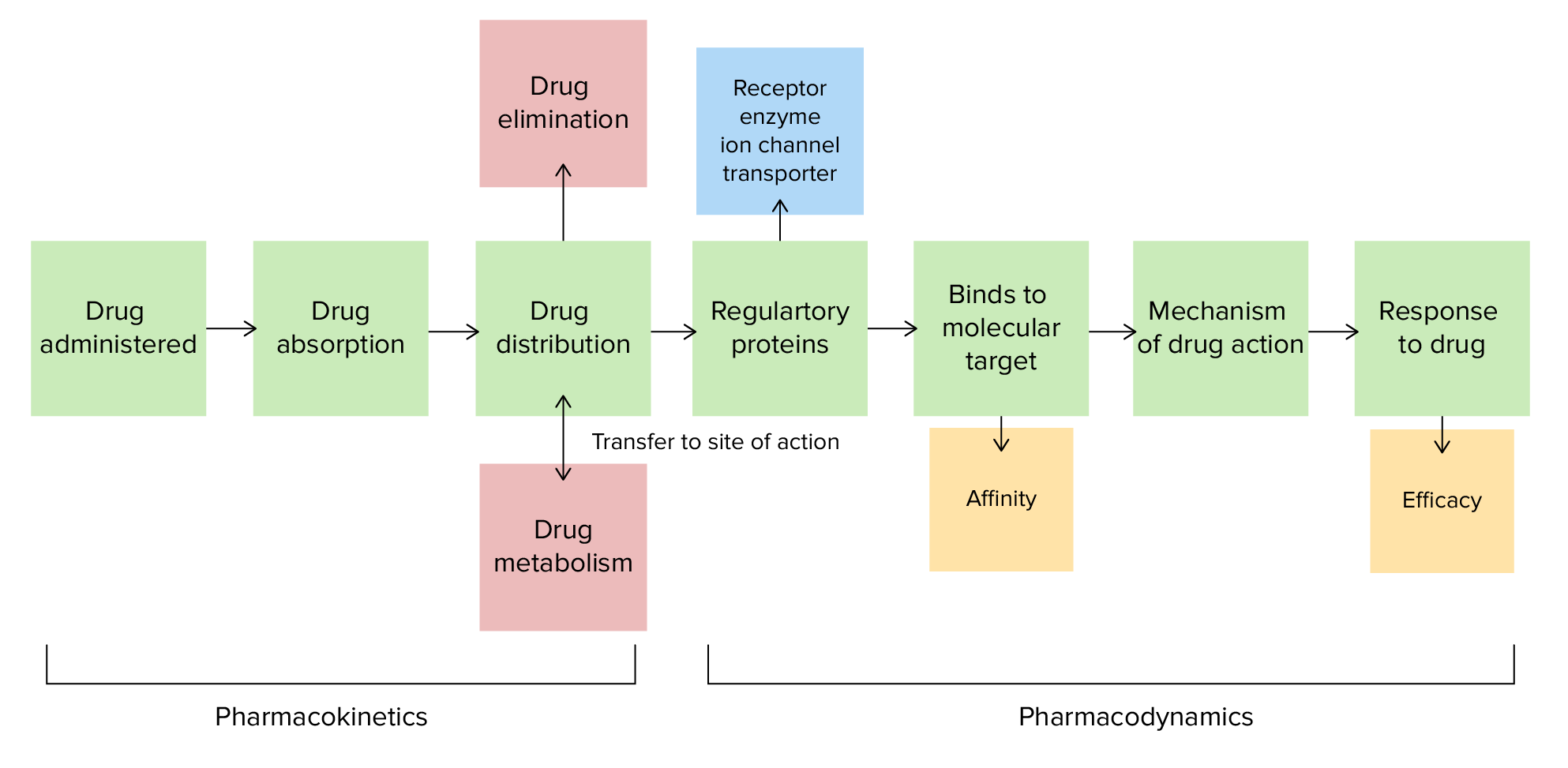
00:01 Welcome to Pharmacology by Lecturio. 00:04 My name is Dr. PJ Shukle and I'm going to introduce you to the science of Pharmacology which is the science of drugs. 00:11 Today, we're going to talk about introduction to kinetics which is the way drugs interact with the human body. 00:17 One of the things that I wanna put forward to you for your board exams and when you're practicing for your tests, is you don't need to know the brand names. 00:27 I will put them there because they are useful in real practice. 00:30 But remember that brand names are going to differ with time. 00:34 Sometimes some brand names expire and other brand names come into play and they're also different in different regions of the world. 00:42 Let's start with a question. 00:45 The following dose response curve was isolated from a substance. 00:49 Choose the number that defines each substance. 00:52 So you have a green curve. 00:55 You have a black curve. You have a yellow curve, and you have a plum coloured curve. 00:59 So, we're going to define which one each is. 01:03 So, one of them is an allosteric activator. One of them is an active drug. 01:09 One of them is a competitive inhibitor. And one of them is an allosteric inhibitor. 01:14 So what do these terms mean? Before we answer the question, let's take a look at how drugs act on a receptor. 01:21 So you can see the grey ball which is the agonist. 01:25 It goes into a receptor bay and it fits perfectly. That is an agonist. That's a drug. 01:31 A competitive inhibitor will also fit into the same bay, and block the agonist from binding to that receptor. 01:38 An allosteric activator is something that binds to a different place on the same molecule. 01:45 So, allo means different, and steric means shape. 01:48 So it's a different shape, it's a different place on the molecule, but it activates the activity of the drug. 01:55 An allosteric inhibitor is something that acts on the different part of a molecule, but inhibits the action of the drug. 02:03 So now that we understand what each of those types of molecules how they are going to react with your receptor, let's try and answer the question. 02:12 So, A, number 3 is the allosteric activator. So let's take a look at the green curve. 02:19 The green curve is 1 and 3. One is the active drug, and 3 is the allosteric activator. 02:27 So you can see that the curve is much higher. 02:30 So you get a much greater response when you have an activator that is allosteric. 02:36 Let's take a look at C. C, this substance is the competitive inhibitor. 02:41 Notice how the yellow curve is shifted over on the graph. 02:45 That means that you need a higher dose to overcome that competitive inhibitor. 02:50 Now compare that to D which is the allosteric inhibitor. 02:54 Notice that the purple or the plum curve actually starts at the same point, but the total response is much lower and it never gets higher than a certain point and it is always less than 1 alone. So here is a very important difference between competitive inhibitors and allosteric inhibitors. 03:13 Guarantee this is going to be a question on your exam. 03:16 Guarantee this is going to come up again and again. 03:19 When we talk about how cells interact with drugs or how drugs interact with cells, we wanna talk about different structural components. 03:29 So, I'm gonna introduce you to the structures of the cell. 03:32 Well, obviously you know that the membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. 03:36 We also have glycolipids and glycoproteins that are on top of the cell and these interact with drugs. So some glycoproteins connect to drugs, some glycolipids will connect to drugs. We also have integral membrane proteins. 03:52 These are proteins that cross the entire membrane. 03:55 They may or may not be active with a particular drug. 03:58 You have peripheral membrane proteins. 04:01 This one is on the cellular or cytoplasmic surface of the membrane and it works in a different way. 04:08 And we're going to point something like that out to you later. 04:11 The most important thing I want you to understand about a protein channel right there is that it is transmembrane. 04:17 It goes right through the membrane and the core is full of water. 04:23 So if you have a drug that is dissolvable in water, it's going to go through a protein channel. 04:28 Now, inside the cells are filaments of cytoskeleton. 04:34 That's going to be relevant when we start talking about certain types of drugs later on in our lecture series. There you have it the cell membrane.
About the Lecture
The lecture Introduction to Kinetics | Pharmacokinetics (PK) by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics.
Included Quiz Questions
What is true about competitive inhibitors?
- They act at the same site as the drug.
- They promote the binding of an agonist at an active site.
- They bind to a different place on the same molecule.
- Competitive and allosteric inhibitors act at the same place of the molecule.
- They are less effective than agonists.
Which category of substances is most likely to increase an activator's (i.e. an agonist's ) efficacy?
- Allosteric agonist
- Negative allosteric modulator
- Competitive inhibitor
- Allosteric inhibitor
- None
Which of the following drug characteristics makes a drug more likely to enter a cell through a protein channel?
- Water solubility
- Acidophilic property
- Neutrality
- Basophilic property
- Fat solubility
Customer reviews
4,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
0 |
| 4 Stars |
|
1 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
perfect !! i really liked the intro, but there is still some problem with questions..