Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
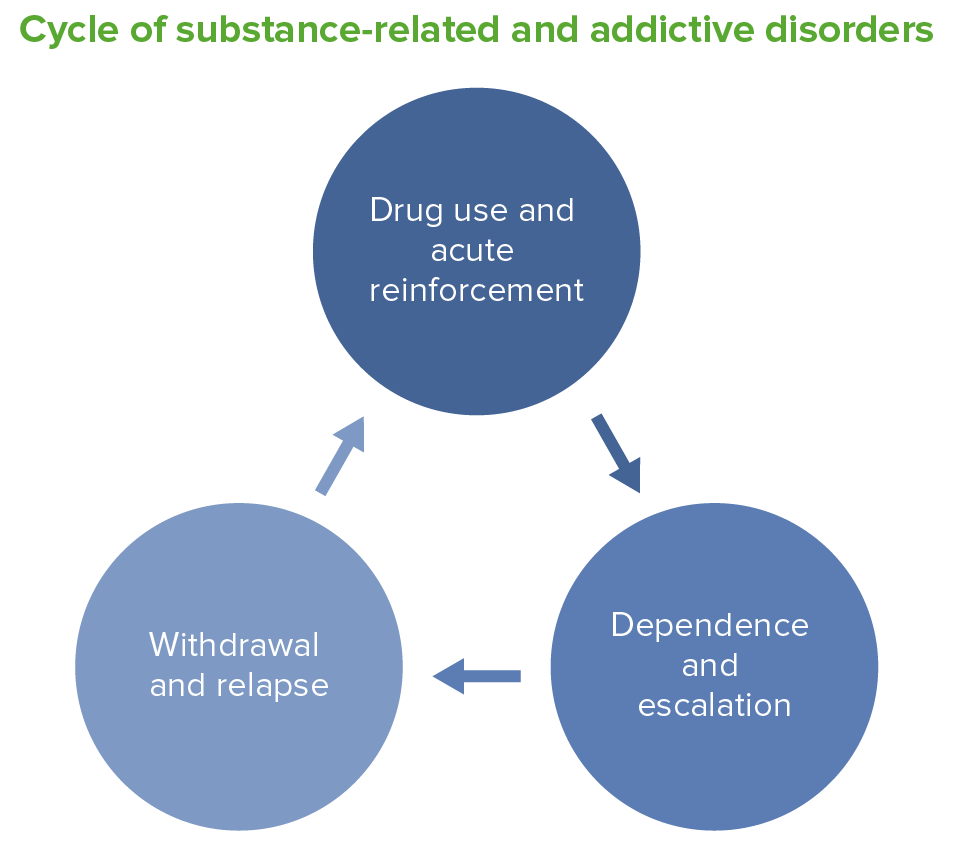
Substance-related Disorders
-
Slides Other Substances.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:01 Next, let's move on to amphetamines or stimulants. 00:04 So, classic amphetamines include things like Dexedrine and Ritalin. 00:09 These release dopamine from nerve endings causing a stimulating effect. 00:14 This is a highly abused substance especially in teenagers and young adults. 00:18 Designer amphetamines are also newer on the markets and include things like MDMA and ecstasy. 00:26 These release dopamine and serotonin from nerve endings and these have both stimulant and also hallucinogenic properties. Clinical uses for amphetamines would include ADHD, narcolepsy, and depression. When somebody has amphetamine intoxication some of the symptoms are gonna be euphoria, changes to their blood pressure and heart rate, nausea, dilated pupils, weight loss, and psychomotor changes. 00:56 They may also have chills, respiratory problems, sweating, seizures, arrhythmia, and hallucinations. 01:04 How long does urine drug screen stay positive for amphetamines? Well, you'll want to know it's 1 to 2 days. So, you can always test for this in a patient's urine when they come to the hospital and in terms of amphetamine withdrawal symptoms, they can experience a crash which is gonna look like irritability and also hypersomnolence. 01:29 PCP is another substance that you'll wanna know a little bit about for your boards. 01:36 It's also called angel dust and it's a hallucinogen and it antagonizes NMDA glutamate receptors and activates dopamine neurons. PCP and ketamine, which is a similar agent, were both developed originally as anesthetics and now they can be actually abused in culture. 01:57 So PCP intoxication will look like restlessness also, reckless behavior and impulsivity, impaired judgement, assaultiveness, and very important to know for your boards, PCP intoxication can actually cause a rotatory nystagmus which is really a cardinal feature of this. 02:18 You may see ataxia in your patient, hypertension, tachycardia, and muscle rigidity, along with a high pain threshold. How long does urine drug screen stay positive for PCP? Do you know' Well, the answer is 1 week. So, actually for quite a while and because of muscle rigidity associated with PCP, because remember these patients are gonna be restless, reckless, agitated, so they may get muscle rigidity and it's important to check their CPK and also their liver function because these two things are often very elevated in PCP users. 02:57 The treatment for PCP is of course to manage the ABCs, airway, breathing, and circulation, stabilize the patient's vital signs and electrolytes, acidify their urine, and treat them medically with benzodiazepines or possibly neuroleptics or low-dose anti-psychotics to help with the agitation and the hallucinatory effects that they're experiencing. Now, let's talk about opiates. Opiates include things like heroin, codeine, dextromethorphan, morphine, methadone, and meperidine. 03:33 There's worldwide, a pretty huge opiate crisis right now. 03:38 So although these medications were originally formed to help people control pain, they're actually highly, highly abused. So, there is this current opioid epidemic and there is now because of that, a push for doctors to prescribe non-opiate medications to elevate pain and even to help patients practice mindfulness which is actually being studied, and researched, and being shown to be very effective for pain management. 04:06 Well, how do opiates actually work? So they stimulate opiate receptors such as mu, kappa, and delta and these are involved in the sedation, analgesia, and dependency. 04:17 Opiate intoxication looks as follows, drowsiness, nausea and vomiting, constipation, slurred speech, constricted pupils. This is very important to note because I've talked about other medications or substances earlier which can cause dilated pupils. However, opiates cause pinpoint or constricted pupils. It can cause seizures and respiratory depression. 04:45 You wanna treat the intoxication phase with ABCs, managing airway breathing and circulation. 04:52 Because opiates can cause respiratory depression, it's extremely important to make sure your patient is breathing. In an overdose, you're gonna give IV naloxone or naltrexone to reverse the effects of opioids. You also will ventilate and intubate. 05:10 In dependency, when patients have had chronic use of opioids over a long period of time, you might consider an out-patient management plan with methadone or suboxone. 05:21 You'll offer them psychotherapy and also narcotics anonymous, through that they can get peer support to help them with their dependency and addiction. 05:30 The withdrawal symptoms of opiates include dysphoria, insomnia, lacrimation or development of tears, rhinorrhea, yawning, and weakness. They may sweat or get piloerection. 05:48 They can be vomiting, have a fever. They'll actually have dilated pupils during the withdrawal syndrome and they'll complain of profuse and very intolerable muscle aches. 06:03 It's extremely important to know that as much as it is uncomfortable to experience opiate withdrawal, it is not deadly nor life threatening. So, what are the 4 types of opiate receptors? We've talked about these before but they're very important to know for your exam. 06:20 So again, they're mu, kappa, lambda, and delta. And something else that you may encounter in clinical practice is a patient who presents with something called skin popping. 06:34 So you wanna know what this looks like both for clinical practice and your exam. 06:38 If you encounter a case scenario of a patient who has circular, depressed scars often in their toes, the back of their thighs and this is what's called skin popping. 06:51 It occurs from injection site use, often of opioids and it can be deadly because patients can develop abscesses here and so it's very important when you're evaluating your patient to do a head-to-toe physical exam and actually be very attuned to looking for any abscesses, checking their vital signs because they may have a fever, and you really wanna treat this very aggressively. 07:15 And because this is so important to note and often comes up on exams, opioid intoxication is going to cause pin point pupils to the eyes. 07:26 So, here is a case example that I want you to consider. 07:31 A teenage boy is brought to the emergency room by his parents. 07:35 You smell an odd odor on his breath. What do you make of it? Well, you should consider in this teenager, inhalant abuse or huffing and what you wanna do clinically is look for a rash near his nose or mouth to help confirm your suspicions. Common problems caused by inhalant use include brain atrophy. 07:58 This is caused by heavy metal exposure such as to copper and zinc. 08:02 Also, encephalopathy, seizures, epilepsy, decreased IQ, ataxia, myoclonus, chorea, other things that can happen are tremor, optic neuropathy, motor and sensory neuropathy, death by respiratory depression, cardiac arrhythmias, aspiration, hepatic and renal failure, and rhabdomyolysis. You wanna treat inhalants with supportive measures and by maintaining the ABCs, their airway, breathing, and circulation. 08:40 This concludes our talk of other substances. You now know about some of the most commonly abused substances, a little bit about what it looks like when a patient is intoxicated and also withdrawing, and you know the importance of first and foremost for every patient, managing their airway, breathing, and circulation. You also have a little bit more background on how to offer further treatment options and even long term substance use options.
About the Lecture
The lecture Substance-related Disorders by Helen Farrell, MD is from the course Control Disorders. It contains the following chapters:
- Phencyclidine (PCP)
- Opiates
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following differentiates MDMA from Dexedrine?
- MDMA releases dopamine and serotonin causing stimulating and hallucinogenic effect.
- MDMA can also be used for depression and ADHD.
- It causes euphoria, nausea, dilated pupils and weight loss.
- The drug screen stays positive for 1-2 days in MDMA abuse.
- It causes psychomotor changes.
Which of the following is the mechanism of action of angel dust (PCP)?
- Antagonizes NMDA glutamate receptors and activates dopaminergic receptors
- Antagonizes dopaminergic receptors and activates NMDA receptors
- Activates serotonergic receptors
- Inhibits serotonergic and activates dopaminergic receptors
- Activates GABA receptors
All the following symptoms are seen in PCP intoxication, EXCEPT:
- Hypotension
- Rotatory nystagmus
- Restlessness
- Impulsivity
- Muscle rigidity
A 22-year-old college student is brought to the emergency department by the police. The patient looks drowsy and is slurring his words. On examination, his pupils are constricted and respiratory rate is marked to be 8 breaths per minute. He has vomited twice since he was brought to the emergency room. Later, he admits to taking "some pills" at a party. Which drug is most likely involved?
- Opiates
- Cocaine
- MDMA
- Marijuana
- LSD
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |