Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade: Diagnosis and Treatment
-
Slides PericardialDisease PericardialEffusion CardiovascularPathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
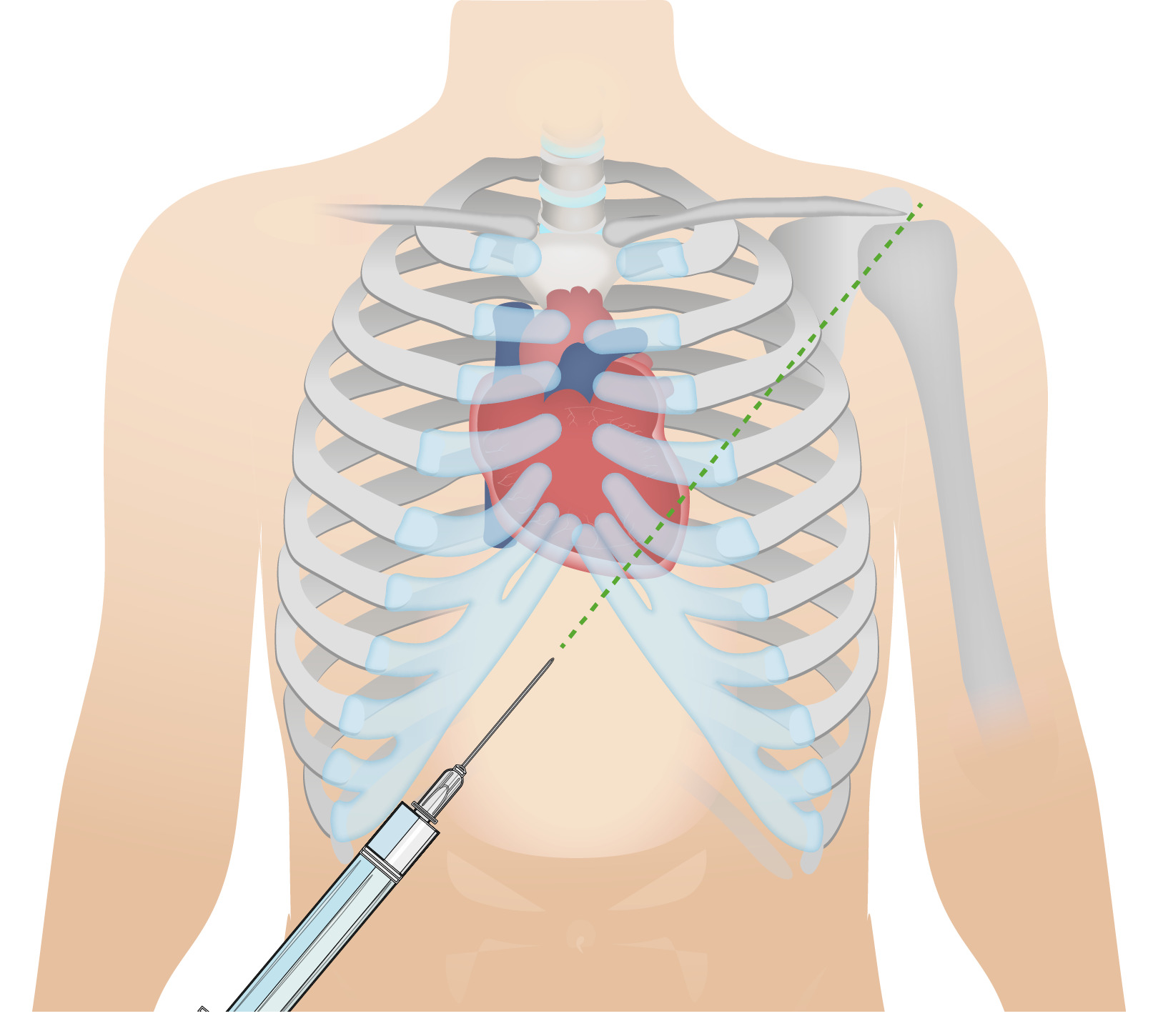
00:01 Physical exam. Pulsus paradoxus, classic sign of cardiac tamponade. What is that mean? Here’s is the definition. Now, in case you actually needed in words here it is, I would recommend that you are able to interpret the graph that we just saw prior. Quite important. 00:13 Cause there was a kind of questions and there was a type of interpretations such as responsible for being an effective clinician. Pulsus paradoxus refers to decrease in systolic blood pressure, decrease of more than 10 millimiters mercury with inspiration. There you have it. Why? More blood? Well, we just walked through that in great detail in a previous discussion. 00:36 Jugular veins will be distended because of restriction. 00:37 Heart sounds, you tell me about those are able to listen to your heart sounds well. 00:42 No, you cannot muffled. Move on. 00:44 What about EKG? You have increased effusion in any of thickness within the pericardium. 00:50 So therefore, when you put electrode to your heart, how well is that going to measure the voltage? Not very well. Low voltage is what you are looking for. What is that even mean? You take a look in an EKG, what is the voltage? Is that the X-axis or Y-axis? Voltage is amplitude. 01:06 Aright, I need you to think, R wave can you see it. 01:09 Close your eyes. R wave, major, major positive deflexion. And that is going to be reduced low voltage because of effusion. 01:16 Electrical alternans, which are alternating large and small QRS complexes, may be seen that’s important because you don’t have the sustained increase in QRS complex consistently because of the increase fluid by pericardial cavity. 01:31 That has to be cleared. So a couple of things that you wanna pay attention to in terms of medical terminology, so that you understand what’s going on with your patient. 01:39 Chest X-ray, well it’s more important that we take a look of our Echo. And where it you are going to find actual increase fluid within the pericardial cavity. 01:49 Echo revels pericardial fluid, collapse the ventricle during diastole. If without hemodynamic consequences, what does this mean to you? Watch while waiting with treatment because ultimately, if your patient goes into decompensation, you need to get in there remove that fluid. 02:04 In draining the fluid, what’s this called pericardiocentesis. 02:07 What you’re doing? You opening up a window and literally removing the fluid especially when you patient pay attention hemodynamically instable. 02:18 Increased risk recurrence may require pericardial window and at some point. Remember, steroids and such sure band aid therapy, anti-inflammatory but ultimately when you have recurrences you’re definitive treatment is going to be your pericardial window. 02:36 And that’s what exactly what you’re seeing here. You will open up a window surgically. 02:39 You will then literally drain the fluid right out of your pericardial cavity. So that you can relieve that pressure ASAP. 02:46 Why how would you know that your patient is going into decompensation? There is going to be a decrease cardiac output. That blood pressure hypotension is what you are looking for. 02:55 Looking for positive JVD and might be looking for dyspnea. So that means that the heart right now is being majorly, majorly handicapped. 03:03 And so, therefore, you need to get in there and relieve your patient.
About the Lecture
The lecture Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade: Diagnosis and Treatment by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Pericardial Disease: Basic Principles with Carlo Raj.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following ECG changes is most suggestive of cardiac tamponade?
- Alternating large and small QRS complexes
- Widened QRS duration
- Diffuse ST segment elevation
- Peaked T waves
- Ventricular bigeminy
Which of the following findings is NOT associated with cardiac tamponade?
- Pulmonary edema
- Decrease of systolic blood pressure by > 10 mmHg on inspiration
- Low voltage ECG
- Electrical alternans on ECG
- Ventricular collapse during diastole on echocardiography
Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic modality for confirming the diagnosis of pericardial effusion?
- Echocardiography
- Chest radiograph
- Electrocardiogram
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Computed tomography
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
2 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
love this guy but I'm sure it's just stockholm syndrome
Honestly, it is a godsend. The videos are clear, concise and fun! Dr. Raj is passionate and amazing! Also I watched many others videoes and all are fantastic! I wish I got to know about this earlier, it would have helped me immensely. It has lectures from MCAT to USMLE 2 so all the courses are covered, never again I'll be stuck with not understanding and never again will reading the book become so time-consuming. The bookmatching aplication that it has is genius and also just makes my life much easier. I am using this program for my PANCE and it facilitates my learning to be more effective! Thank you all so much for putting this together! Highly recommended.