Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Toxic Adenoma and Multinodular Goiter with Case
-
Slides Thyroid Disease.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
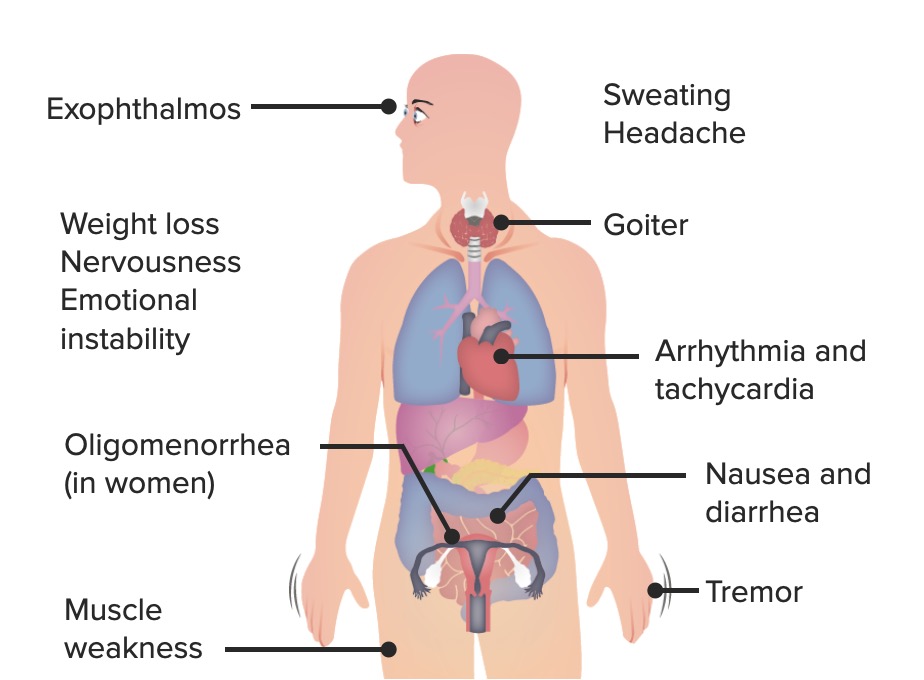
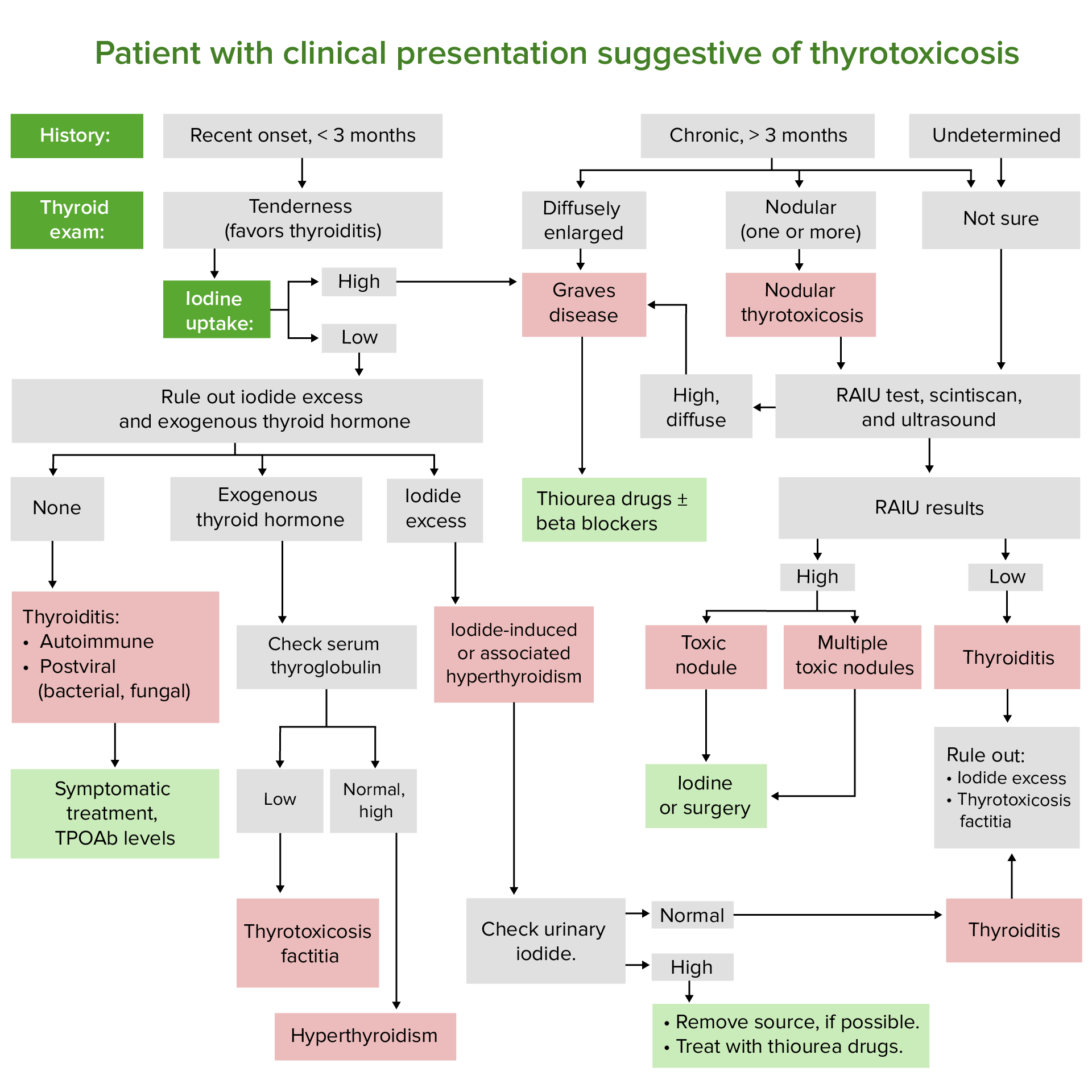
00:01 Let's go on to another case. 00:03 A 55 year old woman was diagnosed with hyperthyroidism one week ago. 00:07 She also has a palpable right thyroid nodule which was found on clinical exam. 00:12 Her TSH was low and her free T4 was elevated. 00:17 She has no weight loss, no history of prior malignancy nor family history of any cancer. 00:23 What is the best next step in managing this patient? So clinically based on the information that we have, she has been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism and she also has a palpable right thyroid nodule. 00:37 This points to the diagnosis of a toxic adenoma. 00:41 The next step in the management would be thyroid scintigraphy scan or radioactive iodine uptake which in this case would show a single area of increased uptake of iodine in the area of the toxic adenoma. 00:58 Thyroid scintigraphy scanning is a nuclear medicine procedure that produces a visual display of functional thyroid tissue based on the selective uptake of radioactive iodine nucleides by the thyroid tissue. 01:13 If you look at this image, you see areas on the gray background of intense uptake which are much, much darker representing large black dots. 01:22 These represent toxic adenomas within the thyroid gland and are very discreet. 01:30 Activating mutations in the TSH receptor gene stimulate the production of thyroid hormone in a toxic nodule, usually referred to as an adenoma. 01:40 or in multiple hyperfunctioning nodules in a toxic multinodular goiter. 01:46 On exam, the nodule may be palpable or diffusely enlarged where it's called a goiter or it may have a nodular contour. 01:55 There is a very low risk of autonomous nodules from malignant transformation. 02:01 Usually in the range of less than 1%. 02:04 The diagnosis is usually made by thyroid scintigraphy. 02:07 In the case of an autonomous toxic nodule, this is described as "hot" or very dark on imaging. 02:17 You should always correlate any nodules found on scintigraphy scanning with an associated ultrasound. 02:23 Any additional nodules that are found on ultrasound that are not seen on scintigraphy scanning may require further investigation by doing a fine needle aspiration. 02:35 Radioactive iodine ablation emits gamma and beta radiation. 02:40 The camera detecting this on a nuclear testing will detect the uptake of the thyroid hormone and generate a picture for diagnosis. 02:51 Indications for surgery in patients with toxic adenomas include very large goiters with compression symptoms on the underlying tissue where there is concern for malignancy. 03:02 TSH secreting pituitary adenomas are extremely rare. 03:06 These are causes of secondary or central hyperthyroidism. 03:10 Serum TSH is detectable or normal with elevated T4 and/or T3 levels. 03:17 A pituitary MRI in these cases will usually demonstrate an adenoma. 03:21 The treatment for these conditions is removal of the pituitary tumor as thyroid-targeted therapy is invariably ineffective.
About the Lecture
The lecture Toxic Adenoma and Multinodular Goiter with Case by Michael Lazarus, MD is from the course Thyroid Disorders. It contains the following chapters:
- Case 1.3
- Thyroid Scintigraphy/RAIU
- Toxic Adenoma and Multinodular Goiter
- Secondary or Central Hyperthyroidism
Included Quiz Questions
What is the management for a TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma?
- Excision
- Levothyroxine
- Firmagon
- Casodex
- Radiation therapy
What should the initial treatment be for a 'hot' nodule?
- I-131 ablation
- Surgical excision
- Methimazole
- Metoprolol
- Propylthiouracil (PTU)
What is the next step in treating the patient described below? Hyperthyroidism was diagnosed in a 55-year-old woman 1 week ago when a palpable right thyroid nodule was found on exam. She has no weight loss, no history of prior malignancy, and no family history of cancer. Lab test results: low TSH, elevated free T4
- Thyroid scintigraphy scan or radioactive iodine uptake test (RAIU)
- Screening for thyroid antibodies
- Ultrasonography of the thyroid gland
- Fine-needle biopsy of the nodule for cytology
Customer reviews
4,5 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
1 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
excellent, good images and clearly explained. Thank you for a good lecture.
Thank you, Dr. Your lecture was simple and easy to understand.