Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
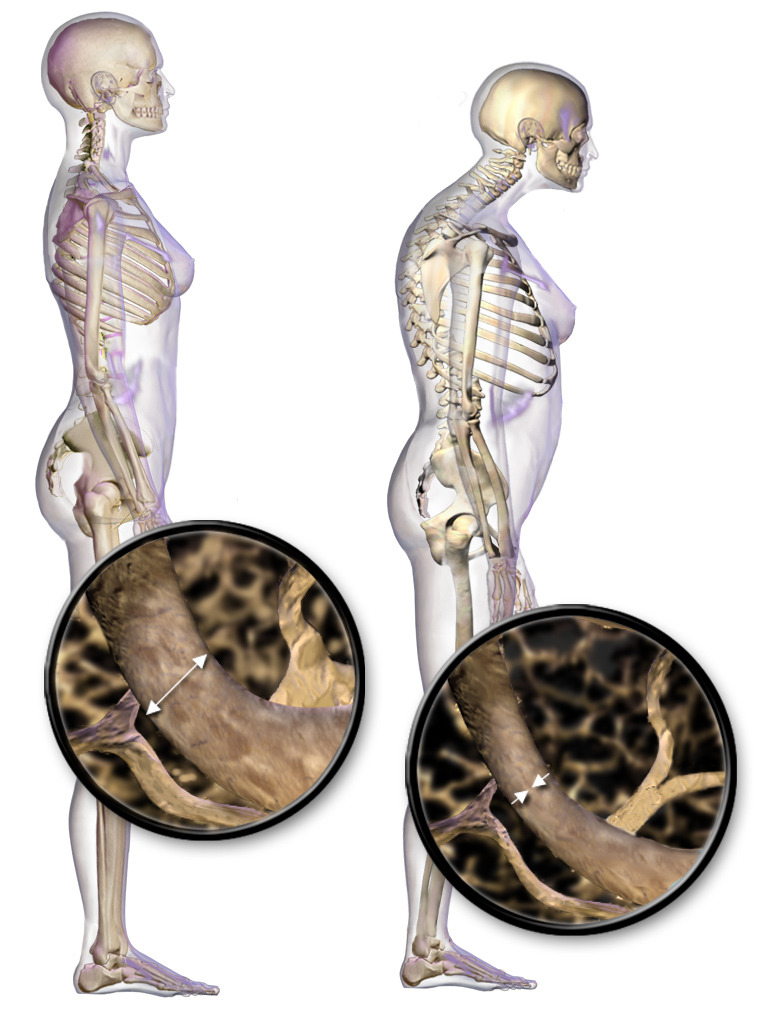
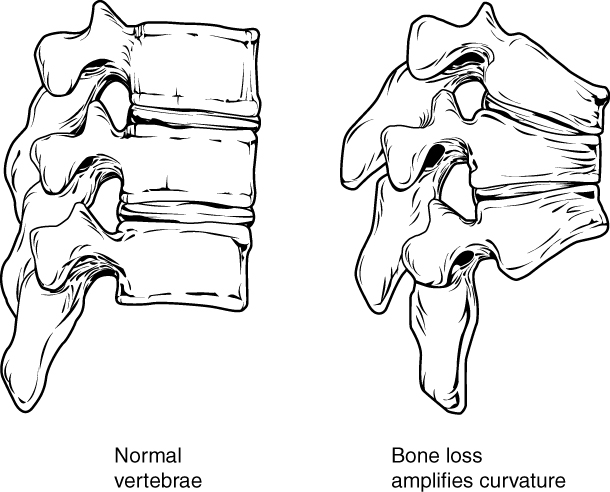
Osteoporosis: Risk Factors
-
Slides Osteoporosis EndocrinePathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:02 Osteoporosis, well, the dosage, you want to give Vitamin D daily for most of your patients. 00:09 There is an absolute emphasis on lifestyle modification. 00:13 So, if the patient is at risk for osteoporosis for reasons we've talked about with the indications, exercise usually with weight bearing is important, stop to smoking. 00:23 Be careful, educate your patient so that he or she is not going to fall, if at all possible and avoid heavy alcohol use. 00:35 Lifestyle modification is where your emphasis should be. 00:39 If you wish to know dosage, the first bullet point with making sure that you're replenishing some of this calcium and Vitamin D. 00:47 Management of osteoporosis: you would think about perhaps administering pharmacology to your patient with osteoporosis in a phase post-menopausal woman with established osteoporosis; also for patients with selected high-risk issues. 01:04 For example, a 10 year probability of hip fracture or a combined major osteoporotic fracture such as maybe a fracture in the leg, hip combined of greater than 3 or 20 percent respectively in post-menopausal women with osteopenia. 01:27 You're paying attention to your T score that we talked about earlier. 01:31 Management, bisphosphonates: first line of therapy; anti-resorptive, what does that mean? It means that this hopefully will prevent the resorption of calcium and such from the bone. 01:45 Increases bone mineralization density more than raloxifene and has proven to perhaps prevent fractures within the spine and the hip, the two major places that you're worried, alendronate and risedronate only. 02:02 Upper GI irritation is what you're worried about as a side effect of bisphosphonate. 02:07 Small risk of osteonecrosis, especially affecting the jaw is with IV bisphosphonate therapy. 02:15 Look for osteonecrosis or AV or, excuse me, avascular necrosis and especially in the jaw area and GI irritation as being major side effects of bisphosphonates. 02:27 Let's talk about raloxifene, the synthetic estrogen receptor agonist and antagonist. 02:33 So, therefore, it's a protagonist and those areas in the body in which maybe perhaps your post-menopausal... post-menopausal woman requires estrogen activity, it acts as an agonist; in other areas, as an antagonist. 02:48 Proven spine, but not hip fracture prevention. 02:53 And there is a thromboembolic risk. 02:55 Then you have PTH analogue and is called a teriparatide. 03:01 Severe osteoporosis unable to tolerate bisphosphonate or continuing fracture one year after administration of bisphosphonate. 03:12 Theoretical risk of osteosarcoma with long term therapy. 03:16 Keep that in mind as a PTH analogue, teriparatide. 03:23 Bisphosphonate, stabilizes your hydroxyapatite bone structure; bisphosphonate induces osteoblasts to secrete inhibitors of osteoclasts. 03:32 Be careful as I told you earlier that you're all worried about GI irritation and the fact that there might be avascular necrosis taking place of the jaw specifically. 03:42 Bisphosphonates, let's talk about the clinical uses. 03:46 With osteoporosis, the one that you should be paying attention to more so, alendronate. 03:51 With Paget's disease, because of abnormal bone remodelling that you may perhaps use a bisphosphonate to correct things. 04:02 Malignancy-associated hypercalcemia. 04:04 For example, if there is a paraneoplastic syndrome, for example, squamous cell lung cancer and you're producing too much PTHRP in which there is going to be breakdown in bone, the preferred bisphosphonates for this scenario include zoledronic acid or pamidronate. 04:22 Adverse effects' defective mineralization, increased risk of ulcers, talked about GI irritation; rare reports of jaw bone necrosis, but nonetheless, something that you very much want to keep in mind.
About the Lecture
The lecture Osteoporosis: Risk Factors by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Bone Disease.
Included Quiz Questions
What is NOT a modifiable risk factor for osteoporosis?
- Positive family history
- Alcohol use
- Tobacco use
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Dietary deficiency
A 38-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of back pain. Over the last year, she admits to frequent episodes of abdominal pain accompanied by diarrhea and weight loss. On a radiograph, you see a compression fracture of the lumbar spine and diagnose her with osteoporosis. What is the etiology?
- Malabsorption syndrome
- Cushing's syndrome
- Multiple myeloma
- Hypogonadism
- Alcohol use
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Very concise and clear. I like the style of presentation