Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Primary Hyperparathyroidism & Effects of Hyperparathyroidism
-
Slides Hypercalcemia.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
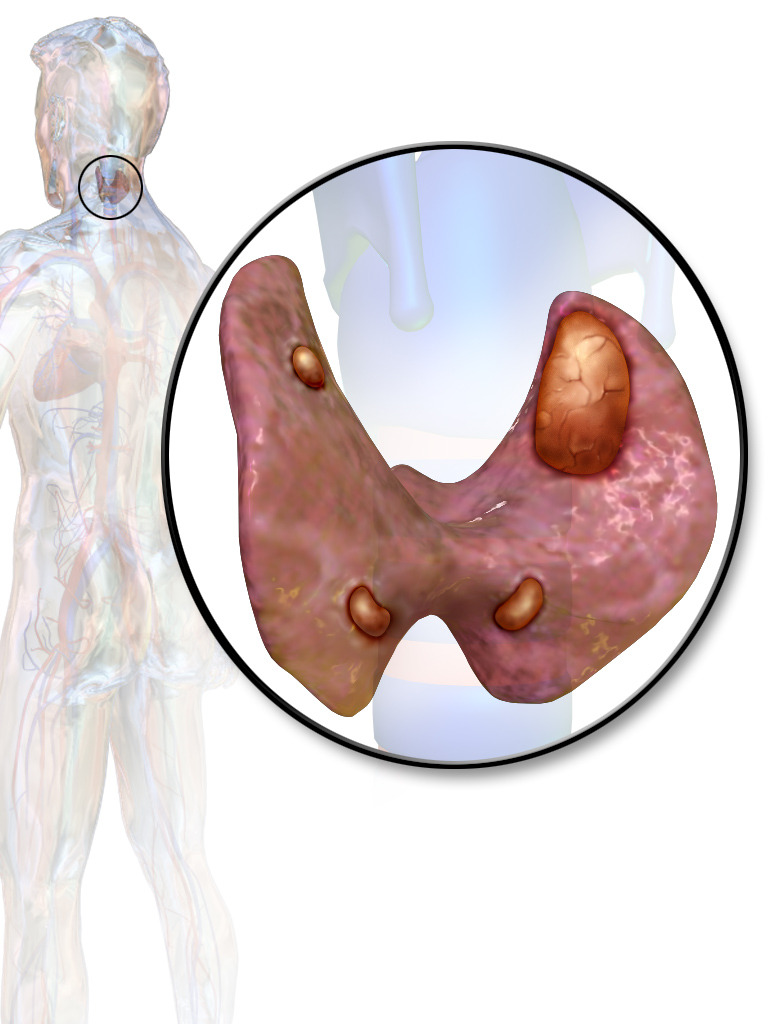
00:02 Let’s take a look at primary hyperparathyroidism in greater detail. 00:05 We said that extremely, if it’s hypercalcemia 90 percent of your patients if you’re thinking about adenoma, which is exactly what we’re seeing here in the picture, an adenoma within your parathyroid gland. 00:17 Solitary, sporadic 85 percent of the time. 00:21 It’s seen on a scan known as your Sestamibi Scan and the darkened area that you see there will be a solitary adenoma in which it’s extremely darkened and enlarged. 00:34 Focus upon your Sestamibi Scan. 00:36 10 to 15 percent hyperplasia of all four glands and majority of your primary hyperparathyroidism would be a solitary adenoma as seen here in the scan; 10 to 15 percent might be hyperplasia of all four glands. 00:52 Perhaps carcinoma, paraneoplastically, squamous and renal-renal cell carcinoma, how will this then produce your hyperparathyroidism? PTHrp, so ectopic production of PTHrp resulting in hypercalcemia where your PTH is actually depressed. 01:17 Risk factors, irradiation to head and neck; usually asymptomatic, diagnosed routine labs. 01:27 Typical symptoms, if you’re thinking about hypercalcemia, would not be tetany; fatigue, nausea, constipation… looking at GI symptoms and you’re looking at neurologic issues as well. 01:38 Dizziness, fatigue, worst case scenario might even be stupor and coma. 01:45 If it’s hyperparathyroidism, you take a look at the bone and its being broken down… bone resorption. 01:51 PTH does not promote bone mineralization, it promotes resorption of calcium from the bone. 02:01 Thus, in the X-ray that we’re seeing is our areas of the bone where it’s extremely lucent, not opaque. 02:10 Remember, if it’s osteopetrosis, if it’s Paget’s disease of the bone, especially the third pattern, triphasic, you would have increased bone. 02:22 You’ve heard of marble bone disease, that’s-that’s opaque, extremely white, this is lucent. 02:29 What may then happen with extreme destruction of the bone and such, obviously fractures and worst case scenario might be called osteitis fibrosa cystica… osteitis fibrosa cystica. 02:42 Check forearm and you do a bone density test. 02:48 Effects of hyperparathyroidism, you’ll notice in the middle figure here in the-in the thyroid and then within the thyroid, we have our parathyroids and you find a solitary nodule or adenoma and with this, you are producing excess PTH or primary hyperparathyroidism. 03:07 What we’ll take a look at in greater detail will be the overview of each one of these organ systems that are affected. 03:16 Let’s now go into the bone and with the assistance of PTH, you might be then breaking down your bone excessively. 03:25 When you do so, you... this cartoon is showing you is osteitis fibrosa cystica, but that area that’s being pointed to is actually called “a brown tumour”, but that’s a misnomer, it’s not a tumour within the bone, it’s not a tumour, but it is is a cavity that’s being filled with haemosiderin. 03:42 Therefore, on imaging study, it might actually look like a tumour, but it’s not, it’s called osteitis fibrosa cystica, breaking down of your bone. 03:51 Fractures may occur because, once again, there’s weakening of your bone. 03:54 Effects of too much or excessive PTH on your bone. 04:01 On the kidney, you might then start reabsorbing more of your calcium. 04:08 What may then happen, interesting enough, is the fact that you might actually develop calcium stones, effect of hyperparathyroidism. 04:16 So, it all depends and with all these calcium, remember even if you’re reabsorbing your calcium from your kidney, at some point, it needs to get filtered, doesn’t it? Because you just said you have hypercalcemia. 04:27 So, be careful. 04:28 So, therefore, it’s very possible that the patient may actually be suffering from calcium stones, polyuria, because of more or less your osmotic diuresis. 04:37 On the brain type of effects that you will find with hypercalcemia, depression, neurologic issues such as lethargy or coma. 04:46 And then in your intestine, you may then find gall stones; peptic ulcers especially in the duodenum and acute pancreatitis. 04:55 Keep all these together, please, when dealing with effects of hyperparathyroidism. 05:00 As a result of hypercalcemia, you have different organ systems that are being affected.
About the Lecture
The lecture Primary Hyperparathyroidism & Effects of Hyperparathyroidism by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Parathyroid Gland Disorders.
Included Quiz Questions
What diagnosis would a single dark mass on a Sestamibi scan of the parathyroid gland suggest?
- Solitary adenoma
- Carcinoma
- Hyperplasia of all 4 glands
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
What is NOT a common presenting symptom of primary hyperparathyroidism?
- Tetany
- Constipation
- Fatigue
- Asymptomatic
- Nausea
What is a possible outcome of advanced hyperparathyroidism?
- Osteitis fibrosis cystica
- Osteopetrosis
- Paget's disease of the bone
- Osteomalacia
- Pathologically increased bone mineralization
What is NOT a common complication associated with hyperparathyroidism?
- Uric acid kidney stones
- Gallstones
- Acute pancreatitis
- Seizures
- Polyuria
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |