Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Menopause: Signs, Symptoms and Management
-
Slides MenopauseManagement Menopause.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
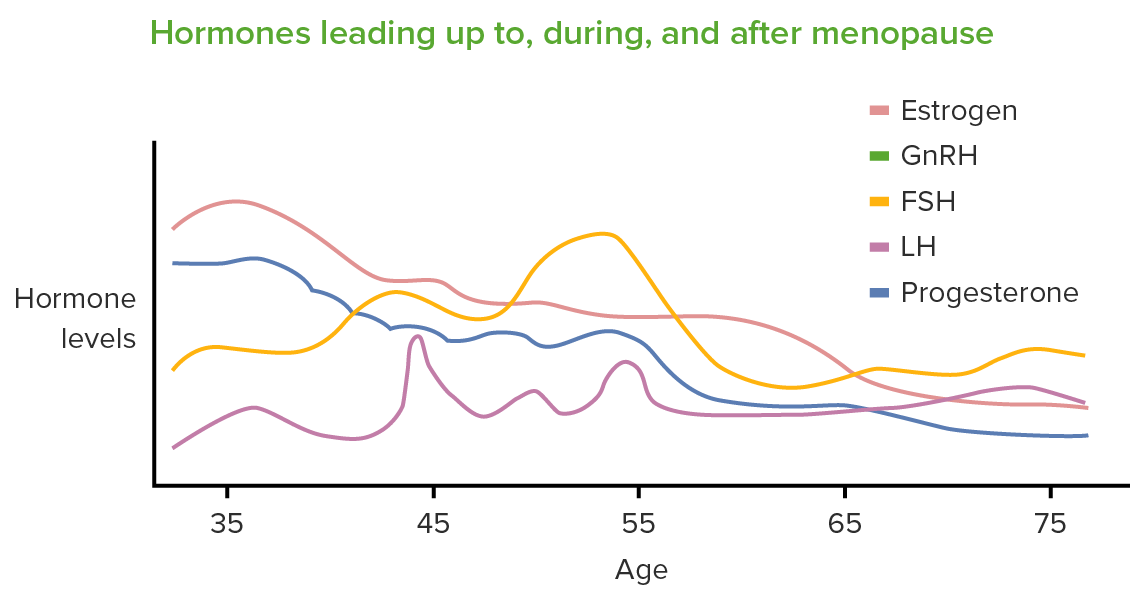
00:01 Let's now review menopause in general. 00:03 95% of women experience menopause between the ages of 44 and 45 with the average age being 51. Menopause before the age of 40 which occurs in 1% of the population is pathologic and this is referred to as POI or Primary Ovarian Insufficiency. There is another lecture set that you can look at to learn more about POI. 00:26 Symptoms of menopause could be characterized as an estrogen withdrawal so their entire reproductive life the female is exposed to estrogen and when the ovaries stops cycling that estrogen is decreased and that causes a withdrawal at the level of the brain even. 00:44 So what are the symptoms' Well, they're typically called vasomotor symptoms but they are described in the medical literature as hot flushes. 00:54 However, your patients' may state, "I'm having hot flashes". Okay, which is different. 00:59 However, they mean the same thing. So the patient can actually present and say, "I usually soak through my pajamas every night", because they're having night sweats. 01:10 Sometimes they can have vaginal dryness and itching. 01:13 It can be so irritated that sex is painful and also they might think they have urinary tract infection because of the itching and burning when they urinate. They may suffer from poor memory because their sleep gets interrupted by the continuous night sweats and the hot flushes even waking them up when they're not aware of it. 01:32 They can have weight gain and trouble losing weight. 01:35 Their hair may thin and they may have irregular periods. 01:40 Now, let's talk about emotional symptoms. In the menopausal transition, a woman can have mood swings and irritability, stress and anxiety, and fatigue mostly because of the night sweats in the vasomotor symptoms could be waking her up from a deep REM sleep. 01:56 In the menopause we can see that hair becomes thinner and loses its luster. 02:03 Breasts often droop and flatten. Nipples become smaller and may as well flatten and the skin and mucous membranes become drier and skin develops a rougher structure. The abdomen loses some muscle tone and the woman can suffer from stress and urge incontinence. 02:20 Again, there's vaginal dryness, itching and shrinking so again which would be normal sexual life may now become painful source of difficulty for the woman. 02:33 The woman also may experience headaches and hot flushes which are sometimes called hot flashes. 02:39 Her teeth can loosen and her gums can recede. 02:42 She may have cardiovascular disease. 02:44 She can suffer from backaches and her body and pubic hair becomes thicker and darker. 02:51 And she may have some bone loss that leads to increased bone fragility and fractures. 02:57 Let's now review some vasomotor symptoms/hot flushes. 03:01 These are very common and occurring in about 50% to 90% of all women. 03:06 Remember, it's a feeling or a rush of warmth in the face that sometimes last up to 45 minutes and this is very disturbing. 03:14 What if this happened to a woman while she's trying to conduct a meeting or present in court? This can happen at night and these are termed night sweats. 03:25 They correlate with declining estrogen levels and they are thought to be a disruption in thermoregulatory process. 03:33 Let's now talk about menopause management. 03:38 First, you wanna do a thorough history in physical especially a history of present illness, a gynecological history, and a sexual history. 03:46 If the patient tells you that she was sexually active but is now stopped, you wanna ask why' Is she having pain? Does she have vaginal dryness? Does she have a loss of libido? And on pelvic exam, that's key to investigate vaginal atrophy especially in the context of sexual complaints. 04:04 There is a system that we use although not something you would typically see in a medical record. There is a system that's accepted in assessing reproductive aging and includes criteria for perimenopause, the final menstrual period, and postmenopause based upon bleeding patterns, endocrine findings, and symptoms. 04:24 Again, we don't typically check an endocrine profile on these patients but if one were to be done you could potentially stage these patients based on a STRAW system. 04:35 Let's now talk about the preventative care in a menopausal woman. 04:39 So women who are in their perimenopause or menopause who come to your clinic provide you with an opportunity to give them anticipatory guidance about aging. 04:48 We should review screening modalities with them and this includes cervical cytology. 04:54 Typically, up to age 65 we do cytology every 3 years. 04:59 However, there is a lecture about cervical cytology and the new recommendations. 05:03 We also test for diabetes at age 45 every 3 years. 05:07 We also encourage patient to undergo colonoscopy at age 45 and if the findings are normal at the time of colonoscopy then every 10 years. 05:17 Mammography should be done annually although there are some recommendations that it should be done biannually. 05:24 And of course, the DEXA should be done at age 65 and every 2 years if there are additional risk factors that are present.
About the Lecture
The lecture Menopause: Signs, Symptoms and Management by Lynae Brayboy, MD is from the course Menopause.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is NOT a sign or symptom of menopause?
- Weight loss
- Hot flushes
- Night sweats
- Dyspareunia
- Emotional instability
What are hot flushes attributed to?
- Decreased estrogen levels
- Increased estrogen levels
- Increased FSH and LH levels
- Decreased FSH and LH levels
- Decreased inhibin levels
Which of the following is wrong regarding current guidelines on screenings in menopausal women?
- TSH screening at age 40/every 5 years
- Mammography screening at age 40/annually
- Diabetes screening at age 45/every 3 years
- Bone mineral density screening at age 65/every 2 years (if risk factors are present)
- Colonoscopy screening at age 45/every 10 years
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |