Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hypercalcemia: Types & Causes
-
Slides Hypercalcemia.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
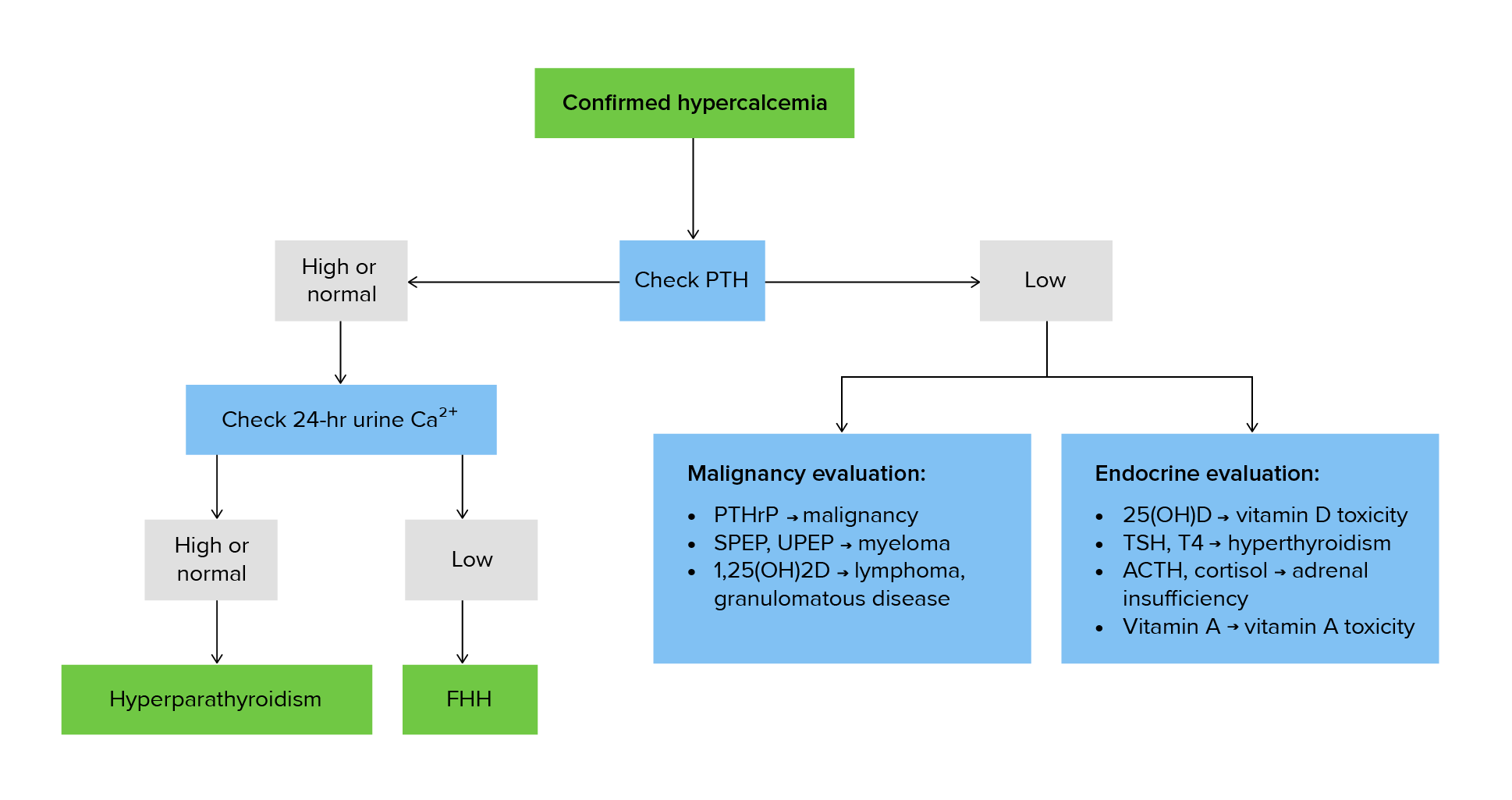
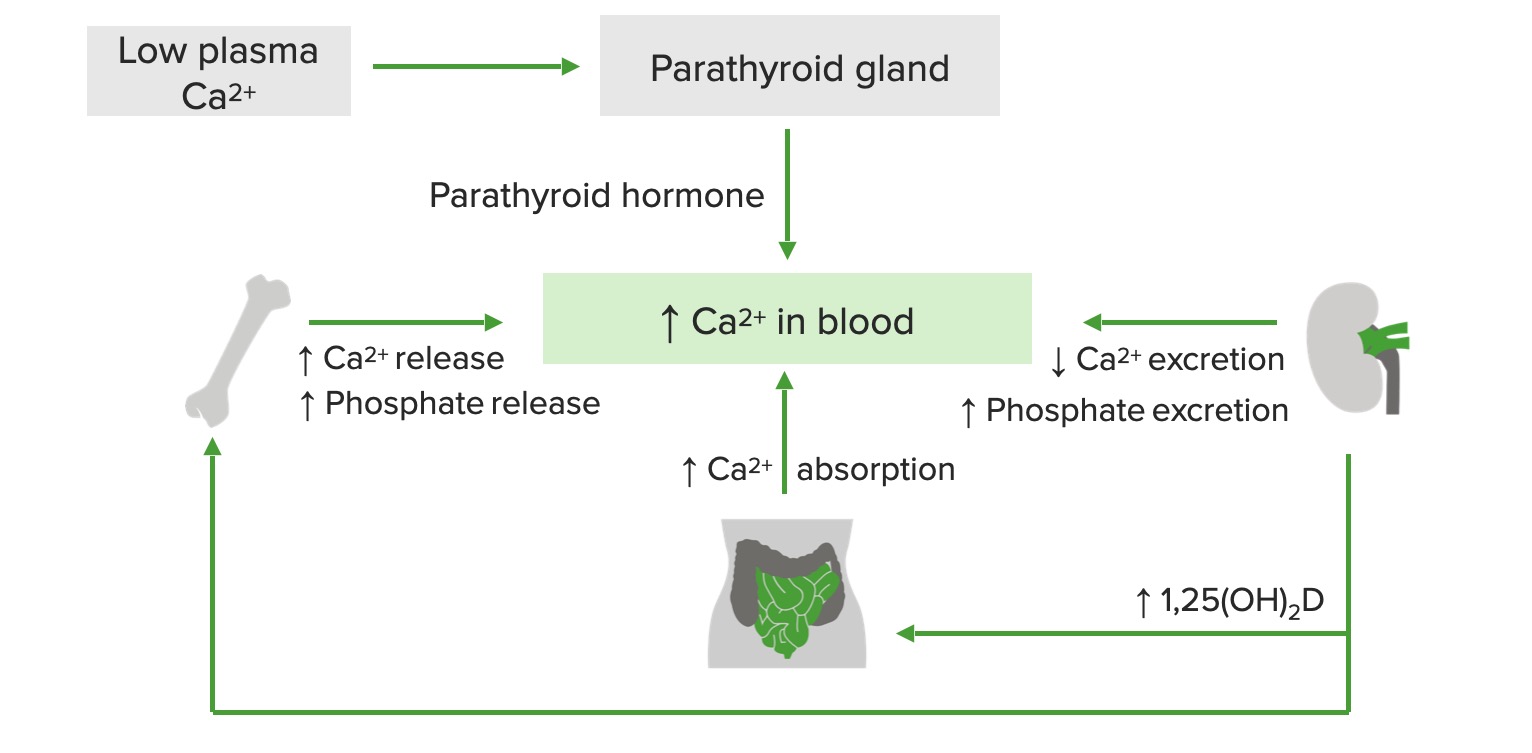
00:02 Hypercalcemia, we talked about the different types. 00:04 If there’s primary hypoparathyroidism, which is a malignancy of your parathyroid glands, and on your boards and on your wards, you usually will not have other issues per se and what I mean by that is the kidney function should be relatively normal. 00:24 With that primary hypoparathyroidism, which could be part of MEN type-1, could be part of 2a, right, MEN, multiple endocrine neoplasia, you are then going to result in hypercalcemia because PTH will resorb your calcium from the kidney and resorb the calcium from the bone. 00:43 The mechanisms of malignancy-related hypercalcemia… bone metastases, resorption; breast, multiple myeloma, prostate, lymphoma, thyroid, lung, so on and so forth. 00:52 So, metastases from different organs, meaning to say primary cancer existed in breast, metastasized to the bone resulting in resorption of it resulting in hypercalcemia. 01:03 Multiple myeloma, you’ve-you’ve heard of that punched-out lytic lesions in the bone. 01:09 Prostate cancer, it might then spread from the prostate out then through the batson-batson paravertebral plexus into the vertebrae therefore bring about hypercalcemia, lymphoma thyroid. 01:23 Humoral hypercalcemia, PTH-related peptide and what that basically means is that you have paraneoplastic. 01:31 Two major paraneoplastic conditions that you want to know of where you may then release PTH-related peptide, number one, will be squamous cell cancer of the lung and the other big one will be renal cell carcinoma. 01:43 Do not forget these two for sure. 01:46 Because of all that PTH-rp then working upon your PTH receptor, you are then going to reabsorb your calcium resulting in hypercalcemia in with your actual PTH level. 01:55 “Dr. Raj, aren’t they the same thing?” No, the PTH-related peptide is different from PTH. 02:02 The PTH is being released from your parathyroid glands and when you have all this hypercalcemia, your parathyroid glands will be shut down. 02:11 Clear? So, your actual PTH levels are decreased, but PTH-rp is increased. 02:18 Same concept as Graves’ disease where you have thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin binding to the TSH receptor. 02:26 All that T3,T4 is going to shut down your anterior pituitary from releasing TSH. 02:30 What’s your TSH level in Graves’? Dramatically decreased. 02:36 What’s your PTH level in this patient? Dramatically decreased. 02:40 Please do some parallels. 02:43 Conversion of 25 type of Vitamin D to 1,25 example such as lymphoma. 02:50 Others, well, if you’re thinking about hypovitamin D-osis, we’re thinking about sarcoidosis. 02:57 These are all the different causes of hypercalcemia, the first one being primary hyperparathyroidism where the 90 percent of hypercalcemia being caused by a type of adenoma. 03:09 Make sure that you know about malignancy-related hypercalcaemia as well, this is a very good [Inaudible 00:03:14] list that you want to be extremely familiar with. 03:20 As mentioned before, sarcoidosis which then increases your activity of 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol or calcitriol; hypervitaminosis D may result in hypercalcemia. 03:31 In pulmonology, we talked about proper management of sarcoidosis; may respond to glucocorticoid… hypercalcemia. 03:41 Continue discussion of hypercalcaemias, take a look at familiar cause. 03:45 Another cause at the bottom of this section will be drugs, keep them separate. 03:49 But, the familiar cause here is hypocalciuric hypercalcemia… allow the name to speak to you. 03:56 There is something going on in the kidney in which the receptors for PTH are responding extremely well, too well to the point where there is increased reabsorption of calcium from the urine, hypocalciuric, and putting it into where? Emia… welcome to familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia. 04:17 With this, look for family history, not necessarily required, but nonetheless, the question might have family history of par-parathyroidectomy. 04:30 Benign clinical manifestation, however, and then drugs such as thiazide diuretics. 04:36 Because of increased reabsorption of calcium from the DCT may result rare, just keep this in mind, maybe hypercalcemia. 04:46 Vitamin D intoxication, hypercalcemia; immobilization, especially in Paget’s disease patients. 04:52 Remember Paget’s disease of the bone, obviously is what our… what we… what I am referring to. 04:59 And with Paget’s disease of the bone, it takes a triphasic type of pathogenesis. 05:06 So, you begin with that osteolytic phase and then you end up with the mosaic pattern. 05:13 The osteoclast will completely burn out, in which you then go into osteosclerotic phase. 05:18 Do you remember? Paget’s disease of the bone. 05:21 Others, thyrotoxicosis, adrenal insufficiency, pheochromocytoma and parenteral nutrition may all result in hypercalcemia.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hypercalcemia: Types & Causes by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Parathyroid Gland Disorders.
Included Quiz Questions
A patient presents with hypercalcemia and low PTH. There are no other symptoms that point to an electrolyte disorder, but the patient does complain of cough and pleuritic chest pain. Which diagnosis ranks high on your differential?
- Squamous cell lung cancer
- Myocardial infarction
- Pneumonia
- Small cell lung cancer
- Congestive heart failure
Which substance is increased in sarcoidosis and causes hypercalcemia?
- Vitamin D
- Calcium
- Phosphate
- PTH
- Potassium
What is the adequate management of hypercalcemia caused by a granulomatous disease?
- Glucocorticoids
- Medications that decrease the absorption of Vitamin D in the gut
- Radiation therapy
- Antibiotics (penicillins or cephalosporins)
- Lifestyle changes
What is NOT a characteristic of familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH)?
- Low PTH
- Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
- Low urinary calcium
- Family history of parathyroidectomy
- Mutations in calcium-sensing receptors
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |