Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Overview – Opioid Analgesics
-
Slides Local Anesthetics CNS Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
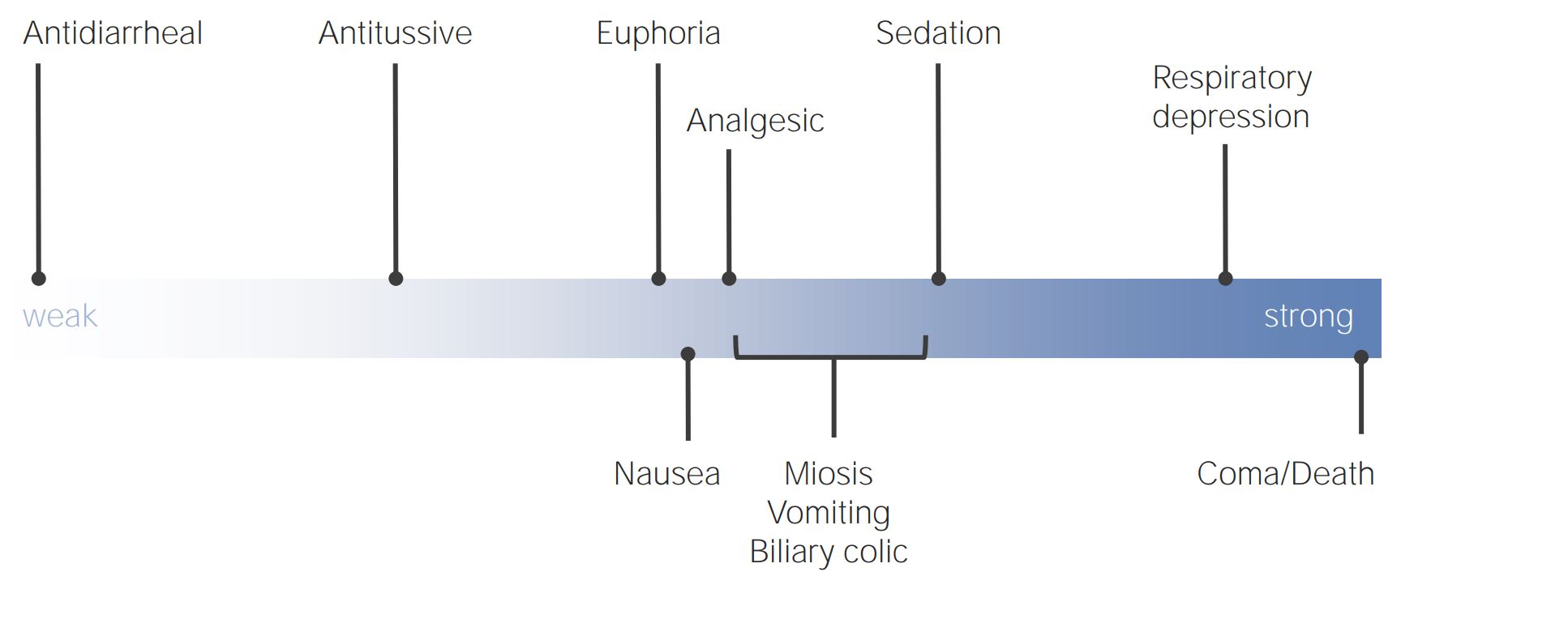
00:01 Let's talk about opioid analgesics. Opiate, opioids and endorphins are three different things, so let's define them clearly before we move on. 00:11 An opiate is a drug derived from the alkaloid of the opium poppy. 00:16 An opioid is a class of drugs that includes opiates, synthetic drugs, and opiopeptins that mimic opiates. 00:27 Endorphins are naturally occuring peptides that are produced by the body, and they act on the very same receptors within the body. 00:38 Opioid analgesics have a wide range of effects, and it really depends on how strong the drug is. 00:44 They can cause anything from an antidiarrheal or antitussive which means stopping cough effect, to euphoria, analgesia, sedation or respiratory depression. 00:55 Some of the adverse events do include nausea, miosis, vomiting, biliary colic, and of course coma and death in severe overdoses. 01:06 Now, there are three major receptors that are involved in opioid pharmacology. 01:10 Unfortunately, you do need to know them, but they do become quite useful in clinical practice later on. 01:17 So, you know, memorize this stuff now and know it on your exams, and eventually you'll use it in clinical practice too. 01:24 Now, the mu receptor is spinal and central in terms of location. The other effects of the mu receptor are respiratory depression. The effect on the GI tract is slowed gastric transit. 01:38 And in terms of habituation, there is almost none. The agonists of the mu receptor include fentanyl and morphines, and also endorphins will act on the mu receptors. 01:52 The kappa receptor is found spinally. Its greatest effect is really about sedation. 01:57 The effect on the GI tract, it causes slowed GI transit, and there is no habituation. 02:03 In terms of the agonists, these are those agents that are more specific for the kappa receptor. 02:09 And finally, there's the delta receptor. We don't know enough about this drug to really comment too much, other than to say that there is some tolerance associated with this drug. 02:20 And morphine, codeine and enkephalins are falling into this category. 02:26 So, have a look at this overall graph or table, and take a look at the information, and try and understand where each of these receptors fit in.
About the Lecture
The lecture Overview – Opioid Analgesics by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course CNS - Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which item is NOT an opioid analgesic?
- Naloxone
- Opium
- Synthetic opiates
- Fentanyl
What is NOT considered an effect of opioids?
- Increased heart contractility
- Sedation
- Cough suppression
- Nausea
- Constipation
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |