Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism: Diagnosis and Management
-
Slides Thyroid and Reproduction.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
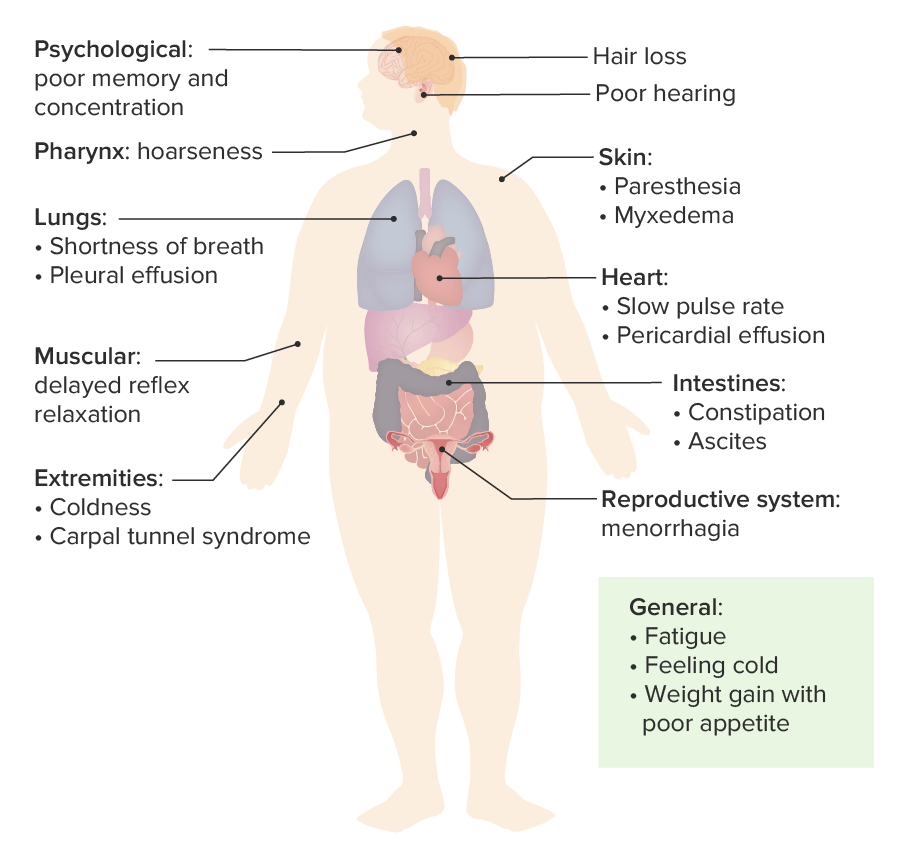
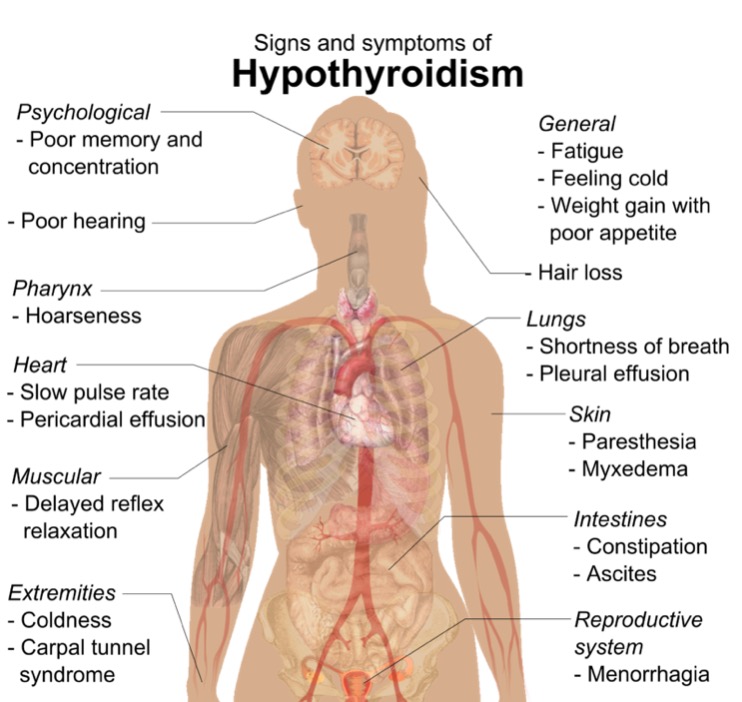
00:00 This is what a goiter looks like. Now this goiter is very large one and is going on for some time. 00:07 Unless you work in undeveloped country, you likely won't see this in western countries or in the US. Let's review the causes of goiter. You can have a sporadic goiter, a diffuse toxic goiter, you can have thyroiditis, it can be as a result of medications or drugs, dietary or environmental goitrogens, and you can have enzymatic defects that actually increased the risk of goiters. Also, diffuse malignant disease of the thyroid can actually lead to a very large goiter. Infiltrative diseases can also lead to goiter. So let's again review hyper versus hypothyroidism. 00:55 Remember, hyperthyroidism is the person who has had too much coffee and they're jittery, can't stop moving, they have anxiety. This is usually caused by Grave's disease. These patients have a low TSH and high T4. They have a persistence of anti-TSH receptor antibodies or antimicrosomal antibodies or antiperoxidase antibodies. Grave's disease in the fetus, however, can cause fetal sinus tachycardia which means a heart rate greater than 160 beats per minute which is worrisome to an obstetrician gynecologist. Now remember hypothyroidism is the opposite. These patients have a slowed function, a slowed metabolism altogether so the thyroid is actually not working. 01:46 They have elevated TSH, low T4, and they can have hypothyroidism in the fetus as well and that that causes growth failure. In this slide, we're going to review thyroid storm in pregnant women. 02:01 I don’t think this will be on your exam and this is a lot of detail that you may not need so if you'd like to skip ahead to the next slide go ahead and do so now. If not, I'll just give you a little bit of detail that propylthiouracil or PTU can be given orally or it can be given IV if oral administration is not possible. Methimazole is an alternative that can be given through rectal suppositories. The most important thing is that you cool the patient who likely has a fever, that you decrease the tachycardia and this can be done with several agents. If you would like more information please download the information on the slide. Now let's review the treatment of hyperthyroidism. So, thioamide drugs such as PTU and methimazole actually block thyroid hormone synthesis by blocking organification of iodine and PTU works by blocking conversion of T4 to T3. 03:00 You can actually also treat a hyperthyroid patient who is resistant to medical therapy with radioactive I-131; however, they need to not breastfeed for at least 120 days after getting radioactive iodine. These patients can then become hypothyroid. 03:19 Methimazole can cause aplasia cuties or choanal atresia. 03:23 So it is avoided in the first trimester of pregnancy. 03:27 PTU on the other hand, is usually associated with liver toxicity. 03:31 So let's now review hypothyroidism. 03:33 Remember, this is the patient who is metabolically very slowed. Normally, levothyroxine is converted from T4 to T3 peripherally. This is not occurring in these patients and replacement needs to occur with levothyroxine. Replacement is usually weight-based and for an adult woman 1 to 2 mcg/kg/day needs to be given. Overdosage can result in signs of hyperthyroidism which we just reviewed. Let's now talk about postpartum thyroiditis. This is an autoimmune inflammation of the thyroid gland that is usually new and is painless that can happen where they have transient thyrotoxicosis or thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism 1 year postpartum. Diagnosis is confirmed by checking a serum TSH and a T4 and a patient who we've previously knew to be euthyroid or to have normal profiles of TSH and T4. So let's now review some quick facts about thyroid and reproduction. Recall that the normal TSH for a woman of reproductive age should be less than 2.5; however, some labs may go up to 4. If the fetal thyroid is dependent on maternal thyroid, remember that maternal hypothyroidism can cause problems in the fetus if she is not given levothyroxine. Abnormal maternal thyroid function leads to obstetric complications and fetal disease. 05:00 Hyperthyroidism in pregnancy is generally treated with PTU or methimazole. 05:05 A thyroid storm during pregnancy can require a more complex treatment regimen, and is usually managed by a maternal fetal medicine specialist or endocrinologist. or a reproductive endocrinologist.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism: Diagnosis and Management by Lynae Brayboy, MD is from the course Reproductive Endocrinology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is NOT a common cause of goiter?
- Anaplastic cancer of thyroid
- Diffuse toxic goiter
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- Nutritional deficiency of Iodine in the diet
- Diffuse malignant disease
For a woman to be considered to have post-partum thyroiditis, features of hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism must be developed within what period of time after childbirth?
- 12 months
- 18 months
- 24 months
- 6 months
- 3 months
Breastfeeding is contraindicated in which of the following therapies used in the management of thyroid problems?
- Radioactive iodine
- Propylthiouracil
- Methimazole
- Levothyroxine
- Post thyroidectomy
Which of the following is contraindicated in the treatment of thyroid storm?
- Levothyroxine
- Propylthiouracil
- Lugol's iodine
- Lithium carbonate
- Propranolol
Customer reviews
2,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
0 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
1 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
What's the point of a lecture if you are just listing things, reading the powerpoint without explaining all the terms for goitre for example? Give us the prevalence of each symptom or of the varieties fo goitre, etc.. so that we know what we should expect in practice. The same applies for all lectures otherwise why pay? I can read it myself.