Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Allergy: Genetics and IgE
-
Slides Hypersensitivity.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
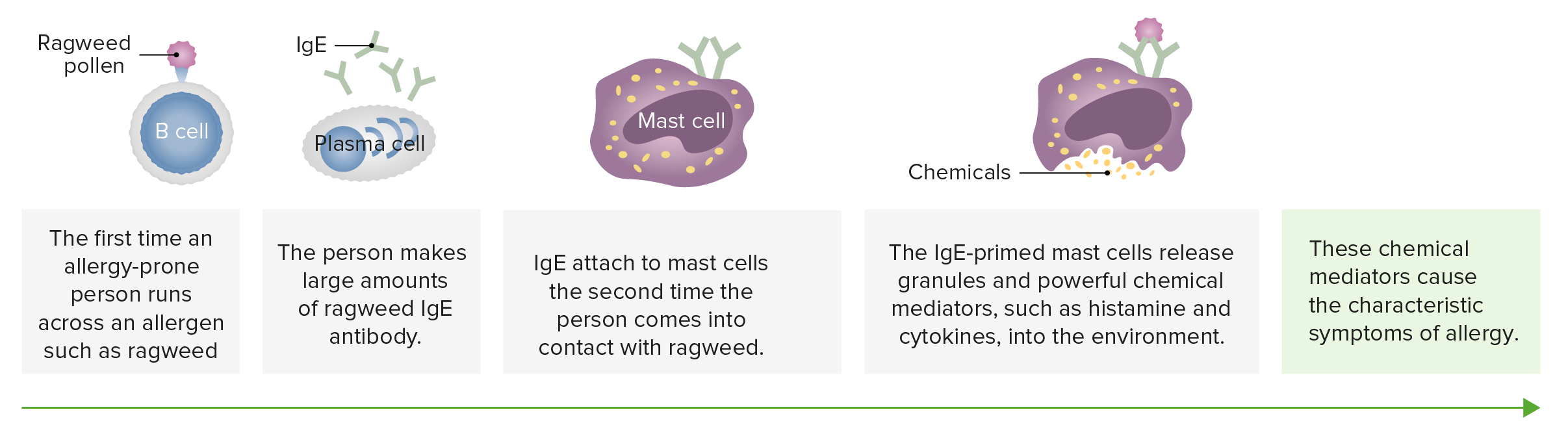
00:01 I’ve already mentioned that genetics are important in the development of allergy. 00:06 So let’s take a couple of minutes to look at some of the genes that have been identified. 00:13 Polymorphisms of genes encoding Pattern Recognition Receptors have been described in patients with allergy. 00:22 So have polymorphisms in the gene encoding the cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin. 00:30 Polymorphisms of the MHC particularly HLA-DQ polymorphisms. 00:37 And polymorphisms in the transcription factor SMAD3. 00:42 Other polymorphisms that have been described are ones for the genes encoding the interleukin-2 receptor β-chain, and indeed for the cytokine itself interleukin-2. 00:54 As well as polymorphisms of the genes for the interleukin-33 receptor and for interleukin-33. 01:02 And as these reactions get going with the dendritic cell stimulating Th2 cells. 01:09 And with the involvement perhaps of induced regulatory T-cells trying to dampen down the allergic response. 01:17 If the balance goes towards the development of an allergic response, the Th2 cells will become dominant with the production of cytokines such as interleukin-4, interleukin-5, interleukin-13. 01:29 Eosinophils will be stimulated, B-cells will be stimulated. 01:33 Those B-cells will class switch to IgE production differentiate into plasma cells that will secrete the IgE antibody that is so characteristic of the Type I hypersensitivity reaction. 01:47 This will then bind to the FCεR1, the high affinity IgE receptor. 01:53 And maybe you won’t be too surprised to hear that polymorphisms in that particular receptor have also been linked to the development of allergic disease. 02:02 And again, mast cells just like Th2 cells have a receptor for interleukin-33 and therefore that polymorphism is acting at several different levels during the allergic response. 02:16 And again, TSLP is influential in modulating the activity of mast cells, just like it can act on dendritic cells.
About the Lecture
The lecture Allergy: Genetics and IgE by Peter Delves, PhD is from the course Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune Disease.
Included Quiz Questions
Genetic polymorphisms in which of the following types of receptors is most closely associated with the development of type I hypersensitivity reaction?
- FcϵRI
- FcαRI
- FcγRI
- FcδRI
- FcμRI
Which of the following cell activation sequences most accurately represents sensitization in type 1 hypersensitivity reaction?
- Dendritic cells stimulate helper 2 T cells to activate class switching of B cells.
- Dendritic cells stimulate helper 1 T cells which activate cytotoxic T cells.
- T helper 1 cells stimulate helper 2 T cells to activate class switching of B cells.
- B cells stimulate cytotoxic T cells to activate helper 1 T cells.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Nice explanation, good pace. Excelent for non English Speakers, like me (Brazil). Thnaks a lot.