Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Macrolides and Ketolides – Bacterial Protein Synthesis Inhibitors (Antibiotics)
-
Slides Antimicrobial Pharmacology Macrolides.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
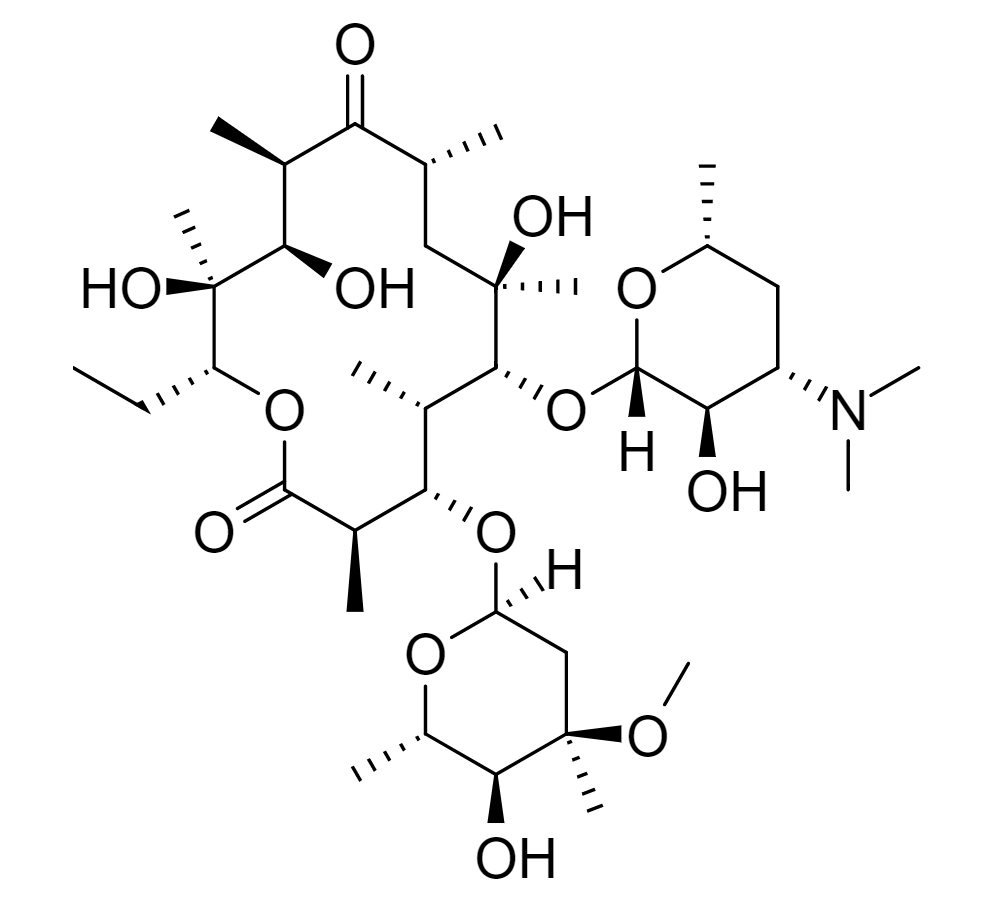
00:00 Let's move on to the macrolides antibiotics. 00:03 These macrolides antibiotics are very important group of medications because we use them all the time. 00:08 Specially in respiratory infections. 00:11 Now these agents are blocking the 50S unit from translation. 00:15 Important agents include erythromycin and clarithromycin. 00:19 They're rapidly eliminated from the body. 00:22 They're considered broad spectrum antibiotics. 00:25 And as I said before they're most commonly used in respiratory infections. 00:29 Azithromycin concentrates into macrophages and other tissues and it is actually eliminated quite slowly. 00:37 It is active against many gram-positive organisms and has more activity against susceptible gram-negative organisms. 00:45 It's also active against several atypical organisms including Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila and Chlamydophila pneumoniae. 00:55 The nice thing about azithromycin is that you can actually give it as a three day set of medications but it will last for ten days. 01:03 So the killing activity actually lasts much longer than the drug is actually in the body. 01:10 Other medications are more narrow spectrum within this drug group. 01:14 The selectivity targets are generally gram positive anaerobes and aerobes. 01:19 And these are used often in clostridioides difficile infections. 01:22 Let's talk about the resistance to macrolides antibiotics. 01:26 It's actually quite an interesting topic because of the mechanism and the resistance patterns. 01:32 Now you actually will develop ejector pump mechanisms in some bacteria that literally pump out the drug, the active drug out of the cell. 01:41 It's quite an interesting phenomenon. 01:43 The other thing that may happen in resistance patterns is changing the binding site of the macrolide by perhaps adding a methyl group. 01:50 Now the problem here is that there is a 100% cross resistance pattern between one macrolide and another. 01:57 So if for example you give a patient clarithromycin for a respiratory infection on week 1, they come back with resistance and you decide to try a different medication, there's going to be cross resistance between those two, say between clarithromycin and azithromycin. 02:13 There's partial cross resistance with drugs like clindamycin and the streptogramins as well. 02:20 And the resistance in the enterobactriaceae species and that is due to the production of drug destroying esterases. 02:29 Not because of the ejector pump. 02:31 So it's a slightly different mechanism but still 100% cross resistant pattern.
About the Lecture
The lecture Macrolides and Ketolides – Bacterial Protein Synthesis Inhibitors (Antibiotics) by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Antimicrobial Pharmacology. It contains the following chapters:
- Macrolides
- Ketolides
Included Quiz Questions
What are bacterial resistance mechanisms to macrolides? Select all that apply.
- Ejector pumps
- Decreased wall permeability
- Gene transfer
- Modification of binding site
- Esterases
What resistance mechanism have Enterobacteriaceae developed against macrolides?
- Drug-destroying esterases
- Ejector pumps
- Potentiation of CYP450 enzymes
- Beta-lactamases
- Adding a methyl group to change the binding site
What statement about azithromycin is INCORRECT?
- It is used in Clostridioides difficile (previously called Clostridium difficile) infections.
- It is eliminated slowly.
- It is effective against gonorrhea.
- It has a potent post-antibiotic effect.
- It concentrates in macrophages and tissues.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |