Snell's Law, Total Internal Reflection, and Dispersion

About the Lecture
The lecture Snell's Law, Total Internal Reflection, and Dispersion by Jared Rovny, PhD is from the course Geometrical Optics. It contains the following chapters:
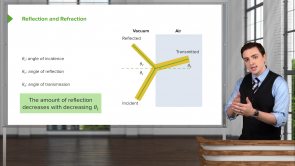
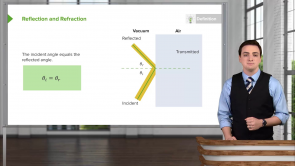
- Total Internal Reflection
- Dispersion
Included Quiz Questions
What would happen if a beam of light is sent into a medium that keeps changing to a higher index of refraction the deeper the beam goes?
- The beam would bend more and more until the refraction angle approaches zero and the beam is traveling vertically relative to the surface of the medium.
- The beam would bend more and more to go parallel to the surface of the medium.
- The beam would stop bending and continue on a straight path.
- A beam cannot get into a medium with an increasing index of refraction
- The beam would entirely reflect from the surface.
Which of the following is an explanation for why total internal reflection CANNOT occur from a lower to a higher index of refraction medium (e.g., from air to glass)?
- Light bends towards the normal when going from a lower to a higher index of refraction medium.
- Light bends away from the normal when going from a lower to a higher index of refraction medium.
- From a lower to a higher index of refraction medium, reflected light bends towards the normal.
- From a lower to a higher index of refraction medium, reflected light bends away from the normal.
- Since the speed of the light decreases when going from a lower index to a higher index medium, total internal reflection cannot occur.
The index of refraction of a cylindrical fiber optic is n₁ = 1.44. Approximately, what is the maximum angle θ₁ that a ray of light, that is traveling within the fiber optic, can make with the axis of the cylinder so that total internal reflection happens and light remains within the fiber optic? Hint: If θ꜀ is the critical angle of the fiber optic then θ₁ = 90° - θ꜀.
- θ₁ = 46°
- θ₁ = 42°
- θ₁ = 36°
- θ₁ = 15°
- θ₁ = 0°
Which of the following is a physical example of dispersion?
- White light enters a prism and splits into many colors
- A beam of monochromatic light enters a lens and bends
- Light moving along a path reflects in such a way that none is transmitted past the boundaries
- Two light rays enter a lens and interfere on the other side
- A beam of light hits a surface and refracts exactly along the surface
These courses may be of interest to you
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |