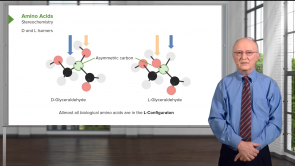
Saccharides – Simple Carbohydrates

About the Lecture
The lecture Saccharides – Simple Carbohydrates by Kevin Ahern, PhD is from the course Biochemistry: Basics.
Included Quiz Questions
Which two monosaccharides are components of lactose?
- Glucose and galactose.
- Two glucose molecules.
- Glucose and fructose.
- Two fructose molecules.
- Fructose and galactose.
Customer reviews
4,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
1 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
The following are the errors in the information you provided: 00:24 The general formula for monosaccharides is Cx(H2O)x, where x is equal to the number of carbon atoms in the monosaccharide. For example, the structural formula for glucose is C6H12O6, which means that it has six carbon atoms and six water molecules. 01:15 The structural formula for lactose is C12H22O11. This means that it is a disaccharide made up of two monosaccharides, glucose and galactose. 01:39 Polysaccharides are polymers of monosaccharides, but they do not necessarily have to have the same repeating sugar unit throughout. For example, amylopectin is a polysaccharide made up of glucose molecules, but it has a branched structure. Here is a corrected version of the information you provided: Carbohydrates are molecules whose name literally means hydrates of carbon. This is because monosaccharides, the simplest carbohydrates, have a ratio of one carbon atom to two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom, the same as water. The general formula for monosaccharides is Cx(H2O)x, where x is equal to the number of carbon atoms in the monosaccharide. For example, the structural formula for glucose is C6H12O6, which means that it has six carbon atoms and six water molecules. Disaccharides are carbohydrates that are made up of two monosaccharides. They are formed by a glycosidic linkage between the two monosaccharides. Disaccharides have the general formula C12H22O11. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), and maltose (glucose + glucose). Polysaccharides are carbohydrates that are made up of many monosaccharides. They are formed by glycosidic linkages between the monosaccharides. Polysaccharides have the general formula (C6H10O5)n, where n is the number of monosaccharides in the polysaccharide. Examples of polysaccharides include cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. Polysaccharides do not necessarily have to have the same repeating sugar unit throughout. For example, amylopectin is a polysaccharide made up of glucose molecules, but it has a branched structure.
Awesome job, I wish you were my teacher at my university! So clear!