Reactions and Enthalpy

About the Lecture
The lecture Reactions and Enthalpy by Jared Rovny, PhD is from the course Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry.
Included Quiz Questions
A squishy ball is compressed from 8 L to half its original volume at atmospheric pressure. How much work is done on the ball? (1 atm ≈ 10⁵ Pa)
- 400 J
- 300 J
- 500 J
- 600 J
- 400 kJ
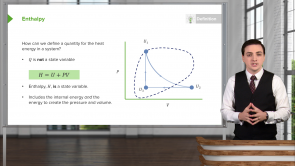
What is the interpretation of the term PV in the enthalpy relation H = U + PV?
- The amount of work done by the system to expand itself into volume V (from approximate 0 initial volume) at constant environmental pressure P.
- It is the product of two state variables pressure P and volume V of the system.
- The amount of heat added to the system in order to expand it from approximately 0 volume to its current volume V at constant pressure P.
- U is the internal energy of the system but U + PV is the total kinetic energy of the system.
- It is the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from the gas if all the kinetic energy of its molecules is turned into work.
Which of the following quantities is NOT a state variable?
- Heat added (Q)
- Enthalpy (H)
- Pressure (P)
- Volume (V)
- Entropy (S)
For constant pressure, what is the change in enthalpy of the system equal to?
- External heat energy added to the system
- Amount of work done on the system
- Change in volume
- Change in the total kinetic energy of the molecules of the system
- Change in entropy
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
- ΔH = Q + PΔV, at constant pressure P
- In a pressure-volume graph, regardless of which path the system takes to return to its original position, the internal energy remains the same.
- Added heat energy is NOT a state variable.
- The formula for enthalpy is H = U + PV.
- Enthalpy is a measure of the amount of external heat energy that is required to bring the system to its current state (plus a constant term related to the systems non-kinetic internal energy).
These courses may be of interest to you
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |