Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hepatitis C
-
Slides GD liver disease.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
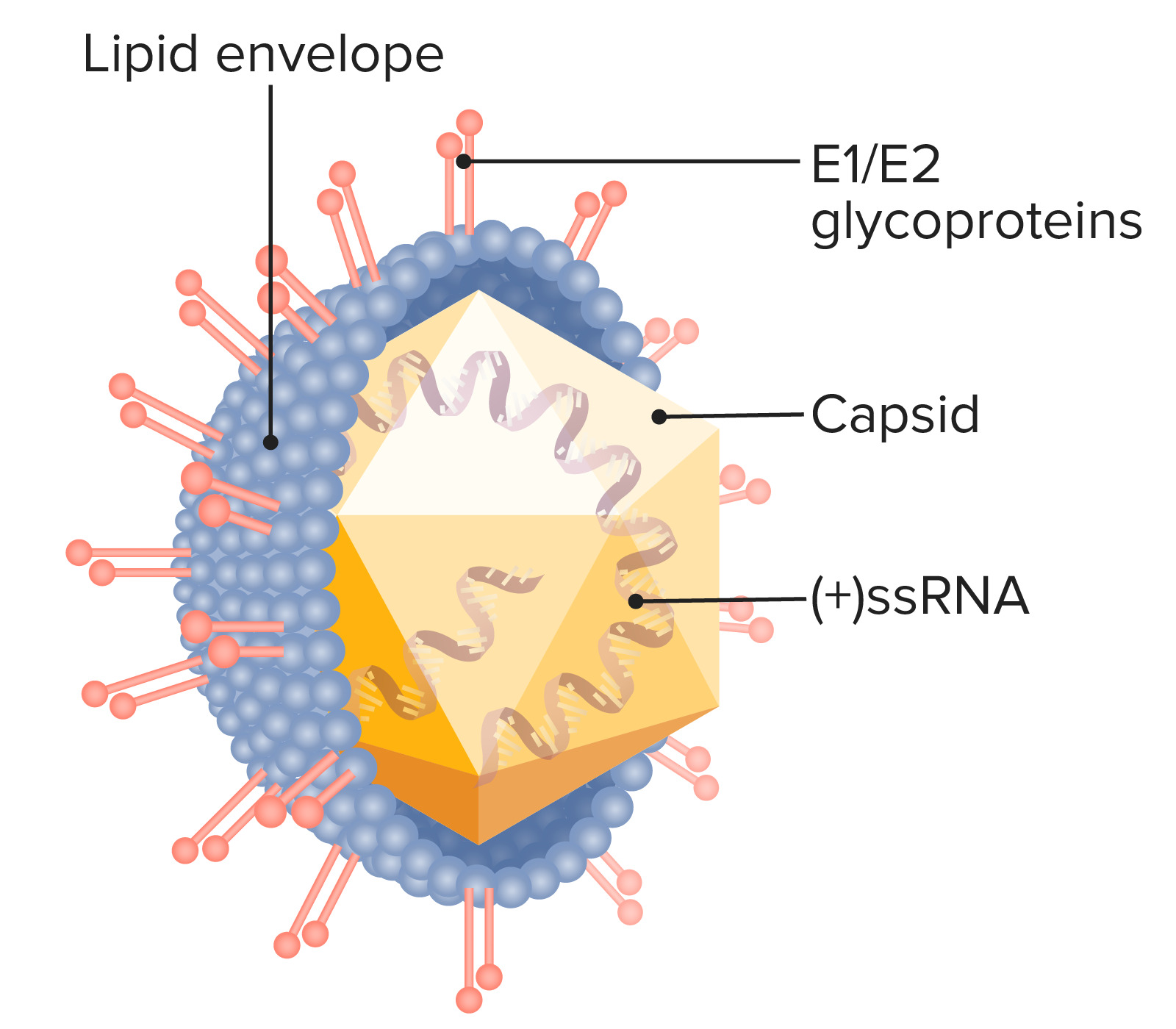
00:01 Hepatitis C is an RNA virus incubation period 2 to 26 weeks. 00:08 These are the type of viral hepatitis in which you worried about chronicity 40 to 80 percent of the cases whenever you have hepatitis C occurring and it go into chronicity. 00:20 What are you worried about? Big Time, Liver Cancer. 00:25 Right, Hepatitis C back in the 70's and 80's was an absolute endemic. 00:32 Since then things have subsided quite a bit and in Pharmacology management, you should definitely but Hepatitis C Genotype 1 you focus on genotype 1 because we can now treat Hepatitis C not just treat, cure a patient between 8 to 12 weeks with Genotype 1. 00:56 This is new information. 00:58 This is research that now turned into clinical application and translating into patients that are completely cured interferon free therapy. 01:10 Amazing, some of these drugs that you should know of include Ledipasvir, Sofosbuvir combination of the 2 without interferon most common reason for liver transplantation because a chronicity if liver dies 4 million cases still in the US. 01:28 Alcohol abuse accelerates the disease progression as you can imagine. 01:35 Risk factors: transfusions prior to 1990, at this point we're good. 01:42 I mean to say that we have enough checks and balances you walk in and there's transfusion, it's required. 01:47 There's going to be a nurse that's always there with you to check things of to make sure that you are not passing hepatitis C into your patient IV drug abusers high risk sexual behavior or tattooing, and Hemodialysis. 02:03 keep in mind what tattoos that you made then pass on Hepatitis C. 02:09 Clinical presentation acute disease usually asymptomatic at some point they made then show jaundice incidental finding on routine physicals mean to say the patient is so asymptomatic. 02:22 They might feel maybe a little bit of fatigue and such but often times in clinical practice. 02:28 It's an incidental finding, dangerous. 02:31 What about the extra Paddock manifestation this, you want to know is being cryoglobulinemia Hepatitis B could also result in cryoglobulinemia. 02:41 But hepatitis C Essential mixed cryo. 02:45 What does that mean to you? upon exposure to cold the immunoglobulins are then going to aggregate, and causing more or less hyperviscosity syndrome throughout the entire body. 02:56 Also MPGN Porphyria cutanea tarda. 03:01 Could be an extra hepatic manifestation what has porphyria cutanea tarda mean to you? your focus should be on Catania skin and upon exposure to UV rays. 03:12 There will be blistering pain that you want to focus upon. 03:17 Often times. 03:19 Let's say that your patient and you see a little bit of redness. 03:24 Where? In the front of your leg, and then upon palpation. You feel it. 03:30 Our patients is aww. 03:31 Stop hurting me Doc. 03:33 Well, I'm sorry. I don't mean to do this. But what is this that you're causing? Why is the patient feeling pain? and what is this redness that you're seeing on the chin? or the inter aspect of the leg erythema nodosum? There's a huge list and dermatology for erythema nodosum, but keep in mind that whenever there's an infection many types including coccidioides immitis such as cryptococcus new from the list is quite large. 04:02 You might find Erythema immitis immitisthe redness in the front of the leg. 04:09 Hepatitis B could be associated with B-cell Lymphoma. 04:15 As could be Hepatitis C. 04:19 Have another graph here for specifically hepatitis C. 04:23 What hepatitis C? you may or may not find symptoms and definitely not as complicated as what we dealt with in Hepatitis B and everything that I've broken down for you in hepatitis B in terms of the markers know them well know that table of interpretation. 04:41 That is money. 04:44 And every possible respect. This is Hepatitis C, the graph here is the following: It's an RNA virus. 04:50 What type of transaminase are you going to find elevated you focus on ALT, and then Anti-HCV kicks in approximately 6 months later. 05:01 You're on your way to recovery. 05:02 As I told you earlier, new information on your boards that you make sure that you're familiar with. 05:07 Please, would be the interferon free therapy at that. 05:10 I'm not going to cover here, but interfer on free therapy with drugs such as simple boast fear and let it pass fear. 05:18 So logic pattern more chronic hepatitis C infection with recovery this time we have HCV you'll notice that the ALT could then fluctuate depending as to whether or not your patient is on the road to recovery or not. 05:32 Chronicity. 05:36 Diagnosis Anti-HCV antibody by Elisa Viral application measured by HCV that is important. 05:45 The replication becomes important because one of the objectives that you will be using clinically is seeing what the rate of the sustained viral replication will be SVR. 05:58 And obviously the less that you find your replication the better of you and your practice and the patient is going to be. 06:05 So viral replication measured by RNA by PCR testing and indicate chronic infection. 06:12 ALT does not indicate degree of liver damage and that's important for you to know, ALT will tell you. 06:17 Oh, yes your patient may be suffering from viral hepatitis, but it will not, it will not be translated into the severity of and that is a discussion we've had many a time. 06:29 Liver biopsy used for staging, staging, staging, especially if you're worried about your patient chronicity going into Hepatocellular Carcinoma for major Genotypes that you want to be very responsible for, we have Genotype 1, which is the most important one that you're paying attention to on your boards US and Europe Genotype 2. 06:55 Take a look at the Mediterranean population, that's where you would be for that. 07:00 Genotype 3 Would bethe Indian subcontinent and that'll be your major type Hepatitis C, and Hepatitis C in Egypt and North Africa. 07:11 In other words, the northern region if you thinking, Egypt, Libya so on and so forth and they'll be Genotype 4 spend a little bit of time, very important, that you know what Genotype is dealing with which population. 07:26 And what the different Genotypes you focus upon the new management therapy and regimen that we have for Genotype 1. 07:35 Please, what about the remainder? Well without I'll give you a brief overview for that coming up. 07:41 The standard of treatment is now to use a combination of Ledipasvir, Simeprevir, Sofosbuvir, Velpatasvir, Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir. 07:52 Interference should be avoided, the goal now is to cure Hepatitis C, not just symptomatic treatment. 08:00 If HTV goes into chronicity to measure things that you're worried about complete death of the liver cirrhosis, and if cirrhosis has kicked in in you need to make sure that you then yearly checkup for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 08:19 What marker do you know of that will then perhaps indicate that your patient has gone on to HCC? Increase in which marker please. 08:29 Good, a feeder protein will be increased.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hepatitis C by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Liver Diseases: Basic Principles with Carlo Raj.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following hepatitis C genotypes is completely curable with the current treatment modalities?
- Genotype 1
- Genotype 2
- Genotype 3
- Genotype 4
- Genotype 5
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for hepatitis C?
- Poor sanitation
- Hemophilia in a patient who was diagnosed before 1990
- Unclean methods of tattooing
- Hemodialysis
A patient positive for hepatitis C develops hyperviscosity syndrome upon exposure to cold. Urinalysis shows proteinuria without casts. Which of the following is the MOST likely diagnosis?
- Mixed essential cryoglobulinemia
- Porphyria cutanea tarda
- Membranous glomerulonephritis
- Erythema nodosum
- B-cell lymphoma
A patient who is positive for hepatitis C develops red discoloration of the skin of the digits akin to digital infarcts and presents with asymmetric neuropathy. Urinalysis shows proteinuria without casts. What is the MOST likely cause of these infarcts?
- Hyperviscosity due to cryoglobulins
- Hyperviscosity due to complement
- Hyperviscosity due to increased immunoglobulins
- Hyperviscosity due to increased leukocyte count
- Hyperviscosity due to drugs used to treat hepatitis C
Which of the following indicates a prior infection of HCV?
- Anti-HCV by ELISA
- Anti-HCV by PCR
- HCV DNA by PCR
- HCV DNA by ELISA
- Serum transaminases
Which of the following leads to further progression of a hepatitis C infection?
- Alcohol
- Smoking
- Gallstones
- Steatorrhea
- Pregnancy
A 55-year-old man is diagnosed with cirrhosis secondary to hepatitis C. Which complication should this patient be screened for yearly?
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Hepatic adenoma
- Focal nodular hyperplasia
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
3 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Informative! There were quite a few different things i learned from this lecture. I now have a better understanding of the disease.
Clear as always. I like the way he emphasizes things. A lot
Since December 2013, Several DAA drugs were approved by FDA. So you can update this lecture.