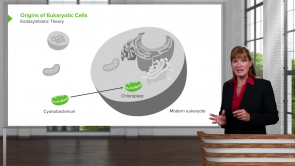
Eukaryotic Transcription

About the Lecture
The lecture Eukaryotic Transcription by Georgina Cornwall, PhD is from the course Gene Expression.
Included Quiz Questions
Which statements best explain one of these differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic transcription?
- In prokaryotes, translation of mRNA begins before transcription is complete. In eukaryotes, transcription and modification of mRNA are completed before translation begins.
- In prokaryotes, genes are transcribed directly into polypeptides. In eukaryotes, genes are transcribed into RNA, which is used to assemble polypeptides.
- In prokaryotes, translation occurs before genes are transcribed into mRNA. In eukaryotes, genes are transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated into polypeptides.
- In prokaryotes, introns are removed before genes are transcribed into mRNA. In eukaryotes, introns are removed after genes are transcribed into mRNA.
- In prokaryotes, elongation factors terminate the transcription process. In eukaryotes, elongation factors attach to RNA polymerase II to start the transcription process.
What is required for the formation of the transcription-initiation complex in eukaryotes?
- Binding of a transcription factor to the TATA box, recruitment of additional transcription factors, and recruitment of RNA polymerase II
- Binding of a transcription factor to the transcription bubble, recruitment of additional transcription factors, and recruitment of RNA polymerase III
- Binding of RNA polymerase II to the TATA box, followed by recruitment of transcription factors
- Binding of a polymerase subunit to the promoter elements at -35 and -10, followed by recruitment of the core polymerase
- Binding of elongation factors to the TATA box, recruitment of additional transcription factors, and recruitment of RNA polymerase II
These courses may be of interest to you
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |