Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Multiphase Abdominal CT
-
Slides Abdominal CT Techniques.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
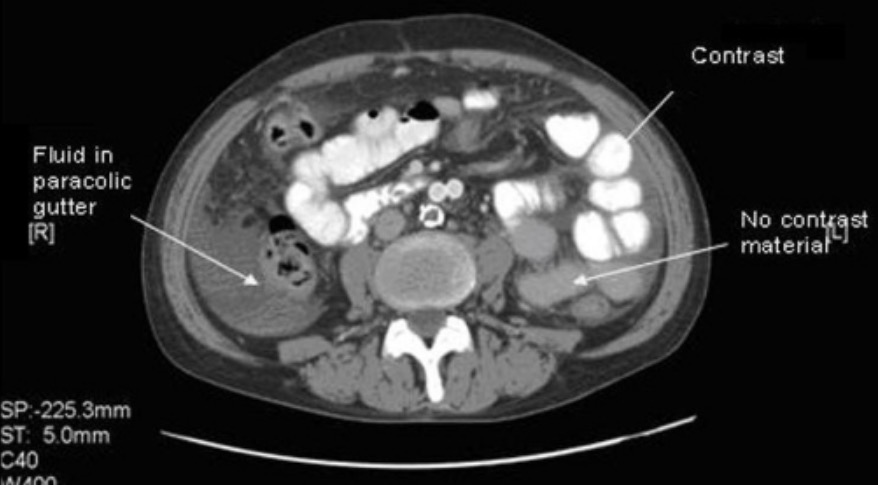
00:01 So what is a multiphase abdominal CT? CT scanning can be performed at various different intervals after contrast administration. 00:09 CT scans that are performed at different intervals have different structures that opacify based on the pathology that?s being evaluated and it?s used to characterize the enhancement of mass lesions that are within solid organs. This is an example of a multiphase abdominal CT. 00:26 It involves a non-contrast image which you can see on the left. 00:30 We then have an early arterial phase image which is performed at about 15-20 seconds after injection, a portal venous phase which is performed about 35-40 seconds after injection and then a delayed phase which is usually performed at about 6-10 minutes after injection although this can be delayed further depending on what?s being evaluated. 00:51 This is an example of a non-contrast study. 00:54 If you take a look at this, it?s actually very hard to differentiate between adjacent solid organs. You can see here the end of the liver and then there?s a soft tissue density here and it?s hard to characterize exactly what this is. 01:07 Again, you see here the kidneys and you can see here a soft tissue density which is probably vascular but again is very hard to characterize what this is without intravenous contrast. 01:18 On the arterial phase you can actually see the aorta and you can see the superior mesenteric artery very well. 01:25 Here we have a small portion of the renal artery and here we have contrast within the kidney which helps you differentiate the cortex from the medulla. 01:35 You can also now see the difference between the margin of the liver and the adjacent gallbladder. This exam is performed in the portal venous phase, so most CT scans are performed on the portal venous phase because it allows for the best evaluation of the solid organs. 01:52 Again, you can see here the liver and you can actually see finer detail within the liver so you can see the vessels within the liver a lot better than you could on the other two scans that we just looked at. 02:03 You can also see the difference between the margin of the liver and the adjacent gallbladder and you can still see very well the difference in the cortex of the kidney and the medulla. 02:12 You now have contrast persistent within the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. 02:18 It?s a little bit less dense than it was on the arterial phase but now you see the venous system a little bit better here so here?s one renal vein and then here?s the other renal vein and you can see the inferior vena cava as well. 02:32 This image is an image of the delayed phase and on this you can see that a large amount of contrast is seen within the renal excreting system. You can see it within the proximal ureter and you can see it within the renal pelvis on both sides as well. 02:47 The delayed phase is often used to evaluate the kidneys and the collecting system, the ureters, and the urinary bladder as well. 02:54 Let?s take a look at this, this is the arterial phase. 02:59 What structures do you see opacified in the arterial phase? So we see the aorta and its branches best opacified. 03:13 You do have some opacification of other structures as well but the best visualized are the aorta and its branches. 03:20 How about the portal venous phase? What structures would you see best identified in the portal venous phase? This actually shows us multiple different structures. 03:37 It shows us the IVC and its branches so the entire venous system is well seen, the portal vein and its branches are well seen as well and this is actually the best phase to evaluate solid organ parenchyma as well. 03:48 And then here we have the delayed phase, and as we discussed the renal collecting system, the ureters, and the urinary bladder are best seen on the delayed phase. 04:07 What phases are most CT scans performed in? It?s actually the portal venous phase as we discussed and this is because the solid organs are best seen on the portal venous phase. 04:27 So we?ve gone over the different techniques that can be used to evaluate an abdominal CT scan and we?ve gone over some of the pros and cons of each one and when each one should be used. 04:38 The 3 major factors are intravenous contrast, oral contrast, and different delays of time after the administration of intravenous contrast.
About the Lecture
The lecture Multiphase Abdominal CT by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Abdominal Radiology.
Included Quiz Questions
When is the delayed phase of an abdominal CT performed?
- 6 to 10 minutes after contrast injection
- 35-40 seconds after contrast injection
- 2-3 minutes after contrast injection
- 4-5 minutes after contrast injection
- 15-20 seconds after contrast injection
Which CT phase is the best for evaluating the solid organs in the abdomen?
- Portal venous phase
- Non-contrast phase
- Active phase
- Delayed phase
- Arterial phase
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |